Kazakh famine of 1932–33
The Kazakh famine of 1930–1933, known in Kazakhstan as the Goloshchyokin genocide (Kazakh: Goloshekındik genotsıd, [ɡɐləˌʂʲokʲinˈdək ɡʲinɐˈt͡sɪt]),[4] also known as the Kazakh catastrophe,[7] was a man-made famine where 1.5 million (possibly as many as 2.0–2.3 million) people died in Soviet Kazakhstan, of whom 1.3 million were ethnic Kazakhs; 38% of all Kazakhs died, the highest percentage of any ethnic group killed in the Soviet famines of the early 1930s.[8][2] Some historians assume that 42% of the entire Kazakh population died in the famine.[9]
| Kazakh famine of 1932–33 | |
|---|---|
 The cube at the site for the future monument for victims of the Soviet famine (1931–1933) in the center of Almaty, Kazakhstan. The monument itself was built in 2017. | |
| Country | Kazakhstan |
| Location | Nationwide |
| Period | 1930–33[1] |
| Total deaths | 1.5 to 2.3 million[2] |
| Observations | Caused by Sovietization under Filipp Goloshchekin causing Kazakhs to call the famine: "The Goloshchekin genocide" |
| Consequences | Kazakhs reduced from 60% to 38% of the republic's population[3][4][5][6] |
| Preceded by | Kazakh famine of 1919–1922 |

Kazakhstan's livestock and grain were largely acquired between 1929 and 1932, with one-third of the republic's cereals being requisitioned and more than 1 million tons confiscated in 1930 to provide food for the cities.[10] Some historians and scholars describe the famine as a genocide of the Kazakhs perpetrated by the Soviet state.[11]
The famine made Kazakhs a minority in the Kazakh ASSR, and not until the 1990s did Kazakhs become the largest group in Kazakhstan again. Before the famine, around 60% of the republic's population were Kazakhs, but after the famine, only around 38% of the population were Kazakhs.[3][4][5][6]
Overview
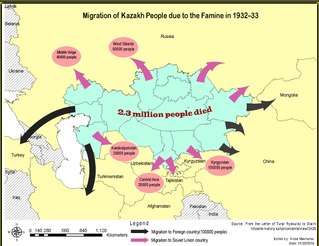
It was the most severe of all regions affected by famine, percentage-wise, though more people died in the Ukrainian Holodomor, which began a year later.[12] In addition to the Kazakh famine of 1919–1922, in 10–15 years Kazakhstan lost more than half of its population due to the actions of the Soviet state.[13][14] The two Soviet censuses show that the number of the Kazakhs in Kazakhstan dropped from 3,637,612 in 1926 to 2,181,520 in 1937.[15] Ethnic minorities in Kazakhstan were also significantly affected. The Ukrainian population in Kazakhstan decreased from 859,396 to 549,859[10] (a reduction of almost 36% of their population), while other ethnic minorities in Kazakhstan lost 12% and 30% of their populations.[10] Ukrainians who died in Kazakhstan are sometimes considered victims of Holodomor. Due to the starvation 665,000 Kazakhs fled the famine with their cattle outside Kazakhstan to China, Mongolia, Afghanistan, Iran and the Soviet republics of Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan, Turkmenistan, Tajikistan and Russia in search of food and employment in the new industrialization sites of Western Siberia with 900,000 head of cattle.[10] The Soviet government worked later to repatriate them.[16] 70% of the refugees survived and the rest died due to epidemics and hunger.[10]
A monument for the famine's victims was constructed in 2017.[17]
Classification as a genocide
Some historians and scholars consider that this famine amounted to genocide of the Kazakhs.[11] The Soviet authorities undertook a campaign of persecution against the nomads in the Kazakhs, believing that the destruction of the class was a worthy sacrifice for the collectivization of Kazakhstan.[18] Europeans in Kazakhstan had disproportionate power in the party, which has been argued as a cause of why indigenous nomads suffered the worst part of the collectivization process rather than the European sections of the country.[19] Regarding the Kazakh catastrophe, Michael Ellman states that it "seems to be an example of ‘negligent genocide’ which falls outside the scope of the UN Convention".[20]
See also
References
- "The Kazakh Famine of the 1930s". 2016-08-24.
- Volkava, Elena (2012-03-26). "The Kazakh Famine of 1930–33 and the Politics of History in the Post-Soviet Space". Wilson Center. Retrieved 2015-07-09.
- Татимов М. Б. Социальная обусловленность демографических процессов. Алма-Ата,1989. С.124
- Қазақстан тарихы: Аса маңызды кезеңдері мен ғылыми мәселелері. Жалпы білім беретін мектептің қоғамдык- гуманитарлық бағытындағы 11-сыныбына арналған оқулық / М.Қойгелдиев, Ә.Төлеубаев, Ж.Қасымбаев, т.б. — Алматы: «Мектеп» баспасы, 2007. — 304 бет,суретті. ISBN 9965-36-106-1
- http://world.lib.ru/p/professor_l_k/070102_koval_drujba.shtml - "Запомнил и долю казахов в пределах своей республики - 28%. А за тридцать лет до того они составляли у себя дома уверенное большинство"
- PIANCIOLA, NICCOLÒ (1 January 2001). "The Collectivization Famine in Kazakhstan, 1931–1933". Harvard Ukrainian Studies. 25 (3/4): 237–251. JSTOR 41036834. PMID 20034146.
- Robert Conquest, The Harvest of Sorrow: Soviet Collectivization and the Terror-famine, 1987
- NICCOLÒ PIANCIOLA (2001). "The Collectivization Famine in Kazakhstan, 1931–1933". Harvard Ukrainian Studies. 25 (3–4): 237–251. JSTOR 41036834. PMID 20034146.
- John Arch Getty, Roberta Thompson Manning, ed. (1993). Stalinist Terror: New Perspectives. Cambridge University Press. p. 265. ISBN 9780521446709.
- Isabelle, Ohayon (13 January 2016). "The Kazakh Famine: The Beginnings of Sedentarization". Archived from the original on 2019-05-29.
- Sabol, Steven (2017). "The Touch of Civilization": Comparing American and Russian Internal Colonization. University Press of Colorado. p. 47. ISBN 9781607325505.
- Pannier, Bruce (2007-12-28). "Kazakhstan: The Forgotten Famine". Rferl.org. Retrieved 2015-07-09.
- "Во время голода в Казахстане погибло 40 процентов населения".
- Snyder, Timothy (2012). Bloodlands: Europe Between Hitler and Stalin. Hachette UK. p. 90. ISBN 9780465032976.
- European Society for Central Asian Studies (2004). Gabriele Rasuly-Paleczek, Julia Katschnig (ed.). Central Asia on Display: Proceedings of the VIIth Conference of the European Society for Central Asian Studies. LIT Verlag Münster. p. 236. ISBN 9783825883096.
- OHAYON, Isabelle, 2006, La Sédentarisation des Kazakhs dans the USSR de Stalin. Collectivization et changement social (1928-1945), : Maisonneuve et Larose.
- "Kazakhstan Unveils Monument to Victims of Soviet-Era Famine".
- PIANCIOLA, Niccolò, 2004, «Famine in the steppe. The collectivization of agriculture and the Kazak herdsmen, 1928-1934 », Cahiers du monde russe, vol. 45, No. 1-2, pp. 137-192. PIANCIOLA, Niccolò, 2009, Stalinismo di frontiera. Colonizzazione agricola, sterminio dei nomadi and costruzione statale in Asia centrale (1905-1936), Rome: Viella.
- PAYNE, Matthew J., 2011, "Seeing like a soviet state: settlement of nomadic Kazakhs, 1928-1934", in Golfo ALEXOPOULOS, Julie HESSLER,
- ""Discussion Article - Stalin and the Soviet Famine of 1932–33" by Michael Ellman, EUROPE-ASIA STUDIES Vol. 59, No. 4, June 2007, pp 663–693" (PDF).
Further reading
- Cameron, Sarah, The Hungry Steppe: Famine, Violence, and the Making of Soviet Kazakhstan, Cornell University Press, 2018.
- Conquest, Robert, The Harvest of Sorrow: Soviet Collectivization and the Terror-famine, Edmonton: The University of Alberta Press in Association with the Canadian Institute of Ukrainian Studies, 1986.
- Kindler, Robert, Stalin's Nomads. Power and Famine in Kazakhstan, Pittsburgh: Pittsburgh University Press, 2018.
- Ohayon, I. La sédentarisation des Kazakhs dans l'URSS de Staline, collectivisation et changement social, Paris, Maisonneuve et Larose, 2006. (in French)
- Sahni, Kalpana. Crucifying the Orient: Russian orientalism and the colonization of Caucasus and Central Asia. Bangkok: White Orchid Press, 1997.
- Ellman, Michael Stalin and the Soviet Famine of 1932–33 Revisited, Europe-Asia Studies, Vol. 59 No. (4), 2007