Kazungula
Kazungula is a small border town in the Southern Province of Zambia, lying on the north bank of the Zambezi River about 70 kilometres (45 mi) west of Livingstone.
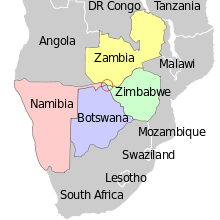

Zambia is on the right; Namibia at the top on the left; Botswana in the middle on the left and Zimbabwe bottom all the way across the bottom of the picture. The Zimbabwe-Botswana border runs only just this side of the ferry pier – or perhaps actually through it: see this map.
At Kazungula the territories of four countries (Zambia, Botswana, Zimbabwe, and Namibia) come close to meeting at a quadripoint. It has now been agreed that the international boundaries contain two tripoints joined by a short line roughly 150 metres (490 ft) long forming a boundary between Zambia and Botswana, now crossed by the Kazungula Bridge. The ever-shifting river channels and the lack of any known agreements addressing the issue before 2000 led to some uncertainty in the past as to whether or not a quadripoint legally existed.[1][2] Thus, Botswana has only about 150 metres (490 ft) of river frontage on the Zambezi, being sandwiched on the south bank between the extreme tip of Namibia's Caprivi Strip and Zimbabwe.
The Chobe River, which divides Namibia and Botswana, enters the Zambezi near Kazungula. Kazungula is also headquarters of a district of Zambia of the same name.
Transport
Kazungula is home to the Kazungula Ferry across the 400 m (1,300 ft) wide Zambezi river to the identically-named village of Kazungula in Botswana, 8 km (5 mi) east of the town of Kasane; it is one of the largest ferries in the region with a capacity of 70 tonnes (69 long tons; 77 short tons).[3] The Kazungula Bridge[4] is to replace it in 2020; the ground-breaking ceremony was held on 12 September 2014.[5] Kazungula lies just 2 km (1.2 mi) from the Livingstone-Sesheke road (M10 Road) which connects to the Katima Mulilo Bridge linking Zambia and Namibia.
The border post between Zimbabwe and Botswana, 4.5 km (2.8 mi) (by road) south-east of the Kazungula Ferry, is also called Kazungula; it is the most direct route leading to Victoria Falls.[6]
General Administration
- Kazungula was elevated to district status in September 1998.
- Government departments, Parastatals, NGOs and ZAWA are;
- Agriculture, Forestry, Fisheries, ZAWA, Council, Education, Health, Police, National Registration, Immigration, Socialwelfare, Community Development, ZESCO
- Banks are ZANACO and Natsavse
Political System, Governance and Traditional Leadership
- The district has one (1) parliamentary constituency, and fourteen (14) political wards which includes; Sikaunzwe, Sekute, Nwezi, Moomba, Nyawa, Nuba, Kauwe and chooma
- Traditionally, the district is divided into five (5) chiefdoms and these are Chief Sekute, Chief Nyawa, Chief Musokotwanwe, Chief Mukuni and Chief Moomba
- The main tribes in the district are Toka laya, Lozi, and Tonga
Local Economy
- The majority (66%) of the population within Kazungula does not receive any form of income (CSO 2010).
- The largest employer is peasant/subsistence farming, cross-border trading and fishing.
The main economic sectors in Kazungula are agriculture, manufacturing, trade and commerce and tourism.
- The informal sector is characterised by fish trading, trading in second hand and new clothes and footwear, small-scale fishing, trading in vegetables and other foodstuffs, beer brewing, carpentry, production and selling of traditional handicrafts, trading in groceries, restaurants, bars and charcoal burning and selling.
- The major activity in the secondary sector is the generation of power at batoka gorge located in mukuni ward. Other secondary sector activities though of less economic significance are the production of timber and carpentry.
Tourism
- Tourism is one of the major sectors of Kazunglula's economy. the sector has had positive impact on the economy of the district. Tourism is labour intensive and hence provides employment to a significant number of people.
- There are several lodges and guest houses in Kazungula Township, along the Zambezi River
- Tourism development still remains far below potential because of challenges of poor and inadequate infrastructure, limited investment, fragmented operations, weak marketing and limited skilled manpower
- Despite the fact that the district lies alongside Zambezi river, activities such as boat cruising, gymnasiums and saunas are not utilized
Infrastructure Development
Infrastructure covers among others the following:
a)Transport infrastructure, including roads, bridges, aerodromes and inland waterways; drainage
b)Building infrastructure, covering office and residential accommodation, schools, health centers, sports complexes, museums, heritage sites, courts and prisons; and
c)Dams used for agriculture-related economic activities
- While the Construction of Kazungula District Hospital is at 90% under phase one of the project.
- Construction of 30 housing units for government department is at various stages 10.
- Construction of Kazungula Bridge has commenced so far Building of pillars and one-quarter of the bridge has been done.
- The construction of the truck yard the superstructure is completed
- Construction of 10 classroom blocks and 10 VIP toilets.
- Construction of CIVIC Center is above ring beam while the District Administration is at slab level.
- The Construction of the post office is at roof level.
- The local court is completed and operational
- Construction of Sibandwa Dam
Agriculture
- There are currently few commercial farmers in the district
- Most of the farming communities in the district are in the category of small-scale farming.
- There are 10,522 small-scale farmers farming a wide range of crops such as maize, sorghum, millet, groundnuts and cotton.
- some farmers have increased their fields to become medium scale farmers. The crops grown by these farmers include but not limited to maize, sorghum, millet, groundnuts, cotton, Cassava and vegetables
- Livestock production in Kazungula District is done on small scale by traditional pastorals.
- There are a number of livestock species that are reared in Kazungula District but the notable ones include cattle, goats, sheep, donkeys, poultry and pigs
water and Sanitation
- In the area of sanitation, improvements under the urban and peri-urban water supply and sanitation were varied, covering the areas of solid waste management and maintenance of water supply schemes.
- Progress was made in the area of construction and rehabilitation of boreholes with 30 new boreholes constructed and 32 boreholes rehabilitated in 2016.
- Kazungula has 380 existing water points which are functional; though, water supply and sanitation service coverage are still very low. The majority of the urban population relied on on-site systems.
Energy
- We have no filling station in the District.
- Wood fuel (firewood and charcoal) remains the dominant source of energy in the district, accounting for almost 80 per cent of total energy consumption.
- Firewood is predominantly consumed by rural households while charcoal is a major source of energy for urban households. The annual loss of forest cover was estimated at 1.2 per cent due to land clearing for agricultural use rather than energy purposes.
Health/ HIV/AIDS
- The Kazungula District HIV/AIDS prevalence is currently at 15.4%, according to the demographic health survey of 2007.
- The drivers of new infections in Kazungula are; Multiple and Concurrent Sex Partners (MCP), Low and Inconsistent condom use, Mobility and labour migration, key populations, early and forced marriages, unemployment and poverty, alcohol and drug abuse, harmful traditional and cultural practices and Mother to Child Transmission.
- Health services in the District are provided through the twenty- two (22) Rural Health Centres (RHCs). The District has two laboratory facilities at Mukuni and Sons of Thunder.
- Prevention of Mother to Child Transmission of HIV is offered at the 22 RHCs while ART at 15 RHCs (3 static, 12 mobiles).
- In conclusion, Kazungula District aims at promoting balanced development, coordinated through a decentralized and coherent process.
- The District has made progress in implementing economic and social investment programmes in all the wards of the district.
- A number of schools, health posts, a district hospital, dams and a feeder road have been constructed and/or rehabilitated. However, development varied because the 90 % of the district is rural and failed to attract investment in key priority areas
See also
References
- Brownlie, Ian; Ian R. Burns (1979). "Botswana-Zambia (Quadripoint issue)". African Boundaries: A Legal and Diplomatic Encyclopaedia. London: C. Hurst & Co. pp. 1098–1108. ISBN 0-903983-87-7.; summarized at African tripoints: Botswana-Namibia-Zambia by Michael Donner / Jesper Nielsen.
- Akweenda, Sackey (1997-04-23). "VI: Quadripoint Theory". International Law and the Protection of Namibia's Territorial Integrity. Netherlands: Martinus Nijhoff. pp. 201–3. ISBN 90-411-0412-7.
- "Kazungula Border Post". huyai.com. Retrieved 2020-05-28.
- http://www.gazettebw.com/?p=8920
- "Zambia : Zambia and Botswana officially launche the construction works for Kazungula Bridge across the Zambezi River". LusakaTimes.com. 2014-09-13. Retrieved 2018-08-06.
- "Kazungula - en.LinkFang.org". en.linkfang.org. Retrieved 2020-05-28.