History of the United Nations
The history of the United Nations as an international organization has its origins in World War II. Since then its aims and activities have expanded to make it the archetypal international body in the early 21st century.
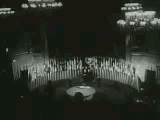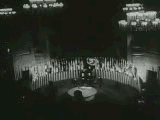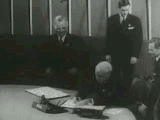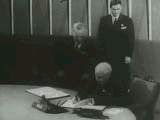
Origins
The earliest concrete plan for a new world organization to replace the ineffective League of Nations began under the aegis of the US State Department in 1939.[1] On 12 June 1941, representatives of the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, the Union of South Africa, and of the exiled governments of Belgium, Czechoslovakia, Greece, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, and Yugoslavia, as well as a representative of General de Gaulle of France, met in London and signed the Declaration of St. James's Palace. This was the first of six conferences that led up to the founding of the United Nations and the Charter of the United Nations.[2]
U.S. President Franklin Roosevelt first suggested using the name United Nations, to refer to the Allies of World War II, to British Prime Minister Winston Churchill during the latter's three-week visit to the White House in December 1941. Roosevelt suggested the name as an alternative to "Associated Powers", a term the U.S. used in the First World War (the U.S. was never formally a member of the Allies of World War I but entered the war in 1917 as a self-styled "Associated Power"). Churchill accepted the idea and cited Lord Byron's use of the phrase "United Nations" in the poem Childe Harold's Pilgrimage, which referred to the Allies at the Battle of Waterloo in 1815.[3][4]
1942 "Declaration of United Nations"

The text of the "Declaration of United Nations" was drafted by U.S. President Franklin D. Roosevelt, British Prime Minister Winston Churchill, and Roosevelt aide Harry Hopkins, while meeting at the White House on 29 December 1941. It incorporated Soviet suggestions, but left no role for France. The first official use of the term "United Nations" was on 1–2 January 1942 when 26 Governments signed the Declaration. One major change from the Atlantic Charter was the addition of a provision for religious freedom, which Stalin approved after Roosevelt insisted.[5][6] By early 1945 it had been signed by 21 more states.[7]
A JOINT DECLARATION BY THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA, THE UNITED KINGDOM OF GREAT BRITAIN AND NORTHERN IRELAND, THE UNION OF SOVIET SOCIALIST REPUBLICS, CHINA, AUSTRALIA, BELGIUM, CANADA, COSTA RICA, CUBA, CZECHOSLOVAKIA, DOMINICAN REPUBLIC, EL SALVADOR, GREECE, GUATEMALA, HAITI, HONDURAS, INDIA, LUXEMBOURG, NETHERLANDS, NEW ZEALAND, NICARAGUA, NORWAY, PANAMA, POLAND, SOUTH AFRICA, YUGOSLAVIA
The Governments signatory hereto,
Having subscribed to a common program of purposes and principles embodied in the Joint Declaration of the President of the United States of America and the Prime Minister of Great Britain dated August 14, 1941, known as the Atlantic Charter,
Being convinced that complete victory over their enemies is essential to defend life, liberty, independence and religious freedom, and to preserve human rights and justice in their own lands as well as in other lands, and that they are now engaged in a common struggle against savage and brutal forces seeking to subjugate the world,
DECLARE:
(1) Each Government pledges itself to employ its full resources, military or economic, against those members of the Tripartite Pact and its adherents with which such government is at war.
(2) Each Government pledges itself to cooperate with the Governments signatory hereto and not to make a separate armistice or peace with the enemies.
The foregoing declaration may be adhered to by other nations which are, or which may be, rendering material assistance and contributions in the struggle for victory over Hitlerism.[8]
During the war, the United Nations became the official term for the Allies. To join countries had to sign the Declaration and declare war on the Axis.[9]
Planning

US President Franklin D. Roosevelt considered his most important legacy the creation of the United Nations, making a permanent organization out of the wartime Alliance of the same name. He was the chief promoter of the United Nations idea. The first plans for the future international organization emerged in declarations signed at the wartime Allied conferences: the Moscow Conference and the Tehran Conference on 30 October 1943.
Roosevelt had been a strong supporter of the League of Nations back in 1919–20, but was determined to avoid the mistakes Woodrow Wilson had made. The United Nations was FDR's highest postwar priority. He insisted on full coordination with the Republican leadership. He made sure that leading Republicans were on board, especially Senators Arthur Vandenberg of Michigan,[10] and Warren Austin of Vermont.[11] In a broad sense, Roosevelt believed that the UN could solve the minor problems and provide the chief mechanism to resolve any major Issues that arose among the great powers, all of whom had a veto. For FDR creating the UN was the most important goal for the entire war effort.[12] Roosevelt was especially interested in international protection of human right, and in this area his wife played a major role as well.[13][14]
The Allies had agreed to the basic structure of the new body at the Dumbarton Oaks Conference in 1944.[15] At Yalta, Roosevelt, Churchill, and Stalin agreed to the establishment of the United Nations, as well as the structure of the United Nations Security Council. Stalin insisted on having a veto and FDR finally agreed. The participants at Yalta also agreed that the United Nations would convene for the first time in San Francisco in April 1945 in the United Nations Conference on International Organization. Roosevelt considered the United Nations to be his most important legacy. He provided continuous backstage political support at home and with Churchill and Stalin abroad. The Big Four of the United States, Britain, Soviet Union and China would make the major decisions, with France added later to provide permanent members of the all-powerful Security Council. Each had a veto power, thus avoiding the fatal weakness of the League of Nations, which had theoretically been able to order its members to act in defiance of their own parliaments.[16]
Roosevelt went public with strong advocacy in the 1944 presidential campaign, and turned detailed planning over to the State Department, where Sumner Welles and Secretary Cordell Hull worked on the project. It was his ideas that "four policemen" would collaborate to keep and enforce the peace. The United States, Britain, Soviet Union and China made the major decisions and became permanent members of the all-powerful Security Council; France was added to make five policemen.[17] Stalin insisted on a veto power. Roosevelt finally agreed, thus avoiding the fatal weakness of the League of Nations, which theoretically could order its members to act in defiance of their own parliaments.[18]
From 21 September to 7 October 1944, representatives of the Republic of China, Britain, the US and the USSR met to elaborate plans at the Dumbarton Oaks Conference in Washington, D.C. Those and later talks produced proposals outlining the purposes of the United Nations organization, its membership and organs, as well as arrangements to maintain international peace and security and international economic and social cooperation. Governments and private citizens worldwide discussed and debated these proposals.[19] Winston Churchill urged Roosevelt to restore France to its status of a major Power after the liberation of Paris in August 1944.
At the Yalta Conference it was agreed that membership would be open to nations that had joined the Allies by 1 March 1945.[20] Brazil, Syria and a number of other countries qualified for membership by declarations of war on either Germany or Japan in the first three months of 1945 – in some cases retroactively.
Establishment

On 25 April 1945, the United Nations Conference on International Organization began in San Francisco. In addition to Governments, a number of non-government organizations, including Rotary International and Lions Clubs International received invitations to assist in the drafting of a charter. After working for two months, the fifty nations represented at the conference signed the Charter of the United Nations on 26 June. Poland, which was unable to send a representative to the conference due to political instability, signed the charter on 15 October 1945. The charter stated that before it would come into effect, it must be ratified by the Governments of the Republic of China, France, the USSR, the United Kingdom, and the United States, and by a majority of the other 46 signatories. This occurred on 24 October 1945, and the United Nations was officially formed.[21]
The date each founding member state deposited their ratification of the UN Charter is as follows:[22]
- USA – 8 Aug 1945
- France – 31 Aug 1945
- Dominican Rep. – 4 Sep 1945
- Nicaragua – 6 Sep 1945
- New Zealand – 19 Sep 1945
- Brazil – 21 Sep 1945
- Argentina – 24 Sep 1945
- El Salvador – 26 Sep 1945
- Haiti – 27 Sep 1945
- China – 28 Sep 1945
- Turkey – 28 Sep 1945
- Denmark – 9 October 1945
- Chile – 11 Oct 1945
- Philippines – 11 Oct 1945
- Paraguay – 12 Oct 1945
- Cuba – 15 Oct 1945
- Lebanon – 15 Oct 1945
- Iran – 16 Oct 1945
- Luxembourg – 17 Oct 1945
- Saudi Arabia – 18 Oct 1945
- Czechoslovakia – 19 Oct 1945
- Syria – 19 Oct 1945
- Yugoslavia – 19 Oct 1945
- UK – 20 Oct 1945
- Egypt – 22 Oct 1945
- Byelorussia – 24 Oct 1945
- Poland – 24 Oct 1945
- Ukraine – 24 Oct 1945
- USSR – 24 Oct 1945 (note - the United Nations was established on this date)
- Greece – 25 Oct 1945
- India – 30 Oct 1945
- Peru – 31 Oct 1945
- Australia – 1 Nov 1945
- Costa Rica – 2 Nov 1945
- Liberia – 2 Nov 1945
- Colombia – 5 Nov 1945
- Mexico – 7 Nov 1945
- South Africa – 7 Nov 1945
- Canada – 9 Nov 1945
- Ethiopia – 13 Nov 1945
- Panama – 13 Nov 1945
- Bolivia – 14 Nov 1945
- Venezuela – 15 Nov 1945
- Honduras – 17 Nov 1945
- Guatemala – 21 Nov 1945
- Norway – 27 Nov 1945
- Netherlands – 10 Dec 1945
- Uruguay – 18 Dec 1945
- Ecuador – 21 Dec 1945
- Iraq – 21 Dec 1945
- Belgium – 27 Dec 1945

The first meeting of the General Assembly was held in Westminster Central Hall, London, on 10 January 1946.[23] The Security Council met for the first time a week later in Church House, Westminster.[24] The League of Nations formally dissolved itself on 18 April 1946 and transferred its mission to the United Nations.
Activities
The United Nations has achieved considerable prominence in the social arena, fostering human rights, economic development, decolonization, health and education, for example, and interesting itself in refugees and trade.
The leaders of the UN had high hopes that it would act to prevent conflicts between nations and make future wars impossible. Those hopes have obviously not fully come to pass. From about 1947 until 1991 the division of the world into hostile camps during the Cold War made agreement on peacekeeping matters extremely difficult. Following the end of the Cold War, renewed calls arose for the UN to become the agency for achieving world peace and co-operation, as several dozen active military conflicts continued to rage across the globe. The breakup of the Soviet Union has also left the United States in a unique position of global dominance, creating a variety of new problems for the UN (See the United States and the United Nations).
Facilities


In June 1945, delegates from around the world gathered in San Francisco to draft the charter for the United Nations.[25] Potential sites for the UN Headquarters included Vienna, Switzerland, Berlin, Quebec, and the Netherlands before the delegation decided on a headquarters in the United States by December 1945.[26] Many U.S. cities vied for the honor of hosting the UN Headquarters site, such as Marin County, California, St. Louis, Boston, Chicago, Fairfield County, CT, Westchester County, NY, Flushing Meadows-Corona Park in Queens, Tuskahoma, Oklahoma, the Black Hills of South Dakota, Belle Isle in Detroit, and a site on Navy Island straddling the U.S.-Canada border were considered as potential sites for the UN Headquarters.[27][28] San Francisco, where the UN Headquarters delegation was held, was favored by Australia, New Zealand, China, and the Philippines due to the city's proximity to their countries.[27] The UN and many of its delegates seriously considered Philadelphia for the headquarters; the city offered to donate land in several select sites, including Fairmount Park, Andorra, and a Center City, Philadelphia location which would have placed the headquarters along a mall extending from Independence Hall to Penn's Landing.[27]
In 1946, John D. Rockefeller III and Laurance Rockefeller each offered their respective residences in Kykuit in Mount Pleasant, New York as headquarters for the UN, but the proposals were vetoed as the sites were too isolated from Manhattan.[29] The Soviet Union vetoed Boston due to the denunciations of Soviet expansion by John E. Swift, a Massachusetts judge and Supreme Knight of the Knights of Columbus.[30]
New York City Planning Commissioner Robert Moses convinced Nelson Rockefeller to purchase a 17 and 18 acres (6.9 and 7.3 ha) piece of land along the East River in New York City from real estate developer William Zeckendorf Sr.;[31] The purchase was funded by Nelson's father, John D. Rockefeller Jr. The Rockefeller family owned the Tudor City Apartments across First Avenue from the Zeckendorf site.[32] The UN ultimately chose the New York City site over Philadelphia after Rockefeller offered to donate the land along the East River.[25] The UN headquarters officially opened on January 9, 1951, although construction was not formally completed until October 9, 1952.[33]
Structure and associated organizations
The basic constitutional makeup of the United Nations has changed little, though vastly increased membership has altered the functioning of some elements. The UN as a whole has generated a rich assortment of non-governmental organizations and special bodies over the years: some with a regional focus, some specific to the various peacekeeping missions, and others of global scope and importance. Other bodies (such as the International Labour Organization) formed prior to the establishment of the United Nations and only subsequently became associated with it.
Milestones
See also
- Growth in United Nations membership
- List of members of the United Nations Security Council
- Timeline of UN peacekeeping missions
- List of UN Secretaries-General
- Attacks on humanitarian workers
- Reform of the United Nations
Further reading
- Baehr, Peter R., and Leon Gordenker. The United Nations in the 1990s (St. Martin's Press, 1992)
- Bellamy, Alex J., and Paul D. Williams, eds. Providing Peacekeepers: The Politics, Challenges, and Future of United Nations Peacekeeping Contributions (Oxford University Press, 2013)
- Bergesen, Helge Ole, and Leiv Lunde. Dinosaurs or Dynamos: the United Nations and the World Bank at the turn of the century (Routledge, 2013)
- Bosco, David L. Five to rule them all: the UN Security Council and the making of the modern world (Oxford University Press, 2009)
- Clark, Ian, and Christian Reus-Smit. "Liberal internationalism, the practice of special responsibilities and evolving politics of the security council." International Politics (2013) 50#1 pp: 38–56.
- Dykmann, Klaas. "On the Origins of the United Nations: When and How Did it Begin?." Journal of International Organizations Studies 3.1 (2012): 79–84. online
- Ferdinand, Peter. "Rising powers at the UN: an analysis of the voting behaviour of brics in the General Assembly." Third World Quarterly (2014) 35#3 pp: 376–391.
- Hanhimäki, Jussi M. The United Nations: a very short introduction (Oxford University Press, 2015).
- Hiscocks, Richard. The Security Council: A study in adolescence (Simon and Schuster, 1974)
- Luck, Edward C. UN Security Council: practice and promise (Routledge, 2006)
- Mazower, Mark.No Enchanted Palace: The End of Empire and the Ideological Origins of the United Nations (Princeton UP, 2009),
- Meisler, Stanley. United Nations: The First Fifty Years (1995)
- Peters, Laurence. The United Nations: history and core ideas (Springer, 2016).
- Plesch, Dan. America, Hitler and the UN: How the Allies Won World War II and Forged a Peace. (Bloomsbury Publishing, 2010); the wartime alliance called the "United Nations"
- Rusell, Ruth B. A History of the United Nations Charter: The Role of the United States, 1940-1945 (Washington: Brookings Institution, 1958.)
- O'Sullivan, Christopher D. The United Nations: A Concise History (The Anvil Series, Krieger Publishing Company, 2005)
- Phillips, Walter Ray. "United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization." Montana Law Review 24.1 (2014): 2.
- Roberts, Adam, and Dominik Zaum. Selective security: war and the United Nations Security Council since 1945 (Routledge, 2013)
- Saltford, John. The United Nations and the Indonesian takeover of West Papua, 1962-1969: the anatomy of betrayal (Routledge, 2013)
- Schlesinger, Stephen C. Act of creation: The founding of the United Nations: A story of superpowers, secret agents, wartime allies and enemies, and their quest for a peaceful world. (Westview Press, 2003).
- Vreeland, James Raymond, and Axel Dreher. The Political Economy of the United Nations Security Council: Money and Influence (Cambridge University Press, 2014)
- Weiss, Thomas G. What's Wrong with the United Nations and how to Fix it (John Wiley & Sons, 2013)
- Wuthnow, Joel. Chinese diplomacy and the UN Security Council: beyond the veto (Routledge, 2012)
Primary sources
- Cordier, Andrew W., and Wilder Foote, eds. Public Papers of the Secretaries General of the United Nations (4 vol; Columbia University Press, 2013)
References
- Townsend Hoopes and Douglas Brinkley, FDR and the Creation of the U.N. (1997) pp 1-55
- "1941: The Declaration of St. James' Palace". United Nations. 2015-08-25. Retrieved 28 March 2016.
- "United Nations". Wordorigins.org. 3 February 2007. Retrieved 28 March 2016.
- Ward, Geoffrey C.; Burns, Ken (2014). "Nothing to Conceal". The Roosevelts: An Intimate History. Knopf Doubleday Publishing Group. ISBN 978-0385353069.
- David Roll, The Hopkins Touch: Harry Hopkins and the Forging of the Alliance to Defeat Hitler (2013) pp 172-75
- Robert E. Sherwood, Roosevelt and Hopkins, An Intimate History (1948) pp 447-53
- Edmund Jan Osmańczyk (2003). Encyclopedia of the United Nations and International Agreements: T to Z. Taylor & Francis. p. 2445. ISBN 9780415939249.
- Text from "The Washington Conference 1941-1942"
- Stephen C. Schlesinger, Act of creation: The founding of the United Nations: A story of superpowers, secret agents, wartime allies and enemies, and their quest for a peaceful world (2003)
- James A. Gazell, "Arthur H. Vandenberg, Internationalism, and the United Nations." Political Science Quarterly 88#3 (1973): 375-394. online
- George T. Mazuzan. Warren R. Austin at the U. N., 1946-1953 (Kent State UP, 1977).
- For FDR, "establishing the United nations organization was the overarching strategic goal, the absolute first priority." Townsend Hoopes; Douglas Brinkley (1997). FDR and the Creation of the U.N. Yale UP. p. 178.
- Ivy P. Urdang, "Franklin and Eleanor Roosevelt: Human Rights and the Creation of the United Nations." OAH Magazine of History 22.2 (2008): 28-31.
- M. Glen Johnson, "The contributions of Eleanor and Franklin Roosevelt to the development of international protection for human rights." Human Rights Quarterly 9 (1987): 19+.
- Hoopes and Brinkley, FDR and the Creation of the U. N. (1997) pp 148-58.
- John Allphin Moore Jr. and Jerry Pubantz, To Create a New World?: American Presidents & the United Nations (1999), pp 27-79.
- Stephen Schlesinger, "FDR's five policemen: creating the United Nations." World Policy Journal 11.3 (1994): 88-93. online
- Townsend Hoopes and Douglas Brinkley, FDR and the Creation of the U. N. (1997)
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2015-10-16. Retrieved 2017-06-28.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- Robert C. Hilderbrand, Dumbarton Oaks: The Origins of the United Nations and the Search for Postwar Security (UNC Press, 2001)
- https://www.un.org/aboutun/sanfrancisco/history.html The 60th Anniversary of the San Francisco Conference
- "Member States: On the Record: Founding Member States". Dag Hammarskjöld Library, Outreach Division, Department of Public Information. UN. 2009-09-28. Archived from the original on 3 July 2010.
- "History of the United Nations 1941 - 1950". United Nations. Archived from the original on 12 March 2015. Retrieved 12 March 2015.
- "What is the Security Council?". United Nations. Retrieved 12 March 2015.
- Historical Society of Philadelphia (November 23, 2018). "When the United Nations Almost Chose Philly For Its HQ". Hidden City Philadelphia. Retrieved March 26, 2019.
- Glynn, Don (October 24, 2011). "Glynn - Navy Island eyed as home for U.N." Niagara Gazette. Retrieved March 26, 2019.
- Atwater, Elton (April 1976). "Philadelphia's Quest to Become the Permanent Headquarters of the United Nations". The Pennsylvania Magazine of History and Biography. Pennsylvania: The Historical Society of Pennsylvania; University of Pennsylvania Press. JSTOR 20091055.
- Mires, Charlene (April 2, 2013). "Detroit's Quixotic Bid to Host the United Nations". Foreign Policy. Retrieved March 26, 2019.
- Harr, John Ensor Harr & Johnson, Peter J. (1988). "Estate offered as site for the UN headquarters". The Rockefeller Century: Three Generations of America's Greatest Family. New York: Charles Scribner's Sons. pp. 432–33.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- Lapomarda, S.J., Vincent A. (1992). The Knights of Columbus in Massachusetts (second ed.). Norwood, Massachusetts: Knights of Columbus Massachusetts State Council. p. 41.
- Gray, Christopher (2010-04-25). "The U.N.: One Among Many Ideas for the Site". The New York Times. Retrieved 2017-12-26.
- Boland, Ed Jr. (June 8, 2003). "F.Y.I." The New York Times. Retrieved July 9, 2010.
- Hamilton, Thomas J. (1952-10-10). "WORK COMPLETED ON U. N. BUILDINGS; $68,000,000 Plant Finished -- Lie Announces a Plan to Reorganize Top Staff WORK COMPLETED ON U. N. BUILDINGS". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 2018-03-29.
- "World lights up in UN blue to mark Organization's milestone anniversary". UN News Centre. 22 October 2015. Retrieved 25 October 2015.
- "Over 200 Landmarks to Light Up UN Blue on 70th Anniversary". The New York Times. 23 October 2015. Retrieved 25 October 2015.
- "Turn the World #UNBlue". United Nations Information Centres. 2015-10-07. Retrieved 25 October 2015.
External links
- UN Intellectual History Project – Academic study of UN history
- United Nations Events Timeline
- Declaration by United Nations, January 1, 1942
- UN History Project – Website providing resources, timelines, lectures, and bibliographies of UN history