Lipoamide
Lipoamide is a trivial name for 6,8-dithiooctanoic amide. It is the functional form of lipoic acid, i.e the carboxyl group is attached to protein via an amine with an amide linkage.[1] Illustrative of the biochemical role of lipoamide is in the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl lipoamide.[2]
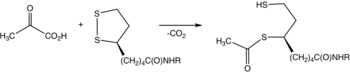
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
5-(1,2-Dithiolan-3-yl)pentanamide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | lipoamide |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H15NOS2 | |
| Molar mass | 205.343 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Lipoamide itself is not naturally occurring.
See also
References
- "Metabocard for Lipoamide". Human Metabolome Database.
- J. M. Berg; J. L. Tymoczko, L. Stryer (2007). Biochemistry (6 ed.). Freeman. ISBN 0-7167-8724-5.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.