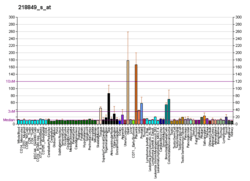
PPP1R13L
RelA-associated inhibitor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PPP1R13L gene.[5][6]
Interactions
PPP1R13L has been shown to interact with Sp1 transcription factor[7] and RELA.[5][7]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000104881 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000040734 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Yang JP, Hori M, Sanda T, Okamoto T (May 1999). "Identification of a novel inhibitor of nuclear factor-kappaB, RelA-associated inhibitor". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 274 (22): 15662–70. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.22.15662. PMID 10336463.
- "Entrez Gene: PPP1R13L protein phosphatase 1, regulatory (inhibitor) subunit 13 like".
- Takada N, Sanda T, Okamoto H, Yang JP, Asamitsu K, Sarol L, Kimura G, Uranishi H, Tetsuka T, Okamoto T (August 2002). "RelA-associated inhibitor blocks transcription of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 by inhibiting NF-kappaB and Sp1 actions". Journal of Virology. 76 (16): 8019–30. doi:10.1128/JVI.76.16.8019-8030.2002. PMC 155123. PMID 12134007.
Further reading
- Liu ZJ, Lu X, Zhong S (September 2005). "ASPP--Apoptotic specific regulator of p53". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Reviews on Cancer. 1756 (1): 77–80. doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2005.08.002. PMID 16139958.
- Takada N, Sanda T, Okamoto H, Yang JP, Asamitsu K, Sarol L, Kimura G, Uranishi H, Tetsuka T, Okamoto T (August 2002). "RelA-associated inhibitor blocks transcription of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 by inhibiting NF-kappaB and Sp1 actions". Journal of Virology. 76 (16): 8019–30. doi:10.1128/JVI.76.16.8019-8030.2002. PMC 155123. PMID 12134007.
- Bergamaschi D, Samuels Y, O'Neil NJ, Trigiante G, Crook T, Hsieh JK, O'Connor DJ, Zhong S, Campargue I, Tomlinson ML, Kuwabara PE, Lu X (February 2003). "iASPP oncoprotein is a key inhibitor of p53 conserved from worm to human". Nature Genetics. 33 (2): 162–7. doi:10.1038/ng1070. PMID 12524540.
- Colland F, Jacq X, Trouplin V, Mougin C, Groizeleau C, Hamburger A, Meil A, Wojcik J, Legrain P, Gauthier JM (July 2004). "Functional proteomics mapping of a human signaling pathway". Genome Research. 14 (7): 1324–32. doi:10.1101/gr.2334104. PMC 442148. PMID 15231748.
- Slee EA, Gillotin S, Bergamaschi D, Royer C, Llanos S, Ali S, Jin B, Trigiante G, Lu X (December 2004). "The N-terminus of a novel isoform of human iASPP is required for its cytoplasmic localization". Oncogene. 23 (56): 9007–16. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1208088. PMID 15489900.
- Issaeva N, Bozko P, Enge M, Protopopova M, Verhoef LG, Masucci M, Pramanik A, Selivanova G (December 2004). "Small molecule RITA binds to p53, blocks p53-HDM-2 interaction and activates p53 function in tumors". Nature Medicine. 10 (12): 1321–8. doi:10.1038/nm1146. PMID 15558054.
- Zhang X, Wang M, Zhou C, Chen S, Wang J (February 2005). "The expression of iASPP in acute leukemias". Leukemia Research. 29 (2): 179–83. doi:10.1016/j.leukres.2004.07.001. PMID 15607367.
- Laska MJ, Nexø BA, Vistisen K, Poulsen HE, Loft S, Vogel U (July 2005). "Polymorphisms in RAI and in genes of nucleotide and base excision repair are not associated with risk of testicular cancer". Cancer Letters. 225 (2): 245–51. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2005.03.021. PMID 15885892.
- Skjelbred CF, Saebø M, Nexø BA, Wallin H, Hansteen IL, Vogel U, Kure EH (July 2006). "Effects of polymorphisms in ERCC1, ASE-1 and RAI on the risk of colorectal carcinomas and adenomas: a case control study". BMC Cancer. 6: 175. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-6-175. PMC 1533843. PMID 16817948.
- Beausoleil SA, Villén J, Gerber SA, Rush J, Gygi SP (October 2006). "A probability-based approach for high-throughput protein phosphorylation analysis and site localization". Nature Biotechnology. 24 (10): 1285–92. doi:10.1038/nbt1240. PMID 16964243.
- Bergamaschi D, Samuels Y, Sullivan A, Zvelebil M, Breyssens H, Bisso A, Del Sal G, Syed N, Smith P, Gasco M, Crook T, Lu X (October 2006). "iASPP preferentially binds p53 proline-rich region and modulates apoptotic function of codon 72-polymorphic p53". Nature Genetics. 38 (10): 1133–41. doi:10.1038/ng1879. PMID 16964264.
- Olsen JV, Blagoev B, Gnad F, Macek B, Kumar C, Mortensen P, Mann M (November 2006). "Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks". Cell. 127 (3): 635–48. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.026. PMID 17081983.
- Zhang X, Diao S, Rao Q, Xing H, Liu H, Liao X, Wang M, Wang J (May 2007). "Identification of a novel isoform of iASPP and its interaction with p53". Journal of Molecular Biology. 368 (4): 1162–71. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2007.03.001. PMID 17391696.
- Laska MJ, Strandbygård D, Kjeldgaard A, Mains M, Corydon TJ, Memon AA, Sørensen BS, Vogel U, Jensen UB, Nexø BA (July 2007). "Expression of the RAI gene is conducive to apoptosis: studies of induction and interference". Experimental Cell Research. 313 (12): 2611–21. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2007.05.006. PMID 17570360.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.