Guaporé River
Guaporé River (Portuguese: Rio Guaporé, Spanish: Río Iténez) is a river in western Brazil and northeastern Bolivia. It is 1,260 km (780 mi) long; 920 km (570 mi) of the river forms the border between Brazil and Bolivia.
| Guaporé River Iténez River | |
|---|---|
Rio Guaporé at Pontes e Lacerda (Brazil) | |
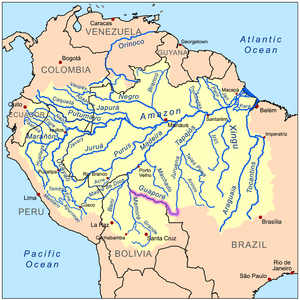 Map of the Amazon Basin with the Guaporé River highlighted | |
| Location | |
| Countries | |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Parecis plateau |
| • location | Mato Grosso, Brazil |
| • coordinates | 14°35′58″S 58°57′11″W |
| • elevation | 631 m (2,070 ft) |
| Mouth | Mamoré River |
• location | Brazil/Bolivia |
• coordinates | 11°53′15″S 65°1′53″W |
• elevation | 131 m (430 ft) |
| Length | 1,260 km (780 mi)[1] |
| Basin size | 235,000 km2 (91,000 sq mi) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | mouth |
| • average | 2,740 m3/s (97,000 cu ft/s) |
| Basin features | |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Alegre River, Verde River, Paragúa River, Río Blanco, Machupo River |
| • right | Guatire River, Branco River, Corumbiara River, Colorado River, Massaco River, Cabixi River |
The Guaporé River is part of the Madeira River basin, which eventually empties into the Amazon River. The Guaporé River crosses the eastern part of the Beni savanna region.[2] It forms the border of the 615,771 hectares (1,521,600 acres) Guaporé Biological Reserve, and is fed by rivers originating in the reserve, the São Miguel, Branco, São Simão, Massaco and Colorado.[3]
About 260 fish species are known from the Guaporé River basin, and about 25 of these are endemic.[4] While many fish species in the river essentially are Amazonian, the fauna in the Guaporé also has a connection with the Paraguay River (part of the Río de la Plata Basin). The Guaporé and the Paraguay, while flowing in different directions, both originate in the Parecis plateau of Brazil.[5] Among the fish species shared between these rivers are the black phantom tetra (important in the aquarium industry) and golden dorado (important in fisheries).[6][7]
References
- Ziesler, R.; Ardizzone, G.D. (1979). "Amazon River System". The Inland waters of Latin America. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. ISBN 92-5-000780-9. Archived from the original on 8 November 2014.
- Robin Sears and Robert Langstroth. "Central South America: Northern Bolivia". Tropical and Subtropical Grasslands, Savannas and Shrublands. WWF. Retrieved 7 October 2012.
- Unidade de Conservação: Reserva Biológica do Guaporé (in Portuguese), MMA: Ministério do Meio Ambiente, retrieved 2016-04-26
- Hales, J., and P. Petry (2013). Guapore - Itenez. Freshwater Ecoregions of the World. Retrieved 28 February 2013
- Ohara, W.M.; and F.C.T. Lima (2015). Moenkhausia uirapuru, a new species from the upper rio Guaporé, Chapada dos Parecis, Mato Grosso, Brazil (Teleostei: Characidae). Ichthyol. Explor. Freshwaters 26(2): 159-170.
- Froese, Rainer and Pauly, Daniel, eds. (2013). "Hyphessobrycon megalopterus" in FishBase. May 2013 version.
- Ziegler, M.F. (29 April 2013). Estudo descobre 78 novas espécies de peixes no Rio Madeira. Ultimosegundo.com. Retrieved 28 February 2017.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Guaporé River. |