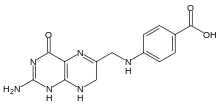
Dihydropteroate
Dihydropteroate is an important intermediate in folate synthesis. It is a pterin created from para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) by the enzyme dihydropteroate synthase.[1]
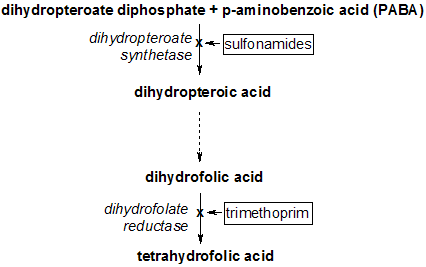
Tetrahydrofolate synthesis pathway
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
4-{[(2-amino-4-oxo-1,4,7,8-tetrahydropteridin-6-yl)methyl]amino}benzoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 1226443 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H14N6O3 | |
| Molar mass | 314.3 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Bacteriostatic agents such as sulfonamides target dihydropteroate synthetase. The effect of dihydropteroate synthetase inhibition is comparable to that of dihydrofolate reductase inhibition by trimethoprim, another bacteriostatic agent. Combinations of these two drug types, such as the combination trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX]), are commonly used to treat recurrent urinary tract, Shigella, Salmonella, and Pneumocystis jivoreci infections.
See also
References
- Hevener, Kirk E; Yun, Mi-Kyung; Qi, Jianjun; Kerr, Iain D; Babaoglu, Kerim; Hurdle, Julian G; Balakrishna, Kanya; White, Stephen W; Lee, Richard E (2010). "Structural Studies of Pterin-Based Inhibitors of Dihydropteroate Synthase". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 53 (1): 166–177. doi:10.1021/jm900861d. PMC 2804029. PMID 19899766.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.