Methyl ethyl ketone peroxide
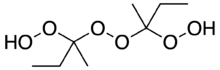
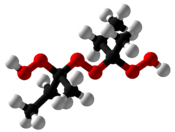
Methyl ethyl ketone peroxide (MEKP) is an organic peroxide, a high explosive similar to acetone peroxide. MEKP is a colorless, oily liquid whereas acetone peroxide is a white powder at STP; MEKP is slightly less sensitive to shock and temperature, and more stable in storage. Depending on the experimental conditions, several different adducts of methyl ethyl ketone and hydrogen peroxide are known. The first to be reported was a cyclic dimer, C8H16O4, in 1906.[3] Later studies found that a linear dimer is the most prevalent in the mixture of products typically obtained,[4] and this is the form that is typically quoted in the commercially available material from chemical supply companies.[5]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,2'-Peroxydi(butane-2-peroxol) | |
| Other names
2-[(2-Hydroperoxybutan-2-yl)peroxy]butane-2-peroxol 2-Hydroperoxy-2-[(2-hydroperoxybutan-2-yl)peroxy]butane Ketonox Mepox Thermacure | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 1759757 | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.014.238 |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | Methyl+ethyl+ketone+peroxide |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 3105 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H18O6 | |
| Molar mass | 210.226 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Density | 1.170 g cm−3 |
| Boiling point | Decomposition beyond 80 °C (176 °F) [1] |
| Soluble[2] | |
| Explosive data | |
| Shock sensitivity | High |
| Detonation velocity | 5200 m/s |
| RE factor | 0.9 |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Explosive, Toxic |
| GHS pictograms |    |
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
GHS hazard statements |
H202, H205, H241, H300, H315, H318, H335 |
| P102, P220, P243, P250, P261, P264, P280, P283, P370+380, P372, P404 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 75 °C (167 °F; 348 K)[1] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible) |
none[2] |
REL (Recommended) |
C 0.2 ppm (1.5 mg/m3)[2] |
IDLH (Immediate danger) |
N.D.[2] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Dilute solutions of 30 to 40% MEKP are used in industry and by hobbyists as the catalyst which initiates the crosslinking of unsaturated polyester resins used in fiberglass, and casting. For this application, MEKP is dissolved in dimethyl phthalate, cyclohexane peroxide, or diallyl phthalate to reduce sensitivity to shock. Benzoyl peroxide can be used for the same purpose.
MEKP is a severe skin irritant and can cause progressive corrosive damage or blindness.
See also
- Methyl ethyl ketone (MEK)
- Acetone peroxide (TATP)
Notes
- Record of 2-Butanone peroxide in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, accessed on March 10, 2013.
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0416". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- Pastureau, P. (1907). "Le superoxyde de la méthyléthylcétone". Comptes Rendus. 144 (2): 90–93.
- Milas, N. A.; Golubović, A. (1959). "Studies in Organic Peroxides. XXV. Preparation, Separation and Identification of Peroxides Derived from Methyl Ethyl Ketone and Hydrogen Peroxide". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 81 (21): 5824–5826. doi:10.1021/ja01530a068.
- "2-Butanone peroxide". Sigma-Aldrich. Retrieved 5 December 2011.
External links

- CDC - NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards
- The Register: Mass murder in the skies: was the plot feasible?
- New York Times: Details Emerge in British Terror Case
- The Free Information Society: HMTD Synthesis
- How MEKP cures Unsaturated Polyester Resin (video animation)
