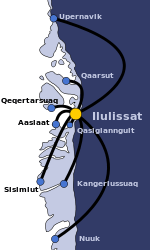
Ilulissat
Ilulissat, formerly Jakobshavn or Jacobshaven,[4] is the municipal seat and largest town of the Avannaata municipality in western Greenland, located approximately 350 km (220 mi) north of the Arctic Circle. With the population of 4,670 as of 2020,[5] it is the third-largest city in Greenland, after Nuuk and Sisimiut. The city is home to almost as many sled-dogs as people.
Ilulissat Jakobshavn | |
|---|---|
   From upper left: Illumiut neighbourhood, Old town, Ilulissat Icefjord, Knud Rasmussen's Museum, Zion's Church | |
 Ilulissat Location within Greenland | |
| Coordinates: 69°13′N 51°06′W | |
| Sovereign state | |
| Autonomous country | |
| Municipality | Avannaata |
| First mention | 15th century |
| City Status | 16th century |
| Area | |
| • City | 11.25 km2 (4.34 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 47.00 km2 (18.15 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 2,010 m (6,590 ft) |
| Lowest elevation | 1 m (3 ft) |
| Population (2020 (city, settlements))[2] | |
| • City | 4,670 |
| • Density | 420/km2 (1,100/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 4,491 (City of Ilulissat) |
| • Metro | 342 (Settlements: Ilimanaq, Oqaatsut, Qeqertaq and Saqqaq) |
| • Metro density | 103.5/km2 (268/sq mi) |
| • Ethnicity | 90.98% Greenlandic 9.02% Other[3] |
| Time zone | UTC-3 (WGT) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-2 (WGST) |
| Postal code | 3952 |
| Area code(s) | (+299) 94 |
In direct translation, Ilulissat is the Kalaallisut word for "Icebergs" (Danish: Isbjerge).[6] The nearby Ilulissat Icefjord is a UNESCO World Heritage Site,[7] and has made Ilulissat the most popular tourist destination in Greenland.[8] Tourism is now the town's principal industry. The city neighbours the Ilulissat Icefjord, where there are enormous icebergs from the most productive glacier in the northern hemisphere.
History

The town was established as a trading post by Jacob Severin's company in 1741 and was named in his honor.[9][10]
The Zion Church (Zions Kirke) was built in the late 18th century, and was the largest man-made structure in Greenland at the time.[10] The final resident of nearby Sermermiut moved to Ilulissat in 1850.[11]
Ilulissat Declaration
The town was the site of the Arctic Ocean Conference in May 2008.[12] The joint meeting between Canada, Denmark, Norway, Russia, and the United States was held to discuss key issues relating to territorial claims in the Arctic (particularly Hans Island and Arktika 2007) and Arctic shrinkage produced by climate change.[13]
The Ilulissat Declaration arose from the conference. It stated that the law of the sea provided for important rights and obligations concerning the delineation of the outer limits of the continental shelf, the protection of the marine environment (including ice-covered areas), freedom of navigation, marine scientific research, and other uses of the sea. It also said that it remained committed to this legal framework and to the orderly settlement of any possible overlapping claims.
With this existing legal framework providing a solid foundation for responsible management, there was no need to develop a new comprehensive international legal regime to govern the Arctic Ocean. The states involved would continue the developments within the Arctic Ocean and continue to implement appropriate measures to further said developments.[14]
Geography and environment
The Ilulissat Icefjord (Greenlandic: Ilulissat Kangerlua) southeast of Ilulissat was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2004.[15]
| Climate data for Ilulissat, 1961-1990 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 12.2 (54.0) |
9.0 (48.2) |
12.0 (53.6) |
10.2 (50.4) |
16.5 (61.7) |
18.0 (64.4) |
20.6 (69.1) |
20.4 (68.7) |
16.1 (61.0) |
12.4 (54.3) |
11.4 (52.5) |
11.6 (52.9) |
20.6 (69.1) |
| Average high °C (°F) | −9.0 (15.8) |
−10.1 (13.8) |
−10.6 (12.9) |
−3.8 (25.2) |
3.4 (38.1) |
8.3 (46.9) |
11.4 (52.5) |
10.2 (50.4) |
5.5 (41.9) |
−0.5 (31.1) |
−4.8 (23.4) |
−7.6 (18.3) |
−0.6 (30.9) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −16.6 (2.1) |
−18.3 (−0.9) |
−19.3 (−2.7) |
−12.6 (9.3) |
−3.4 (25.9) |
1.8 (35.2) |
4.4 (39.9) |
3.3 (37.9) |
−0.8 (30.6) |
−6.7 (19.9) |
−11.1 (12.0) |
−14.8 (5.4) |
−7.8 (17.9) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −33.6 (−28.5) |
−33.6 (−28.5) |
−37.8 (−36.0) |
−29.5 (−21.1) |
−21.1 (−6.0) |
−5.9 (21.4) |
−1.5 (29.3) |
−3.0 (26.6) |
−13.8 (7.2) |
−18.2 (−0.8) |
−27.5 (−17.5) |
−34.0 (−29.2) |
−37.8 (−36.0) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 13 (0.5) |
16 (0.6) |
13 (0.5) |
18 (0.7) |
18 (0.7) |
24 (0.9) |
32 (1.3) |
31 (1.2) |
41 (1.6) |
25 (1.0) |
22 (0.9) |
18 (0.7) |
271 (10.6) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 4.3 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 5.0 | 4.2 | 4.8 | 5.3 | 5.4 | 7.4 | 5.3 | 5.6 | 5.0 | 60.3 |
| Average snowy days | 7.6 | 7.2 | 7.8 | 8.0 | 6.0 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 3.3 | 5.9 | 7.3 | 7.2 | 61.3 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 0 | 28 | 93 | 180 | 279 | 300 | 279 | 217 | 120 | 62 | 30 | 0 | 1,588 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 0.0 | 13.2 | 25.8 | 37.4 | 41.7 | 41.7 | 38.4 | 39.3 | 30.1 | 21.9 | 23.3 | 0.0 | 26.1 |
| Source 1: Danish Meteorological Institute[16] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: World Climate Guide[17] | |||||||||||||
Population
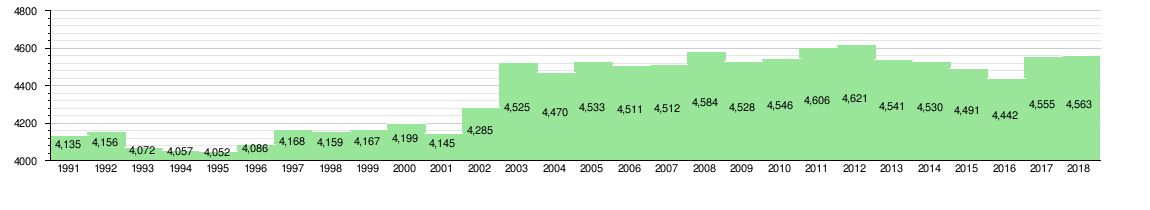
With 4,670 inhabitants in 2020, Ilulissat is the largest town in the Avannaata municipality. The population increased over 8% relative to 1990 levels but has remained steady since around 2003.[18]
Transport
- Air
Ilulissat Airport is located 2.8 km (1.7 mi) to the northeast of the town center and was built in 1983.[19] It serves Ilulissat with connections to towns in northwestern and midwestern Greenland via Air Greenland. Service to Reykjavík, Iceland, began in April 2011 via Air Iceland Connect and Air Greenland in 2017.
- Sea
The Arctic Umiaq ferry links Ilulissat with Sisimiut, Nuuk, and other towns and settlements on the western and southwestern coast of Greenland.
Sport
The town is home to Nagdlunguaq-48 who play in the Greenlandic Men's Football Championship, Greenland's top soccer competition. Nagdlunguaq-48, who play all their league games in Nuuk, have won the championship ten times (as of 2016).
Notable people
- Knud Rasmussen (1879–1933), noted polar explorer and anthropologist, referred to as the "father of Eskimology".[20] Born in Ilulissat,[21] Rasmussen was the first man to cross the Northwest Passage via dog sled. He remains well known in Greenland, Denmark and among Canadian Inuit.[22]
- Jørgen Brønlund (1877–1907), was also a polar explorer born in Ilulissat, He grew up with Rasmussen and accompanied him, along with Harald Moltke and Ludvig Mylius-Erichsen, on the Danish Literary Expedition (1902–1904) to examine Inuit culture. In 1906 he joined Mylius-Erichsen and Peter Høegh Hagen on the Danmark-ekspeditionen to map the northernmost regions of Greenland. Jørgen Brønlund Fjord in Peary Land is named after him.[23]
- Jens Rosing (1925–2008), a Greenlandic artist notable for designing the coat of arms of Greenland, numerous Greenlandic postage stamps, as well as illustrated children's books and water colours − was born in Ilulissat.
- Ricky Enø Jørgensen, racing cyclist.
International relations
Twin towns – Sister cities
Ilulissat is twinned or cooperating with several towns and cities, including:
Gallery
_Greenland._Church_and_doctor's_residence_of_the_town_Jakobshavn_-_Ilulissat_(11340038626).jpg) Church and doctor's residence of the town Jakobshavn (1900)
Church and doctor's residence of the town Jakobshavn (1900) Cruise ships in the fjord front of Ilulissat
Cruise ships in the fjord front of Ilulissat- Drank nettle for boiling blubber in Ilulissat, Greenland
- Knud Rasmussen's birthplace in Ilulissat, Greenland; Knud Rasmussen's Museum
 Kayaking in Ilulissat
Kayaking in Ilulissat Inuit Kajak at Ilulissat
Inuit Kajak at Ilulissat Dog sled sign in Ilulissat
Dog sled sign in Ilulissat Fisherman in Ilulissat
Fisherman in Ilulissat Cruise ship at Ilulissat port
Cruise ship at Ilulissat port Toddlers with their teacher
Toddlers with their teacher Ilulissat, old part of the city with icebergs from the Ilulissat Icefjord in the background
Ilulissat, old part of the city with icebergs from the Ilulissat Icefjord in the background Sailing in Ilulissat Icefjord
Sailing in Ilulissat Icefjord The football field
The football field Ilulissat Airport from the south.
Ilulissat Airport from the south. Blue iceberg in the Ilulissat Icefjord
Blue iceberg in the Ilulissat Icefjord View of Ilulissat city from the sea
View of Ilulissat city from the sea View of Ilulissat city from the sea
View of Ilulissat city from the sea Sailing in Ilulissat Icefjord
Sailing in Ilulissat Icefjord Sailing in Ilulissat Icefjord
Sailing in Ilulissat Icefjord Sailing in Ilulissat Icefjord
Sailing in Ilulissat Icefjord Sailing in Ilulissat Icefjord
Sailing in Ilulissat Icefjord Sailing in Ilulissat Icefjord
Sailing in Ilulissat Icefjord Ilulissat
Ilulissat Ilulissat
Ilulissat Ilulissat
Ilulissat Ilulissat
Ilulissat Ilulissat artic Tv
Ilulissat artic Tv Ilulissat
Ilulissat Ilulissat
Ilulissat Ilulissat
Ilulissat Ilulissat
Ilulissat Ilulissat
Ilulissat Ilulissat
Ilulissat Ilulissat
Ilulissat
References
- "Den Store Danske: Areal fordelt efter kommune / region". Naatsorsueqqissaartarfik. Retrieved 23 January 2014.
- "Naatsorsueqqissaartarfik: Ilulissat City/Settlements (Ilulissat Municipality, Qaasuitsup Kommunia), 2014 (table: BEDST3)". Statistics Greenland. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- Naatsorsueqqissaartarfik: Naatsorsueqqissaartarfik, table BEDST3', period 2014
- i.a., Lieber, Francis & al. Encyclopædia Americana: A Popular Dictionary of Arts, Sciences, Literature, History, Politics and Biography. "Greenland". B.B. Mussey & Co., 1854.
- "Population by Localities". Statistical Greenland. Retrieved 7 April 2020.
- "Ilulissat". Qaasuitsup Municipality. Archived from the original on 2 June 2012. Retrieved 11 July 2010.
- "21 World Heritage Sites you have probably never heard of". Daily Telegraph.
- "Ilulissat Icefjord". Qaasuitsup Municipality. Retrieved 11 August 2012.
- Marquardt, Ole. "Change and Continuity in Denmark's Greenland Policy" in The Oldenburg Monarchy: An Underestimated Empire?. Verlag Ludwig (Kiel), 2006.
- Kjærgaard, Kathrine (2010). "Grønland som del af den bibelske fortælling – en 1700-tals studie Archived 15 July 2012 at the Wayback Machine" ["Greenland as Part of the Biblical Narrative – a Study of the 18th Century"]. Kirkehistoriske Samlinger, 51-130. (in Danish)
- Guide to Ilulissat Museum, Ilulissat Museum
- Arctic Council (26 May 2008). "Conference on the Arctic Ocean". arctic-council.org. Archived from the original on 20 August 2008. Retrieved 6 June 2008.
- "Greenland hosts Arctic sovereignty talks". Reuters. 27 May 2008. Retrieved 5 October 2010.
- "Ilulissat Declaration" (PDF). Government of Greenland. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 March 2012. Retrieved 11 August 2012.
- "UNESCO Listing". Retrieved 11 August 2012.
- Danish Meteorological Institute Archived 30 June 2013 at the Wayback Machine |language=Danish
- "World Weather Information Service – Ilulissat". Weather2Travel.com. Retrieved 30 September 2013.
- Statistics Greenland, Population in districts and municipalities January 1st 1977-2020 BEEST3
- Air Greenland, History Archived 23 May 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- Jean Malaurie, 1982.
- Knud Johan Victor Rasmussen Archived 12 October 2010 at the Wayback Machine, biography by Sam Alley. Minnesota State University.
- Elizabeth Cruwys, 2003.
- Famous sons Archived 25 December 2008 at the Wayback Machine
External links
| Look up Ilulissat in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Ilulissat. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Ilulissat. |
Overviews and data
Government
- Avannaata Official municipal and city website
Maps
- Satellite image of Retreating Terminus of the Ilulissat Glacier at the NASA Earth Observatory.
Travel
- Kangia - Ilulissat Icefjord Official website
- Ilulissat entry at Visit Greenland – the official Greenlandic Tourist Board tourism website
- A Photographer's View of Ilulissat & Disko Bay Documentary produced by Florent Piovesan