Cytochemistry
Cytochemistry is the branch of cell biology dealing with the detection of cell constituents by means of biochemical analysis and visualization techniques. The term is also used to describe a process of identification of the biochemical content of cells. Cytochemistry is a science of localizing chemical components of cells and cell organelles on thin histological sections by using several techniques like enzyme localization, micro-incineration, micro-spectrophotometry, radioautography, cryo-electron microscopy, X-ray microanalysis by energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, immunohistochemistry and cytochemistry, etc.[1]
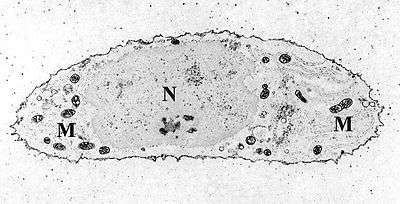
Transmission electron micrograph of a chondrocyte, stained for calcium, showing its nucleus (N) and mitochondria (M).
Footnotes
- Nagata, T (2001). "Special cytochemistry in cell biology". International Review of Cytology. 211: 33–151. PMID 11597006.
References
- Brighton, Carl T. and Robert M. Hunt (1974). "Mitochondrial calcium and its role in calcification". Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research 100: 406-416.
- Brighton, Carl T. and Robert M. Hunt (1978). "The role of mitochondria in growth plate calcification as demonstrated in a rachitic model". Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery, 60-A: 630-639.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.