Plasma sheet
In the magnetosphere, the plasma sheet is a sheet-like region of denser (0.3-0.5 ions/cm3 versus 0.01-0.02 in the lobes) hot plasma and lower magnetic field near the equatorial plane, between the magnetosphere's north and south lobes.[1]
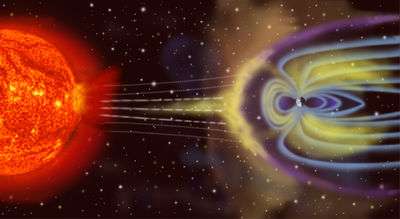
Artistic rendition of a magnetosphere. Sizes are not to scale.
A magnetosphere is produced by the interaction of a stream of charged particles, such as solar wind, with a planet's (or similar body's) magnetic field. All planets with intrinsic magnetic fields, including Earth, are surrounded by a magnetosphere.[1]
References
- Tadanori Ondoh; Katsuhide Marubashi (2001). Science of Space Environment. IOS Press. p. 130. ISBN 978-4-274-90384-7. Retrieved 16 July 2012.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.