Interconnector (North Sea)
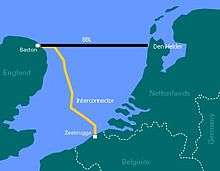
The Interconnector is a natural gas pipeline between the United Kingdom and continental Europe. It crosses the North Sea between Bacton Gas Terminal in England and Zeebrugge in Belgium. Construction of the pipeline was completed in 1998. It provides bi-directional transport capability to facilitate energy trading in both the UK and continental European gas markets. Gas export from the UK is termed "forward flow" and gas import to the UK is termed "reverse flow".
| Interconnector | |
|---|---|
 Location of Interconnector | |
| Location | |
| Country | United Kingdom. Belgium |
| From | Bacton Gas Terminal |
| Passes through | North Sea |
| To | Zeebrugge |
| General information | |
| Type | natural gas |
| Partners | Fluxys, Snam |
| Operator | Interconnector (UK) Limited |
| Construction started | 1996 |
| Commissioned | 1998 |
| Technical information | |
| Length | 235 km (146 mi) |
| Maximum discharge | 25.5 billion cubic meters per year |
| Diameter | 1,016 mm (40 in) |
Economic impact
The UK export capacity of the Interconnector is 20 billion cubic metres per year. Since October 2007 when a project to upgrade the facilities was completed, the UK import capacity is 25.5 billion cubic metres per year. The pipeline provides not only the physical capability to move gas from one end of the pipe to the other, it has been a key factor in the liberation of energy markets across Europe - enabling energy trading and creating economic activity in the process. Such trading can result in future production being bought and sold because of the possibility of the use of the Interconnector. Often in practice, because of the transport cost, gas is not actually transported but sold back into the market where it was originally bought.
See also
- BBL Pipeline
- Zeebrugge Hub
- Nemo link, an electricity interconnector between Belgium and the United Kingdom
References
- "Interconnector". www.fluxys.com.