Parachutist Badge (United States)
The Parachutist Badge, also commonly referred to as "Jump Wings" is a military badge of the United States Armed Forces. The United States Coast Guard is the only branch that does not issue its own Parachutist Badge, but its members are authorized to receive the Parachutist Badges of other services in accordance with their prescribed requirements. The DoD military services are all awarded the same Basic Parachutist Badge. The U.S. Army and U.S. Air Force issue the same Senior and Master Parachutist Badges while the U.S. Navy and U.S. Marine Corps issue the Navy and Marine Corps Parachutist Badge to advanced parachutists. The majority of the services earn their Basic Parachutist Badge through the U.S. Army Airborne School.
| Parachutist Badge | |
|---|---|
 Basic Parachutist Badge | |
| Awarded by United States Armed Forces | |
| Type | Badge |
| Awarded for | Airborne training course |
| Status | Currently awarded |
| Statistics | |
| Last awarded | Currently awarded |
| Army Precedence | |
| Next (higher) | Expert Field Medical Badge |
| Next (lower) | Parachute Rigger Badge[1] |



Army
The Army's Basic Parachutist Badge is awarded to all military personnel of any service who complete the US Army Basic Airborne Course at Fort Benning, Georgia. It signifies that the soldier is a trained military parachutist, and is qualified to participate in airborne operations. The badge and its sew-on equivalent may be worn on the Army Combat Uniform (ACU).[2]
The original Army Parachutist Badge was designed in 1941 by Captain (later Lieutenant General) William P. Yarborough and approved by the Department of War in March of that year. The Parachutist Badge replaced the "Parachutist Patch" which had previously been worn as a large patch on the side of a paratrooper's garrison cap. LTG Yarborough also designed the Senior and Master Parachutist Badges and the addition of stars to portray the number of combat jumps. The flash that is worn behind the badge is also a contribution of William P. Yarborough.[3]
Basic Parachutist Badge
To be eligible for award of the basic Parachutist Badge, an individual must have completed the Basic Airborne Course of the Airborne School of the United States Army Infantry School at Fort Benning, Georgia. To graduate, a student must complete the three-phase course consisting of a ground phase, a tower phase, and a jump phase. By the end of the course, a student will have completed five jumps in varying jump configurations, from a "no load" jump all the way to a full combat load jump at night.[1]
Senior Parachutist Badge
To be eligible for the Senior Parachutist Badge, an individual must have been rated excellent in character and efficiency and have met the following requirements:
- Participated in a minimum of 30 jumps including fifteen jumps with combat equipment to consist of normal TOE equipment including individual weapon carried in combat whether the jump was in actual or simulated combat. In cases of simulated combat the equipment will include water, rations (actual or dummy), ammunition (actual or dummy), and other essential items necessary to sustain an individual in combat. Two night jumps must also be made during the hours of darkness (regardless of time of day with respect to sunset) one of which will be as jumpmaster of a stick. In addition, two mass tactical jumps which culminate in an airborne assault problem with either a unit equivalent to a battalion or larger; a separate company battery; or an organic staff of regimental size or larger. The soldier must fill a position commensurate with his or her rank or grade during the problem.
- Either graduated from the Jumpmaster Course of the Airborne Department of the Infantry School or from the Jumpmaster School of a separate airborne battalion or larger airborne unit, or infantry divisions and separate infantry brigades containing organic airborne elements (e.g. the United States Army Alaska (USARAK) or the United States Army Special Operations Command (USASOC) Jumpmaster Course), or served as jumpmaster on one or more combat jumps or as a jumpmaster on 15 noncombat jumps.
- Have served on jump status with an airborne unit or other organizations authorized parachutists for a total of at least 24 months.[1]
Master Parachutist Badge
To be eligible for the Master Parachutist Badge, an individual must have been rated excellent in character and efficiency and have met the following requirements:
- Participated in a minimum of 65 jumps including twenty-five jumps with combat equipment to consist of normal TOE equipment, including individual weapon carried by the individual in combat whether the jump was in actual or simulated combat. In cases of simulated combat the equipment will include water rations (actual or dummy), ammunition (actual or dummy), and other essential items necessary to sustain an individual in combat. Four night jumps must also be made during the hours of darkness, one as jumpmaster of a stick. Five mass tactical jumps must be made which culminate in an airborne assault problem with a unit equivalent to a battalion or larger; a separate company/battery; or an organic staff of regimental size or larger. The individual must fill a position commensurate with their rank or grade during the problem.
- Either graduated from the Jumpmaster Course of the Airborne Department of the Infantry School or the Jumpmaster School of a separate airborne battalion or larger airborne unit, or infantry divisions and separate infantry brigades containing organic airborne elements, including the U.S. Army Alaska Jumpmaster Course, or served as jumpmaster on one or more combat jumps or as jumpmaster on 33 noncombat jumps.
- Have served on jump status with an airborne unit or other organization authorized parachutists for a total of 36 months (may be non-consecutive).
The 25 combat equipment jumps necessary to qualify for the Master Parachutist Badge must be from a static line.[1]
The master parachutist badge is 1 1⁄2 inches (38 mm) wide at the widest part of the wings and 1 13⁄64 inches (31 mm) from the top of the wreath to the bottom of the parachute where the risers meet in a point.
Airborne background trimming
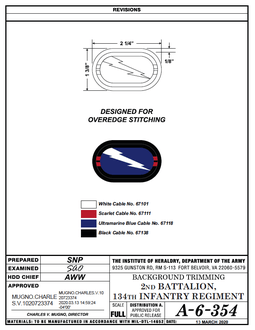
Soldiers assigned to Army units on airborne status wear a cloth oval background trimming underneath their Parachutist Badge,[4] which shares the basic design of the unit's beret flash.[5] This is one method by which an individual can identify a parachute qualified soldier serving in a unit on active jump status, called a "Paratrooper," versus a parachutist serving in a non-airborne unit. The original background trimming was also a contribution of William P. Yarborough.[4] Each unit's background trimming design is created and approved by the U.S. Army Institute of Heraldry (TIOH) who evaluate unit lineage, military heraldry, as well as proposed designs by unit members themselves. Once approved, the institute publishes manufacturing instructions to authorized companies for manufacturing.[6]
Combat Jump Device
If a soldier completes an airborne jump into a combat zone, they are authorized to wear a Combat Jump Device on their Parachutist Badge. The device consists of a star or arrangements of stars, indicating the number of combat jumps.[7] The use of stars as Combat Jump Devices did not gain official approval until after the 1983 invasion of Grenada (Operation Urgent Fury). The stars are awarded as follows:[8][6]
| 1 combat jump | A bronze star on the shroud lines |
| 2 combat jumps | A bronze star on each wing |
| 3 combat jumps | A bronze star on each wing and one on the shroud lines |
| 4 combat jumps | Two bronze stars on each wing |
| 5 + combat jumps | A large gold star on the shroud lines |
| List of Known U.S. Combat Parachute Jumps[9][10][11][12][13] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | Unit | Operation | Troopers | Country | Dropzone |
| 8 Nov. 1942 | 509th Parachute Infantry Battalion (PIB) | Torch | 556 | Algeria | Tafaraoui airfield, La Senia |
| 15 Nov. 1942 | 509th PIB | Torch | 300 - 350 | Algeria | Youks les Bains |
| 24 Dec. 1942 | 509th PIB, Hdqt's. Co. Two French paratroopers | 32 | Tunisia | El Djem | |
| 9 Jul. 1943 | 504th Parachute Infantry Regiment 3rd Battalion (Jumped first); 505th Regimental Combat Team (RCT), Includes: 505th PIR, 456th PFA & Co. B, 307th Engr. | Husky I | 3,406 | Italy | Gela, Sicily |
| 10 Jul. 1943 | 504th Regimental Combat Team (RCT), Includes: 504th PIR, 1st & 2nd Btn.; 376th PFA & Co.A, 307th Engr. | Husky II | 2,304 | Italy | Gela, Sicily |
| 5 Sep. 1943 | 503th PIR | 1,700 | New Guinea | Nadzab, Markham Valley | |
| 13 Sep. 1943 | 504th Regimental Combat Team (RCT) Includes: 504th PIR, 376th PFA & Co. "A" 307th Eng. | Avalanche | 1,300 | Italy | Paestum, Salerno |
| 14 Sep. 1943 | 505th Regimental Combat Team (RCT). Includes: 505th PIR, 456th PFA & Co.B 370th Engr. | Avalanche | 2,105 | Italy | Salerno, Paestum |
| 14 Sep. 1943 | 509th PIB | Avalanche | 640 | Italy | Avellino |
| 6 June 1944 | 82nd Airborne Division (507, 508) 505th RCT, Includes: 505th Parachute Infantry Reg., Co. B/307 Engineer Battalion and 456th Parachute Field Artillery Battalion. 28 Pathfinders, 504th PIR, (7 returned). | Overlord, Titanic (Dropping of parachute dummies, "Oscar"). | 6,418 | France | Normandy |
| 6 June 1944 | 101st Airborne Division [326, 377, 501, 502, 506] | Overlord, Titanic (Dropping of parachute dummies, "Oscar"). | 6,638 | France | Normandy |
| 3 July 1944 | 503rd PRCT, 1st Bn. | Table Tennis | 739 | New Guinea | Noemfoor Island |
| 4 July 1944 | 503rd PRCT, 3rd Bn. | Table Tennis | 685 | New Guinea | Noemfoor Island |
| 15 Aug. 1944 | 1st Abn. Task Force (460th PFA, 463rd PFABn.; 509th PIB; 517th PCT; 551st PIB; 596th PCEng. Co.) | Dragoon | 5,607 | France | Cote d' Azur, Riviera |
| 17 Sep. 1944 | 82nd Airborne Division (508), 505th RCT, Includes: 505th PIR, 456th PFA, & Co.B, 307th Engr.; 504th RCT, Includes: 504th PIR, 376th PFA, & Co.A, 307 Engr | Market Garden | 7,250 | Netherlands | Grave & Nijmegen |
| 17 Sep. 1944 | 101st Airborne Division [501, 502, 506] | Market Garden | 6,769 | Netherlands | Eindhoven |
| 29 Nov. 1944, 5 Dec. 1944 | Co.C, 127th Abn.Eng, Bn. Co.C., 1st Pl.., 187th P/GIR 221st AB. Med. Co.; 457th PFA 11th Abn. Div. Hdqt's Group 511th Pcht. Signal Co. 11th Abn. Div. RECON Pl. | Tabletop | 241 | Leyte | Manarawat |
| 3 Feb. 1945 | 511th PIR, 457th FABn. | Shoestring | 1,830 | Philippines | Tagaytay Ridge |
| 16 Feb. 1945 | 503rd PRCT, 462nd PFABn; 161st Airborne Engr. Btn. | Topside | 2,050 | Philippines | Corregidor |
| 23 Feb. 1945 | 511th Parachute Infantry Regiment: 1st Btn., Co.B; Hdqt's Co., 1st Btn.; Hdqt's Co., 1st Btn., Light Machine Gun Platoon | Rescue 2,147 internees | 130 | Philippines | Los Banos Prison Camp |
| 24 Mar. 1945 | 17th Airborne Division (507 PIR, 513 PIR, 464 PFA, 466 PFA, 139 AEB, 224 AMC, 155 AAB, 411 AQM, 517 ASC, 680 GFA 681 GFA, 717 AOC & 194 GIR). Also small units: MP's, Division Artillery, Reconnaissance Platoon, & Parachute Maintenance Co. | Varsity | 4,964 | Germany | Wesel |
| 23 June 1945 | 511th PIR | Gypsy | 1,030 | Philippines | Aparri |
| 20 Oct. 1950 | 187th ARCT, 2nd Battalion | DZ Easy | 1,203 | Korea | Sukchon |
| 20 Oct. 1950 | 187th ARCT, 1st, 3rd. Bn's. | DZ William | 1,470 | Korea | Sukchon |
| 21 Oct. 1950 | 187th Airborne Regimental Combat Team (ARCT). | DZ William | 671 | Korea | Sukchon |
| 23 Mar. 1951 | 187th ARCT, 2nd & 3rd Bns; 674th ABN Field Artillery Bn; 2nd & 4th ABN Ranger Cos, and Indian army surgical team. | Tomahawk | 3,486 | Korea | Munsan-Ni |
| 12 Feb. 1962 | FTT-1 White Star SF Team | Nam Beng Valley Campaign vs. Pathet Lao | 12 | Laos | Nam Tha airstrip |
| 2 Jan. 1963 | Joint General Staff reserve ARVN Paratroopers with U.S. MACV "Red Hat" Advisors from Saigon | Ap Bac | 300 South Vietnamese, 2 Americans | South Vietnam | Ap Tan Thoi |
| 22 Feb. 1967 | 173rd Airborne Brigade, 503rd P.I.R., 2nd & 3rd Btl's,; 3/319 Airborne Field Artillery Regiment (AFAR). | Junction City | 845 | Vietnam | Katum |
| 2 Apr. 1967 | 5th Special Force Group (ABN), 1st Special Forces: Detachments, A-503 Mike Force & A-344, Operation Harvest Moon (Includes Montagnards) | Harvest Moon | 356 (includes Montagnards) | Vietnam | Bunard, Phouc Long "Happy Dragon" Province |
| 5 Sep. 1967 | USMC, 1st Long Range Reconnaissance Patrol (LRRP) | Oregon | 10 | Vietnam | South |
| 5 Oct. 1967 | 5th Special Force Group (ABN), 1st Special Forces: Pathfinder Detachment (12 SF, 37 ARVN Pathfinders), "B" Co II CTZ (Pleiku) Mike Force (50 SF) & 275 LLDB (Includes Montagnards) | Blue Max | 374 | Vietnam | Bu Prang CIDG fighting camp, Quang Duc "Great Virtue" Province |
| 1968-73? | Military Assistance Command, Vietnam – Studies and Observations Group (MACV-SOG) Airborne Studies Group (SOG 36) | Eldest Son, Italian Green, Pole Bean | North Vietnam, Laos, Cambodia | ||
| 28 Nov. 1970 | Recon Team Florida, CCN, MACV-SOG (High Altitude Low Opening [HALO]) | 3 Americans, one ARVN officer and 2 Montagnards | Laos | NVA road inside Laos | |
| 7 May 1971 | Captain Larry Manes' Recon Team, CCN, MACV-SOG (HALO) | 4 Americans | South Vietnam | Between Ashau Valley and Khe Sanh, NVA trail extension of Laotian Highway 921 | |
| 22 June 1971 | Sergeant Major Billy Waugh's Recon Team, CCN, MACV-SOG (HALO) | 4 Americans | South Vietnam | 60 miles SW of Danang | |
| 22 Sep. 1971 | Captain Jim Storter's Recon Team, CCC, MACV-SOG (HALO) | 4 Americans | South Vietnam | Plei Trap Valley, NW of Pleiku | |
| 11 Oct. 1971 | Sgt. 1st Class Dick Gross' Recon Team, CCC, MACV-SOG (HALO) | 5 Americans | Vietnam | 25 miles, SW of Pleiku in the Ia Drang Valley | |
| 23 Oct. 1983 | Navy SEAL Team and USAF CCT | Urgent Fury | 15 | Grenada | Port Salines |
| 25 Oct. 1983 | 75th Ranger Regiment LRS Detachment, 82nd Abn Div. combat controllers (CCT), Air Force Special Operations Command (AFSOC), 12 troopers; 4 troopers, 1st Bn, tactical air control parties (TACP). | Urgent Fury | 16(?) | Grenada | Point Salines |
| 25 Oct. 1983 | Navy SEAL Team | Urgent Fury | 11 | Grenada | Governor's residence |
| 25 Oct. 1983 | 75th Ranger Regiment 1st and 2nd Bns; and two paratroopers (SGT Spain and SPC Richardson from 307th Engineer Bn) | Urgent Fury | 500 | Grenada | Point Salines airfield |
| 20 Dec. 1989 | UNIT: (0100) Rangers, 75th Ranger Regiment; 82nd Airborne Division Ready Brigade | Just Cause | 4,000 | Panama | Rio Hato east to Fort Cimarron |
| 20 Dec. 1989 | (0124) Rangers; (0145) 82nd Abn. Div., 1st Brigade Task Force: 1/504th PIR, 1/505th PIR; 2nd Bn., 504th PIR; 4th Bn., 325th Abn. Inf. Reg., Co. B and C; A Co., 3/505 PIR; 3rd Bn., 73rd Abn. Armor Reg.; 82nd Abn. MP Co., 3 platoons (0411). All joined to form: Task Force Pacific. | Just Cause | 2,176 | Panama | Torrijos-Tocumen Airport |
| 15 Jan. 1991 | Special Forces Operational Detachment-Delta (HAHO) | Desert Storm | 12 | Iraq | Northwest desert |
| Dec. 1991 | Navy SEAL Team 6 | Raw Deal | Haiti | Navassa Island | |
| 19 Oct. 2001 | 75th Ranger Regiment | Operation Enduring Freedom | 200 | Afghanistan | Objective Rhino at Dry Lake Airstrip |
| 13 Nov. 2001 | 75th Ranger Regiment, 3rd Battalion | Operation Enduring Freedom | Afghanistan | In the vicinity of Alimarden Kan-E-Bagat | |
| 25 Feb. 2003 | 75th Ranger Regiment, 2nd Battalion; 504th Infantry, 3rd Battalion | Operation Enduring Freedom | Afghanistan | Near Chahar Borjak, Nimruz Province | |
| 24 Mar. 2003 | 75th Ranger Regiment, 3rd Battalion; 24th Special Tactics Squadron | Operation Iraqi Freedom | Iraq | Northwestern desert region of Iraq, in the vicinity of Al Qaim | |
| 26 Mar. 2003 | 173rd Airborne Brigade | Operation Iraqi Freedom | 954 | Iraq | Bashur Drop zone |
| 28-29 Mar. 2003 | 27th Engineer Battalion; 75th Ranger Regiment, 3rd Battalion; 75th Ranger Regiment, 3rd Battalion; 24th Special Tactics Squadron | Operation Iraqi Freedom | Iraq | At H1 Airfield | |
| 3 Jul. 2004 | 75th Ranger Regiment, Regimental Reconnaissance Detachment (HALO) | Operation Enduring Freedom | Afghanistan | Southeastern Region | |
| 31 Jul. 2004 | USMC 1st Reconnaissance Battalion (HAHO) | Operation Iraqi Freedom | 6 | Iraq | Near Baghdad |
| 30 May 2007 | 10th Special Forces Group, 3rd Battalion, ODA 074 (HALO) | Operation Iraqi Freedom | 11 | Iraq | Ninewah Province |
| 25 Jan. 2012 | Navy SEAL Team 6 | Hostage Rescue | Somalia | ||
Air Force
Like the Army, the Air Force issues the same parachutist badges in the same three degrees (Basic, Senior, & Master) but have different criteria for the awarding of these badges. The level of degree is determined by the number of jumps the wearer has successfully completed, years of service on jump status, and other requirements as specified by AFI 11-402, Aviation and Parachutist Service, Aeronautical Ratings and Badges.[14]



In 1956 the Air Force began issuing a unique Basic, Senior, and Master Parachutist Badges. These parachutist badges were modeled after the Air Force's Medical Badges. Due to popular demand, the Air Force decided to revert to issuing the Army style parachutist badges in 1963.[15]
Basic Parachutist Badge
The Basic Parachutist Badge may be awarded following completion of basic parachute training through a designated Air Force Air-Ground Training Program. Air Force personnel generally earn the basic parachutist badge either through the Army's Airborne School at Fort Benning, or the United States Air Force Academy's AM-490 freefall parachute training course taught by AETC's 98th Flying Training Squadron.[14]
Senior Parachutist Badge
The Senior Parachutist Badge consists of the Basic Parachutist Badge with a star atop the parachute. Awarded for 30 static line jumps with a minimum of 24 months of cumulative time on jump status. The 30 jumps must include: (1) Two jumps during the hours of darkness; (2) Fifteen jumps with operational equipment IAW AFI 11-410; (3) Actually perform one night jump as a Primary JM (PJM); and (4) Seven jumps performing as PJM.[16]
Master Parachutist Badge
The Master Parachutist Insignia consists of the Senior Parachutist Badge with a star centered within the wreath. Awarded for 65 static line jumps with a minimum of 36 months of cumulative time on jump status. The 65 jumps must include: (1) Four jumps during the hours of darkness; (2) Twenty-five jumps with operational equipment IAW AFI 11-410; (3) Two night jumps performing PJM duties; and (4) Fifteen jumps performing as PJM.[16]
Military Freefall Parachutist Badges


Qualified Army and Air Force personnel may go on to earn the Military Freefall Parachutist Badge in special operations training for High Altitude Low Opening (HALO) and High Altitude High Opening (HAHO) jumps. HALO/HAHO training is conducted by the John F. Kennedy Special Warfare Center and School of the US Army Special Operations Command, on behalf of the US Special Operations Command. It is awarded in two degrees: Basic and Master. To earn the basic badge, the jumper must have graduated from Army Airborne School and the Military Free-Fall Parachutist Course.[17] To earn the master badge, jumpers must have graduated from Army Airborne School, Army Jumpmaster School, Military Free-Fall Parachutist Course, and the Military Free-Fall Jumpmaster Course.[18]
As with the Army's Parachutist Badges, US Army parachutist that have earned one of the Military Freefall Parachutist Badges are also eligible to earn Combat Jump Devices.[1][6][12]
Navy and Marine Corps
The United States Navy and Marine Corps issue parachutist insignia in two degrees: the U.S. Military Basic Parachutist Badge, also called the Basic Parachutist Insignia (the same badge that's awarded to all DoD military services), and the Navy and Marine Corps Parachutist Insignia. Parachutist insignia is available to personnel who perform jumps as a:[19]
- Static-Line Parachute Jumper,
- Military Free-Fall Parachute Jumper, and
- High Altitude Low Opening (HALO) Parachute Jumper (used for premeditated personnel parachute (P3) operations).
Training is accomplished by successful completion of the prescribed course of instruction while attending the:[19]
- U.S. Army Airborne School,
- Military Free-Fall Parachutist Course, or
- other training certified by Chief of Naval Education and Training (CNET) or approved by the Chief of Naval Operations (CNO).
Basic Parachutist Insignia
The right to wear the Basic Parachutist Insignia is based on the completion of prescribed training defined in MCO 3120.11.:[19]
When an enlisted member initially qualifies as a static line parachutist, an entry shall be made on NAVPERS 1070/613 (commonly referred to as a "Page 13" entry) of the service record indicating the date of qualification, type(s) of aircraft in which qualified, and unit at which the training was received. Enlisted members are authorized the parachutist (PJ) designator added to their rating.[19]
A qualified static-line parachute jumper who successfully completes the prescribed program of instruction while attending a formal, interservice training facility including a minimum of 10 military free-fall parachute jumps, at least 2 of which must have been conducted carrying full combat equipment (1 day/1 night), may qualify. Enlisted members are authorized the military free-fall parachutist (FPJ) designator added to their rating.[19]
When an officer initially qualifies as a static line parachutist, the additional qualification designator (AQD) of BT1 will be entered into the officer's record by their detailer (NAVPERS). Free-fall qualification will result in an AQD of BT2.[19]
For both Static Line and Military Free Fall Parachutist qualified personnel, a service record entry shall also indicate whether or not the member is HALO-qualified.[19]
The Basic Parachutist Badge is a prerequisite for the Special Warfare Badge since parachutist training is an integral part of the Navy's Basic Underwater Demolition/SEAL (BUD/S) program. SEAL personnel generally do not wear the Basic badge once they earn their Special Warfare insignia, but will wear their Navy and Marine Corps Parachutist Badge in addition to the Special Warfare Badge, the latter nicknamed the "Budweiser" badge. Navy EOD technicians are generally also jump qualified with a number of them also being qualified in military free-fall (HALO/HAHO). Currently, due to a recent change, newly pinned Navy EOD technicians are required to attend the U.S. Army's Basic Airborne School upon graduation. As well, a number of SWCC personnel earn Basic Parachutist badges in conjunction with their assignment to a Special Boat Team detachment that uses the Maritime Craft Air Delivery System (MCADS). This enables them to drop small watercraft and their crews from C-130 aircraft.[19]
Navy and Marine Corps Parachutist Insignia
The Navy and Marine Corps Parachutist Insignia (originally issued as Navy Parachute Rigger wings) is a gold-colored embroidered or metal insignia depicting an open parachute with outstretched wings. It is authorized for officers and enlisted personnel who were awarded the Basic Parachutist Insignia and, under competent orders, have completed a minimum of five additional static-line or P3 jumps, to include: (1) combat equipment day jump, two (2) combat equipment night jumps, and employ at least two (2) different types of military aircraft.[19]
The U.S Navy and Marine Corps Parachutist badge was originally known as the U.S. Navy Certified Parachute Rigger badge and designed by American Insignia Company in 1942 for graduates of the U.S. Navy Parachute Rigger School. During WWII, despite being against uniform regulations it became common for U.S. Marine Corps paratroopers who were issued the silver U.S. Army Basic Parachutist badge to wear the gold Navy Certified Parachute Rigger badge because they believed the gold "Rigger wings" looked better on their uniform.[20] This out of regulations wearing of the Parachute Rigger badge became so common that in July 1963, the Commander of United States Marine Corps Force Reconnaissance Bruce F. Meyers sent a request to the Chief of Naval Operations Admiral George W. Anderson Jr. via Marine Corps Commandant General David M. Shoup requesting to officially make the Navy Parachute Rigger badge the parachutist badge for the Navy and Marine Corps. The request was approved by Admiral Anderson on July 12, 1963 per BuPers Notice 1020.[21] Since 1963, being a graduate of the U.S. Navy Parachute Rigger School is no longer a requirement to earn the badge. To be awarded the Navy and Marine Corps Parachutist Insignia did, however, require the parachutist to have completed the minimum five additional jumps in a jump billet.
See also
- Parachutist Badge
- Air Assault Badge
- Glider Badge
- Pathfinder Badge
- Blood wings
References
- U.S. Army Regulation 600-8-22, Military Awards, Official Department of the Army Regulation, dated 11 Dec 2006, revised 15 Sep 2011, last accessed 4 Oct 2011
- Army Directive 2011-11, Change to Wear of the Army Combat Uniform (ACU) Items Archived 10 May 2012 at the Wayback Machine, Secretary of the Army, 13 June 2011, last accessed 18 February 2013
- Born, K (1998). "U.S. Army Parachute Badge". US Army Quartermaster Museum. Archived from the original on 5 November 2008. Retrieved 22 November 2008.
- Lanham, Howard G. (2001). "Insignia of Airborne Units U.S. Army". American Military Patches, Other Insignia and Decorations of World War Two. Retrieved 15 November 2008.
- "Beret Flashes and Background Trimmings". The Institute of Heraldry. United States Department of the Army. Archived from the original on 22 August 2008. Retrieved 15 November 2008.
- Army Regulation 670-1, Wear and Appearance of Army Uniforms and Insignia, dated 25 May 2017, last accessed 2 January 2020
- "US Army Badges". US Army Institute of Heraldry. Archived from the original on 15 June 2010. Retrieved 8 February 2010.
- U.S. Army Parachute Badge, U.S. Army Quartermaster Museum, last accessed 18 February 2013
- United States Combat Jumps, GlobalSecurity.org, last updated 7 May 2011, last accessed 17 February 2013
- Plaster, John L. (1997). SOG: The Secret Wars of America's Commandos in Vietnam. New York: Simon & Schuster. p. 295-301. ISBN 0-684-81105-7.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Units Credited With Assult Landings, General Orders No. 10, Department of the Army, dated 25 September 2006, last accessed 30 April 2017
- Hitting the ground with coalition partners; Special Warfare Magazine; Valume 21, Issue 6; dated November–December 2008, last accessed 17 February 2013
- History of Military Operational Parachute Jumps, Special Forces Association, dated 7 March 2013, last accessed 30 April 2017
- AFI 11-402, Aviation and Parachutist Service, Aeronautical Ratings and Badges Archived 12 January 2014 at the Wayback Machine, U.S. Air Force Instructions, dated 13 December 2010, last accessed 11 January 2014
- Obsolete USAF Insignia Archived 2 November 2016 at the Wayback Machine, USAF Flag Ranks website, last accessed 1 June 2012
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 December 2016. Retrieved 25 March 2018.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- MFFPC ATRRS Information Changes, U.S. Army Special Operations Center of Excellence, last accessed 22 April 2017
- Military Free-Fall Jumpmaster Course (MFFJMC), U.S. Army Special Operations Center of Excellence, last accessed 22 April 2017
- U.S. Marine Corps Order 3120.11, U.S. Marine Corps Parachuting Policy and Program Administration, dated 4 May 2009, last accessed 18 February 2013
- Mason, Chris (2004). Paramarine!: Uniforms and Equipment of Marine Corps Parachute Units in World War II. Schiffer Pub Ltd. pp. 175–177. ISBN 9780764319242.
- "Evolution of Naval Wings" (PDF). Coast Guard Aviation History. THE U.S. COAST GUARD AVIATION ASSOCIATION. Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 February 2016. Retrieved 25 January 2016.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Parachutist Badges of the US Army. |

