Kongu Chera dynasty
Kongu Chera dynasty, or Cheras/Keralas of Kongu/Karur, or simply as the Chera/Kerala dynasty, were a medieval royal lineage in south India, initially ruling over western Tamil Nadu and central Kerala.[1] The headquarters of the Kongu Cheras was located at Karur-Vanchi (Karur) in central Tamil Nadu.[1][2] The Chera rulers of Kongu were subordinate to or conquered by Chalukya, Pallava and Pandya kings.[1] Rashtrakuta and Chola rulers are also said to have overrun the Kongu Chera country.[3][4]
Kongu Chera dynasty Cheras of Karur (Vanchi) | |
|---|---|
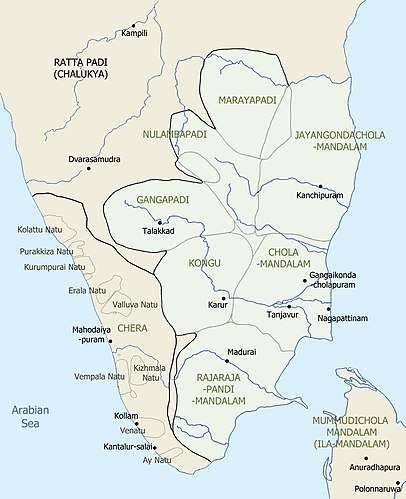 Kongu country with respect to the Chola Empire and the Chera/Perumal kingdom (marked as "Chera") | |
| Capital | |
| Common languages | |
| Religion | Hinduism |
| Today part of | India |
Present-day central Kerala detached from Kongu Chera kingdom around 8th-9th century AD to form the Chera Perumal kingdom (fl. 9th – 12th century AD).[1] The exact relationship between the two branches of the Chera family is not known to scholars.[2]
The Kongu Cheras are often described as the members of Chandra-Aditya Kula (the Luni-Solar Race) (around 9th-11th centuries). Kongu Cheras appear to have been absorbed into the Pandya political system by 10th/11th century AD.[5]
Political history
Corrections by M. G. S. Narayanan on K. A. Nilakanta Sastri and Elamkulam P. N. Kunjan Pillai are employed.
Medieval Cheras/Keralas
Kongu Cheras/Keralas of Karur initially appear as the rulers of western Tamil Nadu and central Kerala in the medieval period.[1] The family claimed that they were descended from the Cheras who flourished in pre-Pallava (early historic) south India.[1] It is likely that the Cheras had a system of joint rule with each prince from the family ruling in a different province (Karuvur Vanchi, Muchiri Vanchi or Thondi).[6][7]
An inscription of Kadamba king Vishnu Varma, dated 5th or 6th century, can be found at Edakkal cave in Wayanad.[8] An early historic Chera graffiti containing the phrase "Kadummi Putra Chera" was also discovered from the cave.[9]
The earliest Chalukya king to claim overlorship over Chera/Kerala is Kirttivarman I (fl. 566 - 598 AD) (this claim is generally considered as a "boastfull exaggeration" by historians). A later grant (695 AD) of king Vinayaditya II Satyasraya, with reference to the vassalage of the Kerala country, is now reckoned as a more dependable record.[10] Several Chalukya records of the 7th and 8th centuries speak of the conquest and vassalage of the Kerala country.[10]
A number of Pallava records also mention the vassalage of the Kerala/Chera country.[10]
By the beginning of early medieval period, Karur (in interior Tamil Nadu) had acquired much prominence with respect to the other two centers, Muchiri-Vanchi and Thondi (both in Kerala).[1] Karur came to be known by the 8th – 9th centuries AD as "Vanchi manakaramana Karur".[11][12] There was a domination of present-day Kerala regions of the old Chera country by the Kongu Cheras of Karur (probably via some form of viceregal rule).[1]
Cheras as Pandya vassals
There are clear attestations of repeated Pandya conquests of the Kerala country in the 7th and 8th centuries AD.[10] Pandya king Sendan/Jayantan (fl. 645 – 70 AD) was known as the Vanavan, an ancient name for the Chera king.[10] Arikesari Maravarman (670 – 710 AD), another Pandya ruler, probably defeated the Keralas/Cheras on several occasions.[10][4] His successor Ko Chadayan Ranadhira also made gains against the Cheras.[13]
The so-called "renewal of the capital city of Vanchi (Karur) along with Kudal (Madurai) and Kozhi (Uraiyur)" by the Pandya king Rajasimha I (730 – 65 AD), described in the Madras Museum Plates of Jatila Parantaka Varaguna, may suggest a Pandya occupation of the Kongu Chera capital Karur.[3] It is known that when Pandya king Jatila Parantaka (765 – 815 AD) went to war against the Adigaman of Tagadur (Dharmapuri), the Keralas and the Pallavas went to the aid of the latter though "the Pandyas drove them back to the quarters from which they had emerged" (Madras Museum Plates of Jatila Parantaka, 17th year).[3] Perhaps the Chera branch from present-day Kerala had crossed the Ghat Mountains to offer support to the Adigaman and after defeat they were pursued up to the Palghat Gap by the Pandya forces.[14]
Rashtrakuta inscriptions mention "an alliance of Dravida kings including Kerala, Pandya, Chola and Pallava who were defeated" (E. I., XVIII). The Keralas mentioned there might be the Kongu Cheras who had already submitted to the Pandyas (not Chera Perumals of Kerala).[3]
Detachment of central Kerala
.jpg)
The ancient Chera country, except central Kerala, gradually passed into the Pandya sphere of influence.[3] The western portions of the Chera country became (slowly but surely) an independent kingdom, the Chera Perumal kingdom, with its own headquarters at Makotai (Kodungallur).[3] The branch of Chera family survived in Kongu country, now Pandya vassals, are described in later inscriptions (9th-11th centuries) as members of Chandra-Aditya Kula (the Luni-Solar Race).[4] This seems to suggest a process of integration with the Pandya royal family (the Lunar Race) via royal marriages.[3]
The two branches of the Chera family, the Kongu Cheras and the Chera Perumals, supported by the Pandyas and the Cholas respectively, were rivals in this period.[15] Chera Perumal king Sthanu Ravi was a junior partner in a Chola campaign in the Kongu country.[16] The Pandyas are known to have made a defensive alliance with the Cheras of Kongu country (who were under their influence) in this period.[17] Pandya king Parantaka Vira Narayana (c. 880 – 900 AD) is known to have married a Kerala (Kongu Chera) princess "Vanavan Maha Devi".[18] The son of this alliance, Rajasimha, described as a member of Chandra-Aditya Kula (Sinnamanur copper plates), was "destroyed by the Chola king Parantaka".[18] It was initially assumed by K. A. N. Sastri and E. P. N. K. Pillai that the Vira Narayana had married a Chera Perumal princess of Kerala.[18] Reciprocal marriage alliances between the Chera Perumals and the Cholas are also recorded in several inscriptions (see Kizhan Adigal).[18]
The Kongu country was conquered by the Cholas (either by Srikantha or Aditya I Chola) in the last years of the 9th century AD (this campaign probably involved battles between Aditya I and Parantaka Vira Narayana). The Pandyas were eventually defeated in the "great battle" of Sripurambiyam (c. 885).[19]
When the Chola king Parantaka conquered the Pandyas in 910 AD, the Chera Perumals might have allowed to have rule parts of Kongu country (the fate of the Kongu Chera country, then ruled by Kongu Cheras, upon the fall of Madurai is not known).[15] Pandya king Rajasimha II, who was defeated by Parantaka Chola, is known to have found asylum in Kerala (c. 920 AD).[15] Chola king Sundara (c. 956 – c. 973 AD) had a Chera or Kerala princess among his queens.[20]
Chola influence in Kongu country
Kongu Chera country was subsequently conquered by the Cholas.[4] Amara Bhujanga Deva, one of the princes defeated by Chola king Rajaraja (Tiruvalangadu Grant), was probably a Pandya or a Kongu Chera prince.[21] There are records of a king named Vira Kerala Amara Bhujanga Deva from Kongu region.[21] Chola king Rajadhiraja is known for defeating certain Vira Kerala, one of the so-called "thennavar muvar", and trampling him to death by his war elephant.[22] This royal was probably a Kongu-Chera of Chandra-Aditya Kula or a Pandya prince (son of a Pandya and a Kongu Chera princess).[23] Vira Kerala was previously considered as a Chera Perumal king (K. A. N. Sastri and E. P. N. K. Pillai).[24]
Kongu Chera genealogy
Several stone and copper inscriptions of the Kongu Cheras, probably Chola vassals, dated by palaeography to 9th – 11th centuries AD, are found in places like Vellalur Namakkal, Pazhani, Perur, Dharmapuram, Erode and Tirukkannapuram.[4] They are generally described in inscriptions as members of Chandra-Aditya Kula (the Luni-Solar Race).[4]
| Kongu Chera
(Pandya princes) |
Notes |
|---|---|
| Ravi Kota[26] |
|
| Kantan Ravi[25] | |
| Vira Kota[25] | |
| Vira Narayana[25] | |
| Vira Chola[25] | |
| Vira Kerala Amara Bhujanga Deva[23][27] | |
| Amara Bhujanga Deva[26] | |
| Vira Kerala[26] |
|
| Kerala Kesari Adhirajaraja Deva[25][29] |
Kongu Chera coins
Unlike the Chera Perumals of the west coast, the Kongu Cheras are known for their signature coins.[30]
A silver coin with Nagari legend "sri vira keralasya" (11th-12th centuries AD) in British Museum is generally attributed to Kongu Cheras.[30] Another coin known as "anai achu" (the elephant mould"), with the bow and arrow symbol, can also be a Kongu Chera product.[30] The anai achu coin was current in western Tamil Nadu and to some extend in Kerala in the 12th-13th centuries AD.[30]
References
- Narayanan, M. G. S. Perumāḷs of Kerala. Thrissur (Kerala): CosmoBooks, 2013. 89-90 and 92-93.
- Narayanan, M. G. S. Perumāḷs of Kerala. Thrissur (Kerala): CosmoBooks, 2013. 80-81.
- Narayanan, M. G. S. Perumāḷs of Kerala. Thrissur (Kerala): CosmoBooks, 2013. 93-95.
- Narayanan, M. G. S. Perumāḷs of Kerala. Thrissur (Kerala): CosmoBooks, 2013. 80-81.
- Narayanan, M. G. S. Perumāḷs of Kerala. Thrissur (Kerala): CosmoBooks, 2013. 80-81.
- Narayanan, M. G. S. Perumāḷs of Kerala. Thrissur (Kerala): CosmoBooks, 2013. 104.
- Gurukkal, Rajan. “Classical Indo-Roman Trade: A Historiographical Reconsideration.” Indian Historical Review, vol. 40, no. 2, Dec. 2013, pp. 181–206.
- Fawcett, F. 1901. Notes on the Rock Carvings in the Edakal Caves, Wynaad. The Indian Antiquary vol. XXX, pp. 409-421.
- Subramanian, T. S. (9 February 2012). "Edakal cave yields one more Tamil-Brahmi inscription". The Hindu. ISSN 0971-751X. Retrieved 2018-11-19.
- Narayanan, M. G. S. Perumāḷs of Kerala. Thrissur (Kerala): CosmoBooks, 2013. 90-91 and 103-04.
- Epigraphia Indica, volume XVII, p. 298.
- South Indian Inscriptions, volume VIII, no. 441.
- Dalziel, N.R. (2016). Pandyan Empire. In The Encyclopedia of Empire (eds N. Dalziel and J.M. MacKenzie). doi:10.1002/9781118455074.wbeoe416
- Narayanan, M. G. S. Perumāḷs of Kerala. Thrissur (Kerala): CosmoBooks, 2013. 93-95 and 107.
- Narayanan, M. G. S. Perumāḷs of Kerala. Thrissur (Kerala): CosmoBooks, 2013. 98-99 and 111.
- Narayanan, M. G. S. Perumāḷs of Kerala. Thrissur (Kerala): CosmoBooks, 2013. 65-66.
- Dalziel, N.R. (2016). Pandyan Empire. In The Encyclopedia of Empire (eds N. Dalziel and J.M. MacKenzie). doi:10.1002/9781118455074.wbeoe416
- Narayanan, M. G. S. Perumāḷs of Kerala. Thrissur (Kerala): CosmoBooks, 2013. 95-96 and 108.
- Narayanan, M. G. S. Perumāḷs of Kerala. Thrissur (Kerala): CosmoBooks, 2013. 97.
- Narayanan, M. G. S. Perumāḷs of Kerala. Thrissur (Kerala): CosmoBooks, 2013. 100-01.
- Narayanan, M. G. S. Perumāḷs of Kerala. Thrissur (Kerala): CosmoBooks, 2013. 116-117 and 136.
- Narayanan, M. G. S. Perumāḷs of Kerala. Thrissur (Kerala): CosmoBooks, 2013. 121-122.
- Narayanan, M. G. S. Perumāḷs of Kerala. Thrissur (Kerala): CosmoBooks, 2013. 304-05 and 322-23.
- Narayanan, M. G. S. Perumāḷs of Kerala. Thrissur (Kerala): CosmoBooks, 2013. 84-85.
- Narayanan, M. G. S. Perumāḷs of Kerala. Thrissur (Kerala): CosmoBooks, 2013. 80-81.
- Narayanan, M. G. S. Perumāḷs of Kerala. Thrissur (Kerala): CosmoBooks, 2013. 80-81.
- Narayanan, M. G. S. Perumāḷs of Kerala. Thrissur (Kerala): CosmoBooks, 2013. 136.
- Narayanan, M. G. S. Perumāḷs of Kerala. Thrissur (Kerala): CosmoBooks, 2013. 140.
- Narayanan, M. G. S. Perumāḷs of Kerala. Thrissur (Kerala): CosmoBooks, 2013. 63.
- Narayanan, M. G. S. Perumāḷs of Kerala. Thrissur (Kerala): CosmoBooks, 2013. 304-05 and 322.