Crato Formation
The Crato Formation is a geologic formation of Early Cretaceous (Aptian) age in northeastern Brazil's Araripe Basin. It is an important Lagerstätte (undisturbed fossil accumulation) for palaeontologists. The strata were laid down mostly during the early Aptian age, about 113 million years ago, in a shallow inland sea. At that time, the South Atlantic was opening up in a long narrow shallow sea.
| Crato Formation Stratigraphic range: Latest Aptian ~115–113 Ma | |
|---|---|
| Type | Geological formation |
| Unit of | Santana Group |
| Sub-units | Nova Olinda Member |
| Underlies | Romualdo & Ipubi Formations |
| Overlies | Barbalha Formation |
| Lithology | |
| Primary | Mudstone, limestone |
| Other | Siltstone |
| Location | |
| Coordinates | 7.1°S 39.7°W |
| Approximate paleocoordinates | 8.6°S 8.0°W |
| Region | |
| Country | |
| Extent | Araripe Basin |
| Type section | |
| Named for | Crato, Ceará |
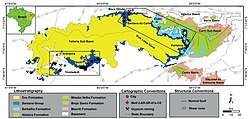 Extent of the Santana Group, to which the Crato Formation belongs, in blue | |
The Crato Formation earns the designation of Lagerstätte due to an exceedingly well preserved and diverse fossil faunal assemblage. Some 25 species of fossil fishes are often found with stomach contents preserved, enabling paleontologists to study predator-prey relationships in this ecosystem. There are also fine examples of pterosaurs, reptiles and amphibians, invertebrates (particularly insects), and plants. Even dinosaurs are represented: a new maniraptor was described in 1996. The unusual taphonomy of the site resulted in limestone accretions that formed nodules around dead organisms, preserving even soft parts of their anatomy.
History

Fish fossils in the area were noted in 1823. When they were first methodically published, in 1993, the Crato Formation limestones provided a new site for pterosaurs, one that also preserved insects that fell into a brackish lagoon and semionotid fish preserved in phosphatized nodules. The fossils are usually compacted and preserved in layers of limestone. Fossil Odonata (dragonflies) and damselflies are especially rich in the Crato lagerstätte: currently 384 specimens have been recovered, 264 adults and 120 larvae. Hemiptera (true bugs) and Orthoptera (grasshoppers and crickets) are also abundant in number of species and in number of specimens. There are also plant remains.
Local mining activities for cement and construction damage the sites. Trade in illegally collected fossils has sprung up in the last decade, driven by the remarkable state of preservation and beauty of these fossils and amounting to a considerable local industry. An urgent preservation program is being called for by paleontologists.
In addition, the weathering of Crato and Santana Formation rocks has contributed soil conditions unlike elsewhere in the region. The Araripe manakin (Antilophia bokermanni) is a very rare bird that was discovered only in the late 20th century; it is not known from anywhere outside the characteristic forest that grows on the Chapada do Araripe soils formed ultimately from Crato and Santana Formation rocks.
Definition
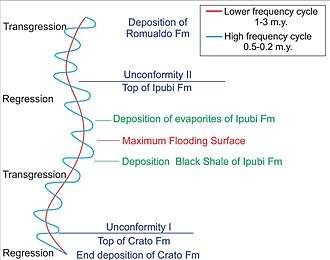
The Crato Formation has often historically been considered the lowest member of the Santana Formation (or, alternatively, the Araripina Formation) of the Araripe Group,[1] later redefined as the Romualdo Formation of the Santana Group.[2][3] The Crato Member is the product of a single phase, where complicated sequence of sediment strata reflect changeable conditions in the opening sea. The age of this strata has been controversial, though most workers have agreed that it lies on or near the Aptian-Albian boundary, about 112 million years ago.[4]
The extent of the Crato unit and its relationship to the Romualdo Formation had long been ill-defined. It was not until a 2007 volume on the unit by Martill, Bechly and Loveridge that the Crato Formation was given a formal type locality, and was formally made a distinct formation separate from the Santana, which is about 10 Ma younger.[4] The Crato Formation is considered time equivalent with the Paracuru Formation.[5]
Fossil content
Insects
| Insects of the Crato Formation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Presence | Description | Images |
|
A. seldoni |
Nova Olinda Member |
A Nymphid lacewing |
||
|
G. pulchra |
A Eolepidopterigidae moth |
|||
|
M. adamsi |
A Kalligrammatid lacewing |
|||
|
M. longimanus |
A Coxoplectopteran insect |
 Mickoleitia longimanus | ||
|
N. nana |
A Eolepidopterigidae moth |
|||
|
P. incerta |
An Ithonidae lacewing, type species of Principiala |
|||
|
P. calipsa |
A Eolepidopterigidae moth |
|||
|
R. maxima |
||||
|
U. cariensis |
An Eolepidopterigidae moth |
|||
Arachnids
| Arachnids of the Crato Formation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Presence | Description | Images |
| Protoischnurus | P. axelrodorum | Scorpion | ||
Fish
| Fish of the Crato Formation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Presence | Description | Images | Notes |
| Araripelepidotes | Araripelepidotes temnurus | ||||
| Belonostomus | Belonostomus sp. | ||||
| Calamopleurus | Calamopleurus cylindricus | ||||
| Cladocyclus | Cladocyclus gardneri | An Ichthyodectidae fish | |||
| Cratoamia | Cratoamia gondwanica | ||||
| Dastilbe | Dastilbe crandalli | ||||
| Lepidotes | Lepidotes wenzae | ||||
| Placidichthys | Placidichthys bidorsalis | ||||
| Santanichthys | Santanichthys diasii | ||||
Amphibians
| Amphibians of the Crato Formation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Presence | Description | Images |
|
Arariphrynus[18] |
Arariphrynus placidoi[18] |
|||
|
Cratia gracilis[18] |
||||
|
Eurycephalella alcinae[18] |
||||
|
Possible indeterminate pipoid remains.[18] |
||||
Squamata
| Squamatans of the Crato Formation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Presence | Description | Images |
|
C. alamoi |
A non-iguana lizard |
|||
|
T. amplectus |
A stem group snake with limbs |
 | ||
Dinosauria
| Dinosaurs and birds of the Crato Formation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Presence | Notes | Images |
|
?Avialan species |
Numerous isolated feathers |
 | ||
|
C. cearensis |
 Reconstruction of Cratoavis and Mirischia | |||
|
?Spinosaur species |
Isolated tooth |
|||
Crurotarsans
| Crocodylomorphs of the Crato Formation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Presence | Description | Images |
|
Susisuchus anatoceps[19] |
||||
|
cf. Susisuchus sp.[20] |
Undescribed species | |||
Pterosaurs
| Pterosaurs of the Crato Formation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Presence | Description | Images |
|
A. conandoylei |
||||
|
A. cearensis |
A basal member of the Tapejarinae. | Holotype | ||
|
B. sp. |
||||
|
L. magnificens |
Nova Olinda Member |
|||
|
L. sibbicki |
An ornithocheirid |
 Ludodactylus sp. | ||
|
T. imperator |
 Tupandactylus navigans | |||
|
?T. sp. |
 Tupuxuara sp. | |||
Flora
| Flora of the Crato Formation | |
|---|---|
| Species | Notes |
| Araucaria cartellei, Brachyphyllum obesum, B. castilhoi, B. insigne, Iara iguassu, Caytoniales sp., Ephedra sp., Araripia florifera, Araucarites vulcanoi, Cariria orbiculiconiformis, Cearania heterophylla, Cratonia cotyledon, Endressinia brasiliana,Klitzchophyllites flabellatus, Novaolindia dubia, Pluricarpellatia peltata, Podozamites lanceolatus, Protananas lucenae, Ruffordia goeppertii, Tomaxellia biforme, Welwitschiaprisca austroamericana, Welwitschiophyllum brasiliense, Welwitschiostrobus murili, Araucariostrobus sp., Frenelopsis sp., Isoetites sp., Lindleycladus sp., Schizoneura sp. | |
Other fossils
- Araripenaeus timidus[22]
- †Cratoalloneura
- †Cratoalloneura acuminata
- †Cratoalloneura verdandia
- †Cratoatractocerus
- †Cratoatractocerus grimaldii
- †Cratoborellia
- †Cratoborellia gorbi
- †Cratochrysa
- †Cratochrysa martinsnetoi
- †Cratochrysa sublapsa
- †Cratochrysa willmanni
- †Cratocora
- †Cratocora crassa
- †Cratocordulia
- †Cratocordulia borschukewitzi
- †Cratocoris
- †Cratocoris shevchenkoae
- †Cratocorydalopsis
- †Cratocorydalopsis brasiliensis
- †Cratocossus
- †Cratocossus magnus
- †Cratodactylus
- †Cratodactylus ferreirai
- †Cratodactylus kellneri
- †Cratoelcana
- †Cratoelcana damianii
- †Cratoelcana zessini
- †Cratoenigma
- †Cratoenigma articulata
- †Cratogomphus
- †Cratogomphus erraticus
- †Cratogryllus
- †Cratogryllus cigueli
- †Cratogryllus guimaraesae
- †Cratogryllus pentagonalis
- †Cratohagenius
- †Cratohagenius erichweberi
- †Cratohaglopsis
- †Cratohaglopsis santanaensis
- †Cratohexagenites
- †Cratohexagenites longicercus
- †Cratohexagenites minor
- †Cratokalotermes
- †Cratokalotermes santanensis
- †Cratolindenia
- †Cratolindenia knuepfae
- †Cratolocustopsis
- †Cratolocustopsis araripensis
- †Cratolocustopsis contumax’ – type locality for species
- †Cratolocustopsis cretacea
- †Cratomacer
- †Cratomacer ephippiger
- †Cratomacer immersus
- †Cratomastotermes
- †Cratomastotermes wolfschwenningeri
- †Cratomyia
- †Cratomyia cretacica
- †Cratomyia macrorrhyncha
- †Cratonemonyx
- †Cratonemonyx martinsnetoi
- †Cratonemopteryx
- †Cratonemopteryx audax
- †Cratonemopteryx robusta
- †Cratonemopteryx speciosa
- †Cratonepa
- †Cratonepa enigmatica
- †Cratonerthra
- †Cratonerthra corinthiana
- †Cratonerthra estevezae
- †Cratoneura
- †Cratoneura dividens
- †Cratoneura longissima
- †Cratoneura pulchella
- †Cratonympha
- †Cratonympha microcelata
- †Cratopelocoris
- †Cratopelocoris carpinteroi
- †Cratopetalia
- †Cratopetalia whiteheadi
- †Cratopetalura
- †Cratopetalura petruleviciusi
- †Cratopetalura petruleviciusi
- †Cratopsychopsis
- †Cratopsychopsis maiseyi
- †Cratopteryx
- †Cratopteryx nemopteroides
- †Cratopteryx robertosantosi
- †Cratoraricrus
- †Cratoraricrus oberlii
- †Cratoscalapha
- †Cratoscalapha electroneura
- †Cratosisyrops
- †Cratosisyrops gonzagai
- †Cratosmylus
- †Cratosmylus magnificus
- †Cratosolpuga
- †Cratosolpuga wunderlichi
- †Cratostenophlebia
- †Cratostenophlebia schwickerti
- †Cratotabanus
- †Cratotabanus stonemyomorphus
- †Cratotetraspinus
- †Cratotetraspinus fossorius
- †Cratotipula
- †Cratotipula latialata
- †Cratovitisma
- †Cratovitisma oldreadi
- †Cratovoluptia
- †Cratovoluptia criptoneura
- †Cratozeunerella
- †Cratozeunerella amedegnatoi
- †Cratozeunerella godoii
- †Cratozeunerella neotropica
- †Cratozeunerella nervosa
- †Cratozeunerella soaresi
- †Cratozeunerella titanella
References
- Scherer et al., 2013, p.28
- Assine, 1992, p.291
- Fabin et al., 2018, p.2050
- Martill et al., 2007
- Leite da Silva, 2003
- Myskowiak, 2016
- Bechly et al., 2016
- Makarkin & Menon, 2007
- Aparecida et al., 2015, p.25
- Aparecida et al., 2015, p.35
- Aparecida et al., 2015, p.29
- Aparecida et al., 2015, p.36
- Aparecida et al., 2015, p.31
- Aparecida et al., 2015, p.51
- Aparecida et al., 2015, p.26
- Aparecida et al., 2015, p.33
- Aparecida et al., 2015, p.47
- Báez et al., 2009
- Salisbury et al., 2003
- Figueiredo & Kellner, 2009
- Jorge de Lima et al., 2015, p.102
- Pinheiro, 2014, p.4
Bibliography
- Aparecida dos Reis Polck, Márcia; Marise Sardenberg Salgado de Carvalho; Raphael Miguel, and Valéria Gallo. 2015. Guia de identificação de peixes fósseis das Formações Crato e Santana da Bacia do Araripe, 1–74. Serviço Geológico do Brasil (CPRM).
- Assine, Mario L. 1992. Análise estratigráfica da Bacia do Araripe, Nordeste do Brasil. Revista Brasileira de Geociências 22. 289–300. Accessed 2018-10-05.
- Báez, A.M.; G.J.B. Moura, and R.O. Gómez. 2009. Anurans from the Lower Cretaceous Crato Formation of northeastern Brazil: implications for the early divergence of neobatrachians. Cretaceous Research 30. 829–846. Accessed 2018-10-06.
- Bechly, G., and V. N. Makarkin. 2016. A new gigantic lacewing species (Insecta: Neuroptera) from the Lower Cretaceous of Brazil confirms the occurrence of Kalligrammatidae in the Americas. Cretaceous Research 58. 135–140. Accessed 2018-10-06.
- Fabin, Carlos E.; Osvaldo J. Correia Filho; Márcio L. Alencar; José A. Barbosa; Tiago S. de Miranda; Virgínio H. Neumann; Igor F. Gomes, and Felipe R. de Santana. 2018. Stratigraphic Relations of the Ipubi Formation: Siliciclastic-Evaporitic Succession of the Araripe Basin. Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências 90. 2049–2071. Accessed 2018-10-05.
- Figueiredo, R.G., and A.W.A. Kellner. 2009. A new crocodylomorph specimen from the Araripe Basin (Crato Member, Santana Formation), northeastern Brazil. Paläontologische Zeitschrift 83. 323–331. Accessed 2018-10-06.
- Jorge de Lima, Flaviana; Antonio Álamo Feitosa Saraiva, and Juliana Manso Sayão. 2012. Revisão da paleoflora das Formações Missão Velha, Crato e Romualdo, Bacia do Araripe, nordeste do Brasil. Estudos Geológicos 22. 99–115.
- Leite da Silva, Agnelo, and Virginio Enrique Neumann. 2003. Formação Crato da Bacia do Araripe: um reservatório análogo ao Calcário Trairí (Formação Paracuru), Bacia do Ceará, 1–6. 2o Congresso Brasileiro de P&D em Petróleo & Gás. Accessed 2018-10-06.
- Makarkin, V.N., and F. Menon. 2007. First record of fossil 'rapismatid-like' Ithonidae (Insecta, Neuroptera) from the Lower Cretaceous Crato Formation of Brazil. Cretaceous Research 28. 743–753. Accessed 2018-10-06.
- Martill, David M.; Günter Bechly, and Robert F. Loveridge. 2007. The Crato Fossil Beds of Brazil: Window into an Ancient World, 236. Cambridge University Press. Accessed 2018-10-06. ISBN 978-1-139-46776-6
- Pinheiro, Allysson P.; Antônio Á.F. Saraiva, and William Santana. 2014. Shrimps from the Santana Group (Cretaceous: Albian): new species (Crustacea: Decapoda: Dendrobranchiata) and new record (Crustacea: Decapoda: Caridea). Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências _. 1–8. Accessed 2018-10-06.
- Salisbury, S.W.; E. Frey; D.M. Martill, and M.C. Buchy. 2003. A new crocodilian from the Lower Cretaceous Crato Formation of north-eastern Brazil. Palaeontographica, Abteilung A 270. 3–47. Accessed 2018-10-06.
- Scherer, C.M.d.S.; E.F. Jardim de Sá; V.C. Córdoba; D.d.C. Sousa; M.M. Aquino, and F.M.C. Cardoso. 2013. Tectono-Stratigraphic evolution of the upper Jurassic-Neocomian rift succession, Araripe Basin, Northeast Brazil. Journal of South American Geosciences _. 1–43. Accessed 2018-10-05.
- Weishampel, David B. et al. 2004. Dinosaur distribution (Early Cretaceous, South America) in: Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; and Osmólska, Halszka (eds.): The Dinosauria, 563–570. Berkeley: University of California Press. ISBN 0-520-24209-2
Further reading
- Bétard, François; Jean-Pierre Peulvast; Alexsandra de Oliveira Magalhães; Maria de Lourdes Carvalho Neta, and Francisco Idalecio de Freitas. 2017. Araripe Basin: A Major Geodiversity Hotspot in Brazil. Geoheritage _. 1–18. Accessed 2018-10-06.
- Neumann, V.H.; A.G. Borrego; L. Cabrera, and R. Dino. 2003. Organic matter composition and distribution through the Aptian–Albian lacustrine sequences of the Araripe Basin, northeastern Brazil. International Journal of Coal Geology 54. 21–40. Accessed 2018-10-05.