Homoranthus thomasii
Homoranthus thomasii is a plant in the myrtle family Myrtaceae and is endemic to Queensland. It is a small shrub with spoon-shaped, greyish green leaves and small, pendulous, pink flowers in the upper leaf axils.[2][3][4]
| Homoranthus thomasii | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Homoranthus thomasii in the Australian National Botanic Gardens | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Myrtales |
| Family: | Myrtaceae |
| Genus: | Homoranthus |
| Species: | H. thomasii |
| Binomial name | |
| Homoranthus thomasii | |
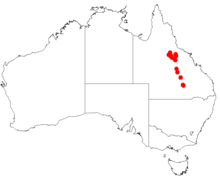 | |
| Occurrence data from AVH | |
| Synonyms[1] | |
| |
Description
Flowers and fruits sporadically throughout the year. Sepals 3–4 mm (0.1–0.2 in)long white or pink; style 15–20 mm (0.6–0.8 in) long, white or pink. Homoranthus thomasii is distinguished from most other species of Homoranthus by its tall growth habit, axehead-shaped leaves and pendulous flowers. [5]
Taxonomy and naming
This species was first formally described in 1864 by Ferdinand von Mueller who gave it the name Chamelaucium thomasii and published the description in the journal Fragmenta phytographiae Australiae.[6][7] In 1991, Lyndley Craven and S.R.Jones changed the name to Homoranthus thomasii.[8] The specific epithet (thomasii) honours the Melbourne doctor David John Thomas (1813–1871).[7][9]
Distribution and habitat
Homoranthus thomasii grows in heath and woodland from Pentland to Mitchell. Grows on shallow, sandy soils derived from sandstone, mostly in woodland or heath.[10]
Conservation
Although widely distributed, H. thomasii is of sporadic occurrence and was considered rare by Briggs and Leigh (1996). Given several recent discoveries of species in conservation areas. Now considered a ROTAP conservation 3RCa.[11]
References
- "Homoranthus thomasii". World Checklist of Selected Plant Families (WCSP). Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew.
- "Homoranthus thomasii". Native Plants Queensland. Retrieved 25 August 2018.
- Craven, Lyndley A.; Jones, S R. (1991). "A taxonomic review of Homoranthus and two new species of Darwinia (both Myrtaceae, Chamelaucieae)". Australian Systematic Botany. 4 (3): 513. doi:10.1071/SB9910513. Retrieved 19 August 2018.
- "Homoranthus homoranthoides". Goldfields Revegetation Plant Catalogue. Retrieved 24 August 2018.
- Copeland, Lachlan M.; Craven, Lyn A.; Bruhl, Jeremy J. (2011). "A taxonomic review of Homoranthus (Myrtaceae: Chamelaucieae)". Australian Systematic Botany. 24 (6): 351. doi:10.1071/SB11015.
- "Chamelaucium thomasii". APNI. Retrieved 25 August 2018.
- von Mueller, Ferdinand (1864). Fragmenta phytographiae Australiae. Melbourve. pp. 137–138. Retrieved 25 August 2018.
- "Homoranthus thomasii". APNI. Retrieved 25 August 2018.
- Gandevia, Bryan. "Thomas, David John (1813–1871)". Australian Dictionary of Biography. Retrieved 25 August 2018.
- Copeland, Lachlan M.; Craven, Lyn A.; Bruhl, Jeremy J. (2011). "A taxonomic review of Homoranthus (Myrtaceae: Chamelaucieae)". Australian Systematic Botany. 24 (6): 371–372. doi:10.1071/SB11015.
- Copeland, Lachlan M.; Craven, Lyn A.; Bruhl, Jeremy J. (2011). "A taxonomic review of Homoranthus (Myrtaceae: Chamelaucieae)". Australian Systematic Botany. 24 (6): 351. doi:10.1071/SB11015.