Nigerian heraldry
Nigerian heraldry is the system of heraldry that exists in Nigeria. It dates to the country's pre-colonial period, and due to an absence of a central heraldic authority, it is currently largely unregulated.
Components
Although Nigeria's hereditary signifiers are primarily oral (e.g. oriki) and performance based (e.g. masquerades) in nature, the country nevertheless has a vibrant heraldic tradition. Its principal components are:
Quasi-heraldic customs
Vexillology

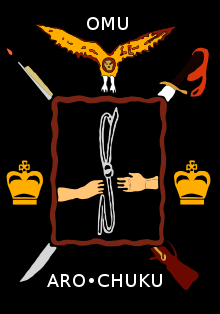

The flags that have been used to represent the various Nigerian kingdoms over the centuries have all followed general rules and have much in common. That of Sokoto, for example, references the Prophet Muhammad's ascribing of the colour green to paradise.[1][2][3] By using a colour that many have therefore come to identify with the prophet himself to embody the Sultan of Sokoto, a symbolic continuity between this monarch and the religious leader whom he claimed to succeed was implied. The flag of the Aro Confederacy, meanwhile, was designed to inspire awe in all that saw it. The two crowns symbolized the Eze Aro, ruler of the Aro, while the musket and the lance were intended to represent the state's warriors, who fought a famous battle against the British in the colonial era.
Totemism

A number of kingdoms and clans in Nigeria have also had totems. Mostly taking the form of animals, these generally represented religious and/or social commonalities, and often had a series of taboos associated with them.
For example, leopards are an important totem in many parts of Southern Nigeria. Intelligent and courageous, they were seen in Benin symbolism as the Obas' animal counterparts - The "Lords of the Bush".[4] Even today, they often still serve as ciphers for powerful individuals (such as the Oba of the Akure Kingdom amongst the Yoruba people[5]) and associations (such as Ekpe[6] amongst the Efik).
Pictograms
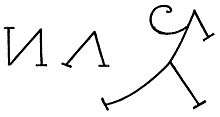
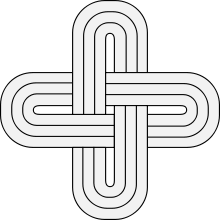
Some kingdoms also made use of pictograms in their traditions. These were often quite unique, and a number of them were passed down by way of heredity thereafter.
Amongst the Yoruba, Solomon's knot is commonly viewed as a royal cipher. In addition to its usage on regal robes, crowns, stools and sceptres as a result, it also appears in associated court art.[7]
Private heraldry


Private heraldry is, like the quasi-heraldic customs described above, unregulated in Nigeria. Most of its practices are therefore governed more by loose convention than they are by official statute, and it is technically legal to assume another's arms in the absence of copyright protection - the only judicial protection for such works for every component besides public heraldry (see below).
Many of these coats of arms (including a great number of those that are connected to members of the Nigerian chieftaincy system, such as the Erunmu coat rendered here) are composed of similar imagery. For example, both the Erunmu arms and the Okpe ones - as well as the flag of the Aro Confederacy from earlier - include blades of some kind. Although these usually take the form of Ida swords, Erunmu's coat displays a machete instead. Both this and the accompanying hoe are an obvious reference to the Owu's long history of farming.
Public heraldry


The coat of arms of the Federal Republic of Nigeria is a legally enforced aspect of the country's identity. It consists of a black shield with a wavy white pall, symbolizing the meeting of the Niger and Benue Rivers at Lokoja. The black shield represents Nigeria's fertile soil, while the two supporting horses or chargers on each side represent dignity. The eagle represents strength, while the green and white bands on the top of the shield represent the rich soil.[8]
The red flowers at the base are Costus spectabilis, Nigeria's national flower. This flower was chosen for inclusion in the coat of arms as it is found all over Nigeria and also stands for the beauty of the nation. On the banderole around the base is Nigeria's national motto since 1978: "Unity and Faith, Peace and Progress" (formerly "Peace, Unity, Freedom").
The various states also have public symbols, known as seals, that are independent of those of the Federal Government. They too are defined and protected by law.
Foreign heraldry



Lastly, there is an old tradition of Nigerians or their heirs holding or otherwise being entitled to achievements of arms in other heraldic traditions.
Starting with the politician and newspaper publisher Sir Kitoyi Ajasa (who arguably became the first Nigerian to theoretically qualify for British arms when he was knighted by the colonists in 1928),[9][10] many of the country's most prominent figures over the course of the succeeding three decades were awarded membership in the imperial gentry in a de facto sense by way of knighthoods, although their not having had legal achievements assigned to them by the College of Arms or the Court of the Lord Lyon during their lifetimes due to either their indifference or their lack of knowledge of what was due to them meant that this was not enshrined in heraldic law, nor was this gentry status subsequently regularized or otherwise bequeathed to any of their lineal successors. In fact, many of these knights - like Sir Adeyemo Alakija, Sir Louis Odumegwu Ojukwu and Sir Ladapo Ademola - did indeed leave behind nationally influential descendants that could well have inherited and used their progenitors' arms in their own careers had they received some upon their being honoured by the British monarch.
Since Nigerian independence in 1960, the knights have been supplanted by clerics as the country's largest body of people that are entitled to claim foreign arms. Both of the cardinals whose arms are displayed above are - by virtue of their religious titles - princes of the church, and each therefore holds his ecclesiastical arms under Vatican law.
A unique modern case is that of John Alexander Ladi Thynn, Viscount Weymouth, who is currently the heir apparent to the arms (and associated titles) of his father Ceawlin Thynn, the Marquess of Bath. Through his mother Emma, he is of Nigerian descent.[11]
Links to the Nigerian chieftaincy system
As previously alluded to, many of the people in Nigeria that have, once had or were technically entitled to have arms were or are linked to the country's chieftaincy system. This is very much in keeping with the traditional connections that exist between heraldry and the aristocracy in other countries.
For example, the first four presidents of Nigeria's fourth republic - including current incumbent Chief Muhammadu Buhari - have all been chiefs of various Nigerian tribes. As president, they each customarily supervised the usage of the national heraldic symbols (such as the seal of the president).
Sir Ladapo Ademola was himself a traditional ruler as the Oba of Egbaland, while Sir Adeyemo Alakija and Cardinal Arinze have both also held chieftaincies - the former in the court of Sir Ladapo (his brother-in-law) and the latter amongst the Igbo people.
For their part Cardinal Okogie is a prince of the Esan people as a direct descendant of King Ogbidi Okojie of Uromi, while both Lord Weymouth and his younger brother Lord Henry Richard Isaac Thynn are the maternal grandsons of Chief Ladi Jadesimi, a Yoruba chief.
See also
References
- Sura 55, verse 76."Sura 55". The Quran. Retrieved April 14, 2020.
- Sura 76, verse 21."Sura 76, The Human (Al-Insaan)". The Quran. Retrieved April 14, 2020.
- "Sura 18, The Cave (Al-Kahf)". The Quran. Retrieved April 14, 2020.
- "Oba with Animals, Altar to the Hand (Ikegobo) of Ezomo Ehenua [Nigeria; Edo peoples, court of Benin] (1991.17.113,1996.11)". Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History. The Metropolitan Museum of Art. Retrieved 14 April 2020.
- "Akure: City Swallowed By Rocks". The Sun. Retrieved 14 April 2020.
- "The Most Prominent Secret Societies In Nigeria". The Guardian. Retrieved 14 April 2020.
- Laine, Daniel. African Kings. Berkeley, Toronto: Ten Speed Press, 1991, ISBN 1-58008-272-6. (Two Nigerian chiefs wear garments with embroidered Solomon's Knots, p. 63.)
- "National Symbols - Emblem". Nigeria's 50th Independence: Celebrating Greatness. Archived from the original on May 6, 2011. Retrieved 14 April 2020.
- "Sir Kitoyi Ajasa: The First Knighted Nigerian Who Devoted His Newspaper To Sensitize Nigerians When 1918 Epidemic Was Killing Thousands". Neusroom.com. Retrieved May 9, 2020.
- Macmillan, Alistair (1920). The Red Book of West Africa. Frank Cass and Co.
- "Lord Bath's Vicious Family Feud". The U.K. Mirror. Retrieved 14 April 2020.