Lepeophtheirus elegans
Known fish hosts are the stichaeids Chirolophis japonicus Herzenstein and Pholidapus dybowskii (Steindachner) from Russia, Japan and Korea, the pholid Pholis picta (Kner), the cottid Myoxocephalus brandtii (Steindachner), both from Russian waters and the sebastid Sebastes schlegelii Hilgendorf, the Korean rockfish.[2]
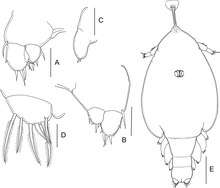
First chalimus:
A, leg 3;
B, leg 3 (other specimen);
C, leg 4;
D, caudal ramus;
E, habitus of putative female, dorsal.
Scale bars: A–D = 0.025 mm; E = 0.2 mm.
A, leg 3;
B, leg 3 (other specimen);
C, leg 4;
D, caudal ramus;
E, habitus of putative female, dorsal.
Scale bars: A–D = 0.025 mm; E = 0.2 mm.
| Lepeophtheirus elegans | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Adult female:
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Subphylum: | Crustacea |
| Class: | Hexanauplia |
| Order: | Siphonostomatoida |
| Family: | Caligidae |
| Genus: | Lepeophtheirus |
| Species: | L. elegans |
| Binomial name | |
| Lepeophtheirus elegans | |
Lepeophtheirus elegans is a species of sea lice.
References
- Parasitic Copepoda of some marine fishes. AV Gusev, Parazitologicheski Sbornik, 1951
- Venmathi Maran, Balu Alagar; Moon, Seong Yong; Ohtsuka, Susumu; Oh, Sung-Yong; Soh, Ho Young; Myoung, Jung-Goo; Iglikowska, Anna; Boxshall, Geoffrey Allan (2013). "The caligid life cycle: new evidence from Lepeophtheirus elegans reconciles the cycles of Caligus and Lepeophtheirus (Copepoda: Caligidae)". Parasite. 20: 15. doi:10.1051/parasite/2013015. PMC 3718518.

External links

This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.