Hydroxy ketone
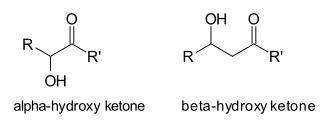
In organic chemistry a hydroxy ketone (often referred to simply as a ketol) is a functional group consisting of a ketone flanked by a hydroxyl group. In the two main classes, the hydroxyl group can be placed in the alpha position (an alpha-hydroxy ketone RCR′(OH)(CO)R) or in the beta position (a beta-hydroxy ketone, RCR′(OH)CR2(CO)R).
- An α-hydroxy ketone can consist of either a primary alcohol (e.g. hydroxyacetone) or a secondary alcohol; the latter are often broadly referred to as acyloins[1]
- Prominent β-hydroxy ketones are aldol adducts.
- α-hydroxy ketones can give positive Fehling's test.
Hydroxy ketones
References
- IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "acyloins". doi:10.1351/goldbook.A00126
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.