Italian resistance movement
The Italian resistance movement (Italian: Resistenza italiana or just la Resistenza) is an umbrella term for Italian resistance groups during World War II. It was opposed to the forces of Nazi Germany as well as Nazi Germany's puppet state local regime, the Italian Social Republic, especially following the German invasion and military occupation of Italy between September 1943 and April 1945, though the resistance to the Fascist Italian government began even prior to World War II. Known as partisans (Italian: partigiani), the brutal conflict they took part in is referred to as the Italian Liberation War (when referring to the part they took in the Italian Campaign against the Nazi Germans and the Axis) or as the Italian Civil War (when referring specifically to their conflict with Italian Fascists). The modern Italian Republic was declared to be founded on the struggle of the Resistance.
| Italian resistance movement | |
|---|---|
| Participant in the Italian Civil War and World War II | |
  Flag of the National Liberation Committee and some members of the Italian resistance in Ossola, 1944. | |
| Active | Most active 1943–1945; the Resistance originated following the rise of Fascist Italy in the 1920s |
| Ideology | Various: Generally anti-fascism Mainly various forms of communism, socialism, and anarchism; Republicanism and liberalism To a lesser extent: Liberal socialism Christian democracy Catholic anti-fascism / Catholic anti-Nazism Catholic socialism Social liberalism Social democracy Monarchism |
| Allies | |
| Opponent(s) | Axis powers (Fascist Italy, Nazi Germany and Italian Social Republic) |
Resistance by Italian armed forces
In Italy

Rome
Armed resistance to the German occupation following the armistice between Italy and Allied armed forces of 3 September 1943 began with Italian regular forces: the Italian Armed Forces and the Carabinieri military police. The period's best-known battle broke out in Rome the day the armistice was announced. Regio Esercito units such as the Sassari Division, the Granatieri di Sardegna, the Piave Division, the Ariete II Division, the Centauro Division, the Piacenza Division and the "Lupi di Toscana" Division (in addition to Carabinieri, infantry and coastal artillery regiments) were deployed around the city and along surrounding roads.
Outnumbered German Fallschirmjäger and Panzergrenadiere were initially repelled and endured losses, but slowly gained the upper hand, aided by their experience and superior Panzer component. The defenders were hampered by the escape of King Victor Emmanuel III, Marshal Pietro Badoglio and their staff to Brindisi, which left the generals in charge of the city without a coordinated defence plan. This caused Allied support to be cancelled at the last minute since the Fallschirmjäger took the U.S. 82nd Airborne Division drop zones; Brigadier General Maxwell D. Taylor had crossed enemy lines and gone to Rome to personally supervise the operation. The absence of the Italian Centauro II Division, with its German-made tanks, contributed to the defeat of the Italian forces by the Germans. The division was composed primarily of ex-Blackshirts and was not trusted.
By 10 September, the Germans had penetrated downtown Rome and the Granatieri (aided by civilians) made their last stand at Porta San Paolo. At 4 pm, General Giorgio Carlo Calvi di Bergolo signed the order of surrender; the Italian divisions were disbanded and their troops taken prisoner. Although some officers participating in the battle later joined the resistance, the clash in Rome was not motivated by anti-German sentiment so much as the desire to control the Italian capital and resist the disarmament of Italian soldiers. Generals Raffaele Cadorna, Jr. (commander of Ariete II) and Giuseppe Cordero Lanza di Montezemolo (later executed by the Germans) joined the underground; General Gioacchino Solinas (commander of the Granatieri) instead opted for the pro-German Italian Social Republic.[1]
Piombino
One of the most important episodes of resistance by Italian armed forces after the armistice was the Battle of Piombino, Tuscany.[2] On 10 September 1943, during Operation Achse, a small German flotilla, commanded by Kapitänleutnant Karl-Wolf Albrand, tried to enter the harbour of Piombino but was denied access by the port authorities.[2] General Cesare Maria De Vecchi, in command of the Italian coastal forces (and a former Fascist Gerarca), commanded the port authorities to allow the German flotilla to enter, against the advice of Commander Amedeo Capuano, the Naval commander of the harbour.[2][3][4] Once they entered and landed, the German forces showed a hostile behaviour, and it became clear that their intent was to occupy the town; the local population asked for a resolved reaction by the Italian forces, threatening an insurrection, but the senior Italian commander, general Fortunato Perni, instead ordered his tanks to open fire on the civilians, to disperse the crowds; De Vecchi forbade any action against the Germans.[2][3][4] This however did not stop the protests; some junior officers, acting on their own initiative and against the orders (Perni and De Vecchi even tried to dismiss them for this), assumed command and started distributing weapons to the population, and civilian volunteers joined the Italian sailors and soldiers in the defense.[2][3][5]
Battle broke out at 21:15 on 10 September, between the German landing forces (who aimed to occupy the town centre) and the Italian coastal batteries, tanks, and civilian population.[3][2][4] Italian tanks sank the German torpedo boat TA11;[6][7] Italian artillery also sank seven Marinefährprahme, the péniches Mainz and Meise (another péniche, Karin, was scuttled at the harbour entrance as a blockship) and six Luftwaffe service boats (Fl.B.429, Fl.B.538, Fl.C.3046, Fl.C.3099, Fl.C.504 e Fl.C.528), and heavily damaged the torpedo boat TA9 and the steamers Carbet and Capitano Sauro (formerly Italian).[8] Sauro and Carbet were scuttled because of the damage they had suffered.[8][9] The German attack was repelled; by the dawn of 11 September, 120 Germans had been killed and about 200-300 captured, 120 of them wounded.[4] Italian casualties had been 4 killed (two sailors, one Guardia di Finanza brigadier, and one civilian) and a dozen wounded;[10][11] four Italian submarine chasers (VAS 208, 214, 219 and 220) were also sunk during the fighting.[8] Later in the morning, however, De Vecchi ordered the prisoners to be released, and had their weapons given back to them.[3][2][12] New popular protests broke out, as the Italian units were disbanded and the senior commanders fled from the city; the divisional command surrendered Piombino to the Germans on 12 September, and the city was occupied.[3][4][2] Many of the sailors, soldiers and citizens who had fought in the battle of Piombino retreated to the surrounding woods and formed the first partisan formations in the area.[3]
Outside Italy
In the days following 8 September 1943 most servicemen, left without orders from higher echelons (due to Wehrmacht units ceasing Italian radio communications), were disarmed and shipped to POW camps in the Third Reich (often by smaller German outfits). However, some garrisons stationed in occupied Greece, Albania, Yugoslavia and Italy fought the Germans. Admirals Inigo Campioni and Luigi Mascherpa led an attempt to defend Rhodes, Kos, Leros and other Dodecanese islands from their former allies. With reinforcements from SAS, SBS and British Army troops under the command of Generals Francis Gerrard, Russell Brittorous and Robert Tilney, the defenders held on for a month. However, the Wehrmacht took the islands through air and sea landings by infantry and Fallschirmjäger supported by the Luftwaffe. Both Campioni and Mascherpa were captured and executed at Verona for high treason.
On 13 September 1943, the Acqui Division stationed in Cefalonia was ordered by Italian High Command to attack the Germans, despite ongoing negotiations. After a ten-day battle, the Germans executed thousands of officers and enlisted men in retaliation. Those killed in the massacre of the Acqui Division included division commander General Antonio Gandin.
Other Italian forces remained trapped in Yugoslavia following the armistice and some decided to fight alongside the local resistance. Elements of the Taurinense Division, the Venezia Division, the Aosta Division and the Emilia Division were assembled in the Italian Garibaldi Partisan Division, part of the Yugoslav People's Liberation Army. When the unit finally returned to Italy at the end of the war, half its members had been killed or were listed as missing in action.
Bastia, in Corsica, was the setting of a naval battle between Italian torpedo boats and an attacking German flotilla.
Italian military internees
Italian soldiers captured by the Germans numbered around 650,000-700,000 (some 45,000 others were killed in combat, executed, or died during transport), of whom between 40,000 and 50,000 later died in the camps. Most refused cooperation with the Third Reich despite hardship, chiefly to maintain their oath of fidelity to the King. Their former allies designated them Italienische Militär-Internierte ("Italian military internees") to deny them prisoner of war status and the rights granted by the Geneva Convention. Their actions were eventually recognized as an act of unarmed resistance on a par with the armed confrontation of other Italian servicemen.[13]
Underground resistance
In the first major act of resistance following the German occupation, Italian partisans and local resistance fighters liberated the city of Naples through a chaotic popular rebellion. The people of Naples revolted and held strong against Nazi occupiers in the last days of September 1943. The popular mass uprising and resistance in Naples against the occupying Nazi German forces, known as the Four days of Naples, consisted of four days of continuous open warfare and guerrilla actions by locals against the Nazi Germans. The spontaneous uprising of Neopolitan and Italian Resistance against German occupying forces (despite limited armament, organization, or planning) nevertheless successfully disrupted German plans to deport Neopolitans en masse, destroy the city, and prevent Allied forces from gaining a strategic foothold.
Elsewhere, the nascent movement began as independently operating groups were organized and led by previously outlawed political parties or by former officers of the Royal Italian Army. Many partisan formations were initially founded by soldiers from disbanded units of the Royal Italian Army that had evaded capture in Operation Achse, and were led by junior Army officers who had decided to resist the German occupation; they were subsequently joined and re-organized by Anti-Fascists, and became thus increasingly politicized.[14]
Later the Comitato di Liberazione Nazionale (Committee of National Liberation, or CLN), created by the Italian Communist Party, the Italian Socialist Party, the Partito d'Azione (a republican liberal socialist party), Democrazia Cristiana and other minor parties, largely took control of the movement in accordance with King Victor Emmanuel III's ministers and the Allies. The CLN was set up by partisans behind German lines and had the support of most groups in the region.[15]
The main CLN formations included three politically varied groups: the communist Garibaldi Brigades, the Giustizia e Libertà (Justice and Freedom) Brigades related to the Partito d'Azione, and the socialist Matteotti Brigades. Smaller groups included Christian democrats and, outside the CLN, monarchists such as the Brigate Fiamme Verdi (Green Flame Brigades) and Fronte Militare Clandestino headed by Colonel Montezemolo. Another sizeable partisan group, particularly strong in Piedmont (where the Fourth Army had disintegrated in September 1943), were the "autonomous" (autonomi) partisans, largely composed of former soldiers with no substantial alignment to any anti-Fascist party; an example were the 1° Gruppo Divisioni Alpine led by Enrico Martini.
Relations among the groups varied. For example, in 1945, the Garibaldi partisans under Yugoslav Partisan command attacked and killed several partisans of the Catholic and azionista Osoppo groups in the province of Udine. Tensions between the Catholics and the Communists in the movement led to the foundation of the Fiamme Verdi as a separate formation.[16]
A further challenge to the 'national unity' embodied in the CLN came from anarchists as well as dissident-communist Resistance formations, such as Turin's Stella Rossa movement and the Movimento Comunista d'Italia (Rome's largest single anti-fascist force under Occupation), which sought a revolutionary outcome to the conflict and were thus unwilling to collaborate with 'bourgeois parties'.[17]
Partisan movement
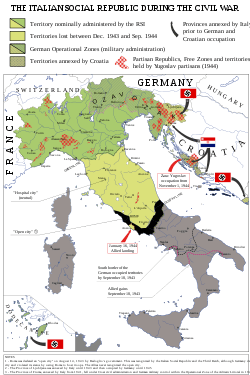
Rodolfo Graziani estimated the partisan strength at around 70,000-80,000 by May 1944.[18] Some 41% in the Garibaldi Brigades and 29% were Actionists of the Giustizia e Libertà Brigades.[19] One of the strongest units, the 8th Garibaldi Brigade, had 8,050 men (450 without arms) and operated in the Romagna area.[18] The CLN mostly operated in the Alpine area, Apennine area and Po Valley of the RSI, and also in the German OZAK (the area northeast of the north end of the Adriatic Sea) and OZAV (Trentino and South Tyrol) zones.[18] Its losses amounted to 16,000 killed, wounded or captured between September 1943 and May 1944.[18] On 15 June 1944, the General Staff of the Esercito Nazionale Repubblicano estimated that the partisan forces amounted to some 82,000 men, of whom about 25,000 operated in Piedmont, 14,200 in Liguria, 16,000 in the Julian March, 17,000 in Tuscany and Emilia-Romagna, 5,600 in Veneto, and 5,000 in Lombardy.[20] Their ranks were gradually increased by the influx of young men escaping the Italian Social Republic's draft, as well as from deserters from the RSI armed forces.[21] By August 1944, the number of partisans had grown to 100,000, and it escalated to more than 250,000 with the final insurrection in April 1945.[22] The Italian resistance suffered 50,000 fighters killed throughout the conflict.[23][24]


Partisan unit sizes varied, depending on logistics (such as the ability to arm, clothe and feed members) and the amount of local support. The basic unit was the squadra (squad), with three or more squads (usually five) comprising a distaccamento (detachment). Three or more detachments made a brigata (brigade), of which two or more made a divisione (division). In some places, several divisions formed a gruppo divisione (divisional group). These divisional groups were responsible for a zona d'operazione (operational group).
While the largest contingents operated in mountainous districts of the Alps and the Apennine Mountains, other large formations fought in the Po River flatland. In the large towns of northern Italy, such as Piacenza, and the surrounding valleys near the Gothic Line. Montechino Castle housed a key partisan headquarters. The Gruppi di Azione Patriottica (GAP; "Patriotic Action Groups") commanded by the Resistance's youngest officer, Giuseppe "Beppe" Ruffino, carried out acts of sabotage and guerrilla warfare, and the Squadre di Azione Patriottica (SAP; "Patriotic Action Squads") arranged strike actions and propaganda campaigns. As in the French Resistance, women were often important members and couriers.[25]
Like their counterparts elsewhere in Europe, Italian partisans seized whatever arms they could find. The first weapons were brought by ex-soldiers fighting German occupiers from the Regio Esercito inventory: Carcano rifles, Beretta M1934 and M1935 pistols, Bodeo M1889 revolvers, SRCM and OTO hand grenades, and Fiat–Revelli Modello 1935, Breda 30 and Breda M37 machine guns. Later, captured K98ks, MG 34s, MG 42s, the iconic potato-masher grenades, Lugers, and Walther P38s were added to partisan kits. Submachine guns (such as the MP 40) were initially scarce, and usually reserved for squad leaders.
Automatic weapons became more common as they were captured in combat and as the Social Republic regime soldiers began defecting, bringing their own guns. Beretta MABs began appearing in larger numbers in October 1943, when they were spirited away en masse from the Beretta factory which was producing them for the Wehrmacht. Additional weapons (chiefly of British origin) were airdropped by the Allies: PIATs, Lee–Enfield rifles, Bren light machine guns and Sten guns.[26] U.S.-made weapons were provided on a smaller scale from the Office of Strategic Services (OSS): Thompson submachine guns (both M1928 and M1), M3 submachine guns, United Defense M42s, and folding-stock M1 carbines. Other supplies included explosives, clothing, boots, food rations, and money (used to buy weapons or to compensate civilians for confiscations).
Countryside
The worst conditions and fighting took place in mountainous regions. Resources were scarce and living conditions were terrible. Due to limited supplies the resistance adopted guerrilla warfare. This involved groups of 40-50 fighters ambushing and harassing the Nazis and their allies. The size of the brigades was reflective of the resources available to the partisans. Resource limits could not support large groups in one area. Mobility was key to their success. Their terrain knowledge enabled narrow escapes in small groups when nearly surrounded by the Germans. The partisans had no permanent headquarters or bases, making them difficult to destroy.[27]
The resistance fighters themselves relied heavily on the local populace for support and supplies. They would often barter or just ask for food, blankets and medicine. When the partisans took supplies from families, they would often hand out promissory notes that the peasants could convert after the war for money. The partisans slept in abandoned farms and farmhouses. One account from Paolino 'Andrea' Ranieri (a political commissar at the time) described fighters using donkeys to move equipment at night while during the day the peasants used them in the fields. The Nazis tried to split the populace from the resistance by adopting a reprisal policy of killing 10 Italians for every German killed by the Partisans. Those executed would come from the village near where an attack took place and sometimes from captive partisan fighters.
The German punishments backfired and instead strengthened the relationship. Because most resistance fighters were peasants, local populations felt a need to provide for their own. One of the larger engagements was the battle for Monte Battaglia (lit. "Battle Mountain"), a mountaintop that was a part of the Gothic Line. On September 26, 1944, a joint force of 250 Partisans and three companies of U.S. soldiers from the 88th Infantry Division attacked the hill occupied by elements of the German 290th Grenadier Regiment. The Germans were caught completely by surprise. The attackers captured the hill and held it for five days against reinforced German units, securing a path for the Allied advance.
Urban areas
Resistance activities were different in the cities. Some Italians ignored the struggle, while others organized, such as the Patriotic Action Squads and issued propaganda. Groups such as the Patriotic Action Groups carried out military actions. A more expansive support network was devised than in the countryside. Networks of safe houses were established to hide weapons and wounded fighters. Only sympathizers were involved, because compulsion was thought to encourage betrayal. People largely supported the resistance because of economic hardships, especially inflation. Pasta prices tripled and bread prices had quintupled since 1938; hunger unified the underground and general population.[27]
Female partisans

Women played a large role. After the war, about 35,000 Italian women were recognised as female partigiane combattenti (partisan combatants) and 20,000 as patriote (patriots); they broke into these groups based on their activities. The majority were between 20 and 29. They were generally kept separate from male partisans. Few were attached to brigades and were even rarer in mountain brigades. Female countryside volunteers were generally rejected. Women still served in large numbers and had significant influence.[28]
1944 uprising
During the summer and early fall of 1944, with Allied forces nearby, partisans attacked behind German lines, led by CLNAI. This rebellion led to provisional partisan governments throughout the mountainous regions. Ossola was the most important of these, receiving recognition from Switzerland and Allied consulates there. An intelligence officer told Field Marshal Albert Kesselring, Germany's commander of occupation forces in Italy, that he estimated German casualties fighting partisans in summer 1944 amounted to 30,000 to 35,000, including 5,000 confirmed killed.[29] Kesselring considered the number to be exaggerated, and offered his own figure of 20,000: 5,000 killed, between 7,000-8,000 missing / "kidnapped" (including deserters), and a similar number seriously wounded. Both sources agreed that partisan losses were less.[30] By the end of the year, German reinforcements and Mussolini's remaining forces crushed the uprising.
In their attempts to suppress the resistance, German and Italian Fascist forces (especially the SS, Gestapo, and paramilitary militias such as Xª MAS and Black Brigades) committed war crimes, including summary executions and systematic reprisals against civilian population. Resistance captives and suspects were often tortured and raped. Some of the most notorious mass atrocities included the Ardeatine massacre (335 Jewish civilians and political prisoners executed without a trial in a reprisal operation after a resistance bomb attack in Rome), the Sant'Anna di Stazzema massacre (about 560 random villagers brutally killed in an anti-partisan operation in the central mountains), the Marzabotto massacre (about 770 civilians killed in similar circumstances) and the Salussola massacre (20 partisans murdered after being tortured, as a reprisal). In all, an estimated 15,000 Italian civilians were deliberately killed, including many women and children.[31]
 A woman executed by public hanging in a street of Rome, early 1944
A woman executed by public hanging in a street of Rome, early 1944.jpg) Three Italian partisans executed by public hanging in Rimini, August 1944
Three Italian partisans executed by public hanging in Rimini, August 1944 German soldier examining the papers of an Italian civilian outside of Milan (1944)
German soldier examining the papers of an Italian civilian outside of Milan (1944)- The Sant'Anna di Stazzema massacre memorial relief
 Memorial stone in Soragna for two Italian partisans – killed in 1944
Memorial stone in Soragna for two Italian partisans – killed in 1944
Foreign contribution

Not all resistance members were Italians; many foreigners had escaped POW camps or joined guerrilla bands as so-called "military missions". Among them were Yugoslavs, Czechs (deserters from the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia army (in Italy for guard/patrol duty in 1944), Russians, Ukrainians, Dutch, Spaniards, Greeks, Poles, German defectors and deserters disillusioned with National Socialism[32] and Britons and Americans (ex-prisoners or advisors deployed by the SAS, SOE and OSS). Some later became well-known, such as climber and explorer Bill Tilman, reporter and historian Peter Tompkins, former RAF pilot Count Manfred Beckett Czernin, and architect Oliver Churchill. George Dunning recorded his experiences of fighting with the partisans in his book "Where bleed the many".[33]
Aid networks
Another task carried out by the resistance was assisting escaping POWs (an estimated 80,000 were interned in Italy until 8 September 1943),[34] to reach Allied lines or Switzerland on paths previously used by smugglers. Some fugitives and groups of fugitives hid in safe houses, usually arranged by women (less likely to arouse suspicion). After the war, Field Marshal Harold Alexander issued a certificate to those who thereby risked their lives.
Italian Jews were aided by DELASEM, a network extending throughout occupied Italy that included Jews and Gentiles, Roman Catholic clergy, faithful/sympathetic police officers and even some German soldiers. Since Jews were considered "enemy aliens" by the Social Republic regime, they were left with little or nothing to live on, and many were deported to Nazi concentration and extermination camps where about 7,000 died. DELASEM helped thousands of Jews by offering food, shelter and money. Some of its members would later be designated Righteous Among the Nations.
Liberation
1945 uprising

On April 19, 1945, the CLN called for an insurrection (the April 25 uprising). In Bologna, the occupying Nazi German forces and their few remaining Italian Fascist allies were openly attacked by Italian partisans on April 19, and by April 21, the city of Bologna was liberated by the partisans, the Italian Co-Belligerent Army, and the Polish II Corps under Allied command; Parma and Reggio Emilia were later freed on April 24 by the Italian Resistance and then the advancing Allied forces. Turin and Milan were liberated on April 25 through a popular revolt and Italian Resistance insurrection following a general strike that commenced two days earlier; over 14,000 German and Fascist troops were captured in Genoa on April 26–27, when General Günther Meinhold surrendered to the CLN.[35] Many of the defeated German troops attempted to escape from Italy and some partisans units allowed the German columns to pass through if they turned over any Italians who were travelling with them. The forces of German occupation in Italy officially capitulated on May 2. Fascists attempted to continue fighting, but were quickly suppressed by the partisans and the Allied forces.
The April insurrection brought to the fore issues between the resistance and the Allies.[36] Given the revolutionary dimension of the insurrection in the industrial centers of Turin, Milan, and Genoa, where concerted factory occupations by armed workers had occurred, the Allied commanders sought to impose control as soon as they took the place of the retreating Germans. While the Kingdom of Italy was the de facto ruler of the South, the National Liberation Committee, still embedded in German territory, existed as a populist organization which posed a threat to the monarchy and property owners in a post-war Italy. However the PCI, under directives from Moscow, enabled the Allies to carry out their program of disarming the partisans and discouraged any revolutionary attempt at changing the social system. Instead, the PCI emphasized national unity and "progressive democracy" in order to stake their claim in the post-war political situation. Despite the pressing need to resolve social issues which persisted after the fall of fascism, the resistance movement was subordinated to the interests of Allied leaders in order to maintain the status quo.[36]
Revenge killings

A score-settling campaign (Italian: resa dei conti)[37] ensued against pro-German collaborators, thousands of whom were rounded up by the vengeful partisans. Controversially, many of those detainees were speedily court martialed, condemned and shot, or killed without trial. Minister of Interior Mario Scelba later put the number of the victims of such executions at 732, but other estimates were much higher. Partisan leader Ferruccio Parri, who briefly served as Prime Minister after the war in 1945, said thousands were killed.[38] Some partisans, such as perpetrators of the Schio massacre, were trialed by an Allied Military Court.[37]
During the waning hours of the war, Mussolini, accompanied by Marshal Graziani, headed to Milan to meet with Cardinal Alfredo Ildefonso Schuster. Mussolini was hoping to negotiate a deal, but was given only the option of unconditional surrender. His negotiations were an act of betrayal against the Germans. When confronted about this by Achille Marazza, Mussolini said, "They [the Nazis] have always treated us as slaves. I will now resume my freedom of action." With the city already held by resistance fighters, Mussolini used his connections one last time to secure passage with an escaping German convoy on its way to the Brenner Pass with his mistress Claretta Petacci.[27] On the morning of 27 April 1945, Umberto Lazzaro (nom de guerre 'Partisan Bill'), a partisan with the 52nd Garibaldi Brigade, was checking a column of lorries carrying retreating SS troops at Dongo, Lombardy, near the Swiss border. Lazzaro recognized and arrested Mussolini. The task of executing Mussolini was, according to the official version, given to a 'Colonel Valerio' (identified as Walter Audisio) and the bodies of Mussolini and Petacci were later brought to Milan and hung upside down in the Piazzale Loreto square. Eighteen executed prominent Fascists (including Mussolini, Fernando Mezzasoma, Luigi Gatti, Alessandro Pavolini and Achille Starace) were displayed in the square; this place was significant because the bodies of 15 executed enemies of Mussolini's regime had been displayed in this square the previous year.
Casualties
According to a book published in 1955 by an Italian ministerial committee on the tenth anniversary of the Liberation, casualties in Italy among the Resistance movement amounted to 35,828 partisans killed in action or executed, and 21,168 partisans mutilated or left disabled by their wounds.[39] Another 32,000 Italian partisans had been killed abroad (in the Balkans and, to a lesser extent, in France).[40] 9,980 Italian civilians had been killed in reprisals by the German and Fascist forces.[41] In 2010, the Ufficio dell'Albo d'Oro of the Italian Ministry of Defence recorded 15,197 partisans killed; however, the Ufficio dell'Albo d'Oro only considered as partisans the members of the Resistance who were civilians before joining the partisans, whereas partisans who were formerly members of the Italian armed forces (more than half those killed) were considered as members of their armed force of origin.[42]
Liberation Day
Since 1949, April 25 has been officially celebrated as Liberation Day, also known as Anniversary of the Resistance. Speaking at the 2014 anniversary, President Giorgio Napolitano said: "The values and merits of the Resistance, from the Partisan movement and the soldiers who sided with the fight for liberation to the Italian armed forces, are indelible and beyond any rhetoric of mythicization or any biased denigration. The Resistance, the commitment to reconquer Italy's liberty and independence, was a great civil engine of ideals, but above all it was a people in arms, a courageous mobilization of young and very young citizens who rebelled against foreign power."[43]
See also
- Anti-fascism
- ANPI, an association of the participants to the Italian resistance
- Volante Rossa an Italian communist antifascist militia active after WWII
- People's Squads, an Italian left-wing antifascist militia active during the early 1920s
- "Bella Ciao", anthem of the anti-fascist resistance
- Mazzini Society, formed by expatriate Italian anti-Fascists in the United States
- Anni di piombo
- Anarchism in Italy
- German Resistance to Nazism
- Japanese dissidence during the Showa period
- Museum of the Liberation of Rome
In works of popular culture
- The Abandoned
- Achtung! Banditi!
- Bebo's Girl
- Beneath a Scarlet Sky
- Blood of the Losers
- Captain Corelli's Mandolin
- Cloak and Dagger
- Cloak & Dagger
- A Day for Lionhearts
- A Day in Life
- The Dirty Dozen: The Deadly Mission
- Escape by Night
- Everybody Go Home
- The Fall of Italy
- The Fallen
- The Fascist
- The Four Days of Naples
- From the Clouds to the Resistance
- General della Rovere
- His Day of Glory
- Hornets' Nest
- The Hunchback of Rome
- Johnny the Partisan
- Last Days of Mussolini
- Little Teachers
- Long Night in 1943
- The Man Who Will Come
- Massacre in Rome
- The Mattei Affair
- Miracle at St. Anna
- Outcry
- Paisan
- The Path to the Nest of Spiders
- Porzûs
- Rome, Open City
- The Seven Cervi Brothers
- Ten Italians for One German
- Two Anonymous Letters
References
- Sanna, Daniele (2005). Da Porta San Paolo a Salò. Gioacchino Solinas comandante antitedesco. AM&D. ISBN 88-86799-86-1.
- "Nell'anniversario della battaglia di Piombino, uno storico racconta perché la città merita l'onorificenza La medaglia d'oro, dopo 55 anni «Il massimo riconoscimento va concesso per ristabilire la verità» - Il Tirreno". Retrieved 25 April 2017.
- "Piombino città di eroi - la Repubblica.it". Retrieved 25 April 2017.
- "8 settembre '43: la breve illusione di pace". Retrieved 25 April 2017.
- "Interventi del Presidente - La Camera dei Deputati". Retrieved 25 April 2017.
- "FR L'Iphigénie of the French Navy - French Torpedo boat of the La Melpoméne class - Allied Warships of WWII - uboat.net". Retrieved 25 April 2017.
- "Seekrieg 1943, September". Retrieved 25 April 2017.
- "Penische fates". Retrieved 25 April 2017.
- "Wrecksite – Carbet". Retrieved 25 April 2017.
- "-La Nazione - PIOMBINO- Taglio del nastro per la banchina «Giorgio Perini»". 26 July 2012. Retrieved 25 April 2017.
- "Marinai d'Italia" (PDF). Retrieved 25 April 2017.
- "DE VECCHI, Cesare Maria in "Dizionario Biografico"". Retrieved 25 April 2017.
- Natta, Alessandro (1997). L'altra Resistenza. I militari italiani internati in Germania. Einaudi. ISBN 978-8806143145.
- Giuseppe Fioravanzo, La Marina dall'8 settembre 1943 alla fine del conflitto, p. 424.
- The Italian Army 1940-45 (3) Osprey Men-at-Arms 353 ISBN 978-1-85532-866-2
- Charles T. O'Reilly; Forgotten Battles: Italy's War of Liberation, 1943-1945; Lexington Books; 2001; p.218
- Corvisieri, Silverio (1968). Bandiera Rossa nella Resistenza romana. Rome: Samona e Savelli.
- Moseley, Roger (2004). Mussolini: The Last 600 Days of Il Duce. Taylor Trade Publishing.
- Longhi, Silvano (2010). Die Juden und der Widerstand gegen den Faschismus in Italien: 1943 - 1945. Berlin.
- Roberto Battaglia, Storia della Resistenza italiana, pp. 336-339.
- Giuseppe Fioravanzo, La Marina dall'8 settembre 1943 alla fine del conflitto, p. 433.
- Resistenzialismo versus resistenza
- "This Day in History — 9/6/1944 - Italian resistance fighters persevere". History.com. Archived from the original on 20 October 2014. Retrieved 30 December 2013.
- “World War II: the Encyclopedia of the War Years, 1941-1945” p. 360
- "H-Net Review: Andrea Peto on Women and the Italian Resistance, 1943–45". H-Net. msu.edu. Archived from the original on 6 December 2006. Retrieved 30 December 2013.
- Balbo, Adriano (2005). Quando inglesi arrivare noi tutti morti. Blu Edizioni. ISBN 88-7904-001-4.
- Behan, Tom. The Italian Resistance: Fascists, Guerrillas and the Allies. London: Pluto, 2009. Print.
- Slaughter, Jane. Women and the Italian Resistance: 1943-1945. Denver, CO: Arden, 1997. Print.
- O'Reilly, Charles (2001). Forgotten Battles: Italy's War of Liberation, 1943-1945. Oxford.
- Italy's Sorrow: A Year of War, 1944-1945. New York: St. Martin's Press. 2008. p. 303. ISBN 9781429945431.
- Gia Marie Amella, Special for CNN. "Hidden archive exposes WWII slaughters - CNN.com". Edition.cnn.com. Retrieved 19 May 2014.
- Incerti, Matteo (2011). Il Bracciale di Sterline - Cento bastardi senza gloria. Una storia di guerra e passioni. Aliberti Editore. ISBN 978-88-7424-766-0.
- Dunning, George (1955). Where bleed the many. London, UK: Elek Books Limited.
- "British prisoners of the Second World War and the Korean War". The National Archives. Archived from the original on 16 June 2013. Retrieved 19 June 2013.
- Basil Davidson, Special Operations Europe: Scenes from the Anti-Nazi War (1980), pp. 340/360
- Ginsborg, Paul (1990). A History of Contemporary Italy. Penguin Book. pp. 57–70.
- Foot, John (2009). "The Resistance". Italy’s Divided Memory. Palgrave Macmillan. pp. 176–179. ISBN 978-0-230-10183-8.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- See the interview with Ferruccio Parri, on "Corriere della Sera" 15th November 1997. (in Italian)
- Giuseppe Fioravanzo, La Marina dall'8 settembre 1943 alla fine del conflitto, p. 433.
- Giuseppe Fioravanzo, La Marina dall'8 settembre 1943 alla fine del conflitto, p. 433.
- Giuseppe Fioravanzo, La Marina dall'8 settembre 1943 alla fine del conflitto, p. 433.
- http://www.campagnadirussia.info/wp-content/uploads/2011/12/I_caduti_del_fronte_orientale.pdf
- "Italy celebrates Liberation Day - Politics - ANSAMed.it". Ansamed.info. 4 June 1944. Retrieved 19 May 2014.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Italian Resistance. |
- Italy | European Resistance Archive
- (in Italian) ANPI – Associazione Nazionale Partigiani d'Italia
- (in Italian) ANCFARGL – Associazione Nazionale Combattenti Forze Armate Regolari Guerra di Liberazione
- (in Italian) INSMLI – Istituto Nazionale per la Storia del Movimento di Liberazione in Italia
- (in Italian) Il portale della guerra di Liberazione
- Anarchist partisans in the Italian Resistance
.jpg)


