Note-taking
Note-taking (sometimes written as notetaking or note taking) is the practice of recording information captured from another source. By taking notes, the writer records the essence of the information, freeing their mind from having to recall everything.[1] Notes are commonly drawn from a transient source, such as an oral discussion at a meeting, or a lecture (notes of a meeting are usually called minutes), in which case the notes may be the only record of the event.

History
Note-taking has been an important part of human history and scientific development. The Ancient Greeks developed hypomnema, personal records on important subjects. In the Renaissance and early modern period, students learned to take notes in schools, academies and universities, often producing beautiful volumes that served as reference works after they finished their studies.[2][3] In pre-digital times, people used many kinds of notebooks, including accounting waste books, marginalia, and commonplace books.[4] Philosopher John Locke developed an indexing system[5] which served as a model for commonplace books; for example, it inspired another book nearly a century later, Bell’s Common-Place Book, Formed generally upon the Principles Recommended and Practised by Mr Locke.
Cognitive psychology
Note-taking is a central aspect of a complex human behavior related to information management involving a range of underlying mental processes and their interactions with other cognitive functions.[6] The person taking notes must acquire and filter the incoming sources, organize and restructure existing knowledge structures, comprehend and write down their explanation of the information, and ultimately store and integrate the freshly processed material. The result is a knowledge representation, and a memory storage.[1] Studies comparing the performance of students who took handwritten notes to students who typed their notes found that students who took handwritten notes performed better on examinations, hypothetically due to the deeper processing of learned material through selective rephrasing instead of word-for-word transcription which is common when typing notes.[7]
Reasons for note-taking
Note-taking is an important skill for students, especially at the college level. In some contexts, such as college lectures, the main purpose of taking notes may be to implant the material in the mind, the written notes themselves being of secondary importance.
Systems
Many different formats are used to structure information and make it easier to find and to understand later. The format of the initial record may often be informal and/or unstructured. One common format for such notes is shorthand, which can allow large amounts of information to be put on paper very quickly. Historically, note-taking was an analog process, written in notebooks, or other paper methods like Post-It notes. In the digital age, use of computers, tablet PCs and personal digital assistants (PDAs) is common.
The note taker usually has to work fast, and different note-taking styles and techniques try to make the best use of time. The average rate of speech is 2–3 words per second (which is 120-180 words per minute), but the average handwriting speed as only 0.2–0.3 words per second (which is 12-18 words per minute).[6]
Regardless of the medium, note-taking can be broadly divided into linear and nonlinear methods, which can be combined.
Regardless of the system used, it can be best to focus on writing down the most important information first.
Linear note-taking
Linear note-taking is the process of writing down information in the order in which you receive it.
Outlining
Outlining [8] is one of the most common note-taking systems. Notes and thoughts are organised in a structured, logical manner, reducing the time needed to edit and review, allowing a lot of information to be digested in a short period of time. Outlining is less effective for classes that involve many formulas and graphs, like mathematics or chemistry. In these situations, a system such as Cornell Notes[9] may be superior.
Outlines generally proceed down a page, using headings and bullets to structure information. A common system consists of headings that use Roman numerals, letters of the alphabet, and Arabic numerals at different levels. A typical structure would be:
- I. First main topic
- A. Subtopic
- Detail
- Detail
- Detail
- B. Subtopic
- Detail
- Detail
- Detail
- A. Subtopic
- II. Second main topic
- A. Subtopic
- Detail
- Detail
- Detail
- B. Subtopic
- Detail
- Detail
- Detail
- A. Subtopic
However, this sort of structure has limitations in non-digital form since it is difficult to go back and insert more information. Adaptive systems are used for paper-and-pen insertions, such as using the reverse side of the preceding page in a spiral notebook to make insertions. Or one can simply leave large spaces in between items, to enable more material to be inserted. (For information about application software that supports outlining, see Category: Outliners.)
Computerized note-taking, whether with a word processor, outliner software, or a digital notebook program such as OneNote, Evernote, or TiddlyWiki, allows note-takers to revise easily and add more entries or rows to the outline.
Sentence method
Sentence note-taking is simply writing down each topic as a short, simple sentence. This method works well for fast-paced lesson where a lot of information is being covered. The note-taker records every new thought, fact, or topic on a separate line. All information is recorded but is not organized into major and minor topics. Notes can be numbered or set off with bullets showing where a new thought begins.
Non-linear note-taking
Approaches to non-linear note-taking include clustering,[10] concept mapping,[11][12] Cornell Notes,[13] idea mapping,[14] instant replays,[15] Ishikawa diagrams,[16] knowledge maps,[17] learning maps,[18] mind mapping,[19] model maps,[20] the pyramid principle,[21] semantic networks,[22] and SmartWisdom.[23]
Charting
This method of note taking is useful for subject matter that can be broken into categories, such as similarities, differences, date, event, impact, etc. Charting works best if students are able to identify categories and draw a table prior to the lecture. This method is also useful as an editing tool. Students may review and rewrite notes using the charting method. The method may work well for students who like to organize information neatly and who learn by recognizing patterns.[24]

Mapping
Mapping uses spatial organization and diagrams to assemble information. Ideas are written in a tree structure, with lines connecting them together. Mind maps are commonly drawn from a central point, purpose, or goal in the center of the page and then branch outward to identify all the ideas connected to that goal. Colors, small graphics, and symbols are often used to help to visualize the information more easily. This note-taking method is most common among visual learners and is a core practice of many accelerated learning techniques. It is also used for planning and writing essays.[25]
Cornell Notes
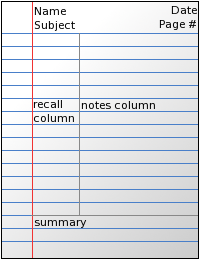
The Cornell Notes method of note-taking was developed by Dr. Walter Pauk of Cornell University and promoted in his bestselling 1974 book How to Study in College. It is commonly used at universities today. The Cornell method consists of dividing a single page into three sections: a right-hand column for notes, a left-hand column for cues, and a strip at the bottom for a summary. Cues are key words or questions that help evoke key aspects of the topic. Cornell notes may be more effective for understanding concepts or producing readable notes, but studies have found that they had no significant effect on student performance.[26][27][28][29]
SQ3R
SQ3R ("Survey, Question, Read, Recite, Review") is a method of taking notes from written material, though it might be better classified as a method of reading and gaining understanding. The reader skims the written material to produce a list of headings (Survey), which are then converted into questions (Question). The reader then considers the questions while reading to provide motivation for what is being covered (Read). The reader writes notes in sections headed by the questions (Recite), then writes a summary from memory and reviews the notes (Review).
Research shows that students who use the SQ3R strategy retain more information and achieve higher test scores.[30]
An updated version called SQ4R,[31] which adds a "Relate” step before "Review", has been used by some students since the early 1960s.
Guided notes
Sometimes lecturers may provide handouts of guided notes, which provide a "map" of the lecture content with key points or ideas missing. Students then fill in missing items as the lecture progresses. Guided notes may assist students in following lectures and identifying the most important ideas from a lecture. This format provides students with a framework, yet requires active listening (as opposed to providing copies of presentation slides in their entirety), and promotes active engagement during lecture or independent reading. The student ends up with full and accurate notes for use as a study guide.
Research suggests that guided notes improve student recording of critical points in lecture, as well as quiz scores on related content. In addition, an investigation carried out on students with learning problems showed that the use of the guided notes is an effective strategy to improve the performance of these students.[32]
Zettelkasten
The zettelkasten method uses individual notes on index cards (or their digital equivalent) that are linked and cross-referenced with tags or other metadata.
Electronic note-taking methods
The growing ubiquity of laptops in universities and colleges has led to a rise in electronic note-taking. Many students write their notes in word processors or prepare digital hand-written notes using a graphics tablet or tablet computer and styli or digital pens, with the aid of note-taking software. Online applications are receiving growing attention from students who can forward notes using email, or otherwise make use of collaborative features in these applications and can also download the texts as a file on a local computer. It has also become common for lecturers to deliver lectures using these and similar technologies, including electronic whiteboards, especially at institutes of technology.
Online note-taking has created problems for teachers who must balance educational freedom with copyright and intellectual property concerns regarding course content.
Electronic note-taking may be less effective than traditional methods of note-taking. A study done by Pam A. Mueller of Princeton University and Daniel M. Oppenheimer of the University of California, Los Angeles showed that students who take notes digitally retain less information than students who take notes on paper, and the digital note-takers have more difficulty remembering what they've written.[33] Electronic note-taking has created computer-aided distractions in class as multitasking on laptops is very easy to accomplish.[34] However, this research only applies to typing notes on laptops, not writing on tablets.
Professional services
Professional note-takers provide access to information for people who cannot take their own notes, such as some deaf and hearing impaired people. They most frequently work in colleges and universities, but are also used in workplace meetings, appointments, conferences, and training sessions.
See also
- Comparison of note-taking software
- Cornell Notes
- E-book
- Forgetting curve
- Handwriting recognition
- List of mind mapping software
References
- British Journal of Educational Technology (2008) doi:10.1111/j.1467-8535.2008.00906.x Optimising the use of note-taking as an external cognitive aid for increasing learning Tamas Makany, Jonathan Kemp and Itiel E. Dror http://www.idemployee.id.tue.nl/g.w.m.rauterberg/amme/makany-et-al-2008.pdf
- Eddy, Matthew Daniel (2018). "The Nature of Notebooks: How Enlightenment Schoolchildren Transformed the Tabula Rasa". Journal of British Studies. 57 (2): 275–307. doi:10.1017/jbr.2017.239.
- Eddy, Matthew Daniel (2016). "The Interactive Notebook: How Students Learned to Keep Notes during the Scottish Enlightenment". Book History. 19: 87–131. doi:10.1353/bh.2016.0002.
- Commonplace Books. Harvard University Library Open Collections Program.
- Locke J. (1706). A new method of making common-place-books. Google Books: [A new method of making common-place-books https://books.google.com/books?id=sF0HMAEACAAJ]. Also included in Locke's
- Piolat, A., Olive, T. & Kellogg, R. T. (2005). Cognitive effort during note-taking. Applied Cognitive Psychology, 19, 291–312.
- Michael C. Friedman (October 15, 2014), Notes on Note-Taking: Review of Research and Insights for Students and Instructors (PDF), Harvard Initiative for Learning and Teaching, Harvard University, archived from the original (PDF) on February 18, 2018, retrieved January 31, 2018
- "Note Taking: Outline Method". www.citruscollege.edu. Retrieved 2018-04-12.
- "Reading a Textbook for True Understanding - Cornell College". www.cornellcollege.edu. Retrieved 2018-04-23.
- Rico, G. L. (1983). Writing the natural way: using right-brain techniques to release your expressive powers. New York: Penguin Putnam.
- Canas, A. J., Coffey, J. W., Carnot, M. J., Feltovich, P., Hoffman, R. R., Feltovich, J. et al. (2003). A summary of literature pertaining to the use of concept mapping techniques and technologies for education and performance support. Report to the Chief of Naval Education and Training Pensacola FL 32500.
- Novak, J. D. & Gowin, D. B. (1984). Learning how to learn. New York: Cambridge University Press.
- Pauk, W. (2001). How to study in college. Boston, MA: Houghton Mifflin.
- Nast, J. (2006). Idea mapping: how to access your hidden brain power, learn faster, remember more, and achieve success in business. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons.
- Turley, J. (1989). Speed-reading in business. An action plan for success. Menlo Park, CA: Crisp Publications.
- Ishikawa, K. (1984). Guide to quality control (2nd revised English ed.). New York: Unipub.
- O’Donnell, A. M., Dansereau, D. F. & Hall, R. F. (2002). Knowledge maps as scaffolds for cognitive processing. Educational Psychology Review, 14, 71–86.
- Rose, C. & Nicholl, M. J. (1997). Accelerated learning for the 21st century: the six-step plan to unlock your master mind. London: Judy Piatkus Publishers.
- Buzan, T. (2000). Use your head. Harlow, England: BBC Active.; Catchpole, R. & Garland, N. (1996). Mind maps: using research to improve the student learning experience. In G. Gibbs (Ed.), Improving student learning: using research to improve student learning (pp. 211–222). Oxford: Oxford Centre for Staff Development at Oxford Brookes University.; Gruneberg, M. M. & Mathieson, M. (1997). The perceived value of minds maps (spider diagrams) as learning and memory aids. Cognitive Technology, 2, 21–24.; Hartley, J. (2002). Note-taking in non-academic settings: a review. Applied Cognitive Psychology, 16, 559–574.
- Caviglioli, O. & Harris, I. (2000). Mapwise accelerated learning through visible thinking. Strafford, NH: Network Educational Press.
- Minto, B. (1987). The pyramid principle. Harlow, England: Financial Times, Prentice Hall, Pearson Education.
- Lehmann, F. (1992). Semantic networks in artificial intelligence. Oxford: Pergamon Press.; Sowa, J. F. (1991). Principles of semantic networks: explorations in the representation of knowledge. San Mateo, CA: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers.
- Kemp, J. (2006). SmartWisdom, Retrieved January 15, 2008, from http://www.smartwisdom.com/
- "Charting Method". Ms. Liew's Class. Retrieved 2018-04-23.
- Cristine, Goldberg (November 2004). "Brain Friendly Techniques: Mind Mapping". School Library Media Activities Monthly. 21 (3). ISSN 0889-9371.
- Jacobs, Keil. A Comparison of Two Note Taking Methods in a Secondary English Classroom Proceedings: 4th Annual Symposium: Graduate Research and Scholarly Projects [79] Conference proceedings held at the Eugene Hughes Metropolitan Complex, Wichita State University, April 25, 2008. Symposium Chair: David M. Eichhorn
- Broe, Duane (Summer 2013). "The Effects of Teaching Cornell Notes on Student Achievement" (PDF). www.minotstateu.edu/#. Retrieved 2017-05-12.
- Quintus, Lori; Borr, Mari; Duffield, Stacy; Napoleon, Larry; Welch, Anita (Spring–Summer 2012). "The Impact of the Cornell Note-Taking Method on Students' Performance in a High School Family and Consumer Sciences Class" (PDF). www.natefacs.org. Retrieved 2018-10-10.
- Zulejka, Baharev (2016). The effects of Cornell note-taking and review strategies on recall and comprehension of lecture content for middle school students with and without disabilities (Thesis). Rutgers University - Graduate School of Education. doi:10.7282/T3HD7XZ8.
- Carlston, David L. (2011-06-14). "Benefits of Student-Generated Note Packets". Teaching of Psychology. 38 (3): 142–146. doi:10.1177/0098628311411786. ISSN 0098-6283.
- "SQ4R Reading Method". brazosport.edu. Retrieved 2018-03-26.
- Hamilton, Sheri L.; Seibert, Marilyn A.; Gardner, Ralph; Talbert-Johnson, Carolyn (May 2000). "Using Guided Notes to Improve the Academic Achievement of Incarcerated Adolescents with Learning and Behavior Problems". Remedial and Special Education. 21 (3): 133–170. doi:10.1177/074193250002100302. ISSN 0741-9325.
- "Attention, Students: Put Your Laptops Away". NPR.org. Retrieved 2018-04-18.
- Cain, J; Bird, ER; Jones, MK (2008). "Mobile computing initiatives within pharmacy education". Am J Pharm Educ. 4 (7): 72. doi:10.5688/ajpe797107. PMC 4812780. PMID 27168620.
- Van Matre, Nicholas H.; Carter, John (1975). The Effects of Note-Taking and Review on Retention of Information. Presented by Lecture. Paper presented at the Annual Meeting of the American Educational Research Association (Washington, D.C., March 30-April 4, 1975).
- Carter, John F.; Van Matre, Nicholas H. (1975). Note Taking Versus Note Having. Journal of Educational Psychology, 67, 6, 900-4, Dec 75
External links
| Wikibooks has a book on the topic of: Note Taking |
- Eck, Allison (June 3, 2014). "For More Effective Studying, Take Notes With Pen and Paper". Nova Next. PBS.
- Suber, Peter. "Taking notes on philosophical texts". Earlham.edu.