Cortex (botany)
A cortex is an outer layer of a stem or root in a plant, lying below the epidermis but outside the vascular bundles.[1] It is also the surface layer or "skin" of the nonfruiting part of the body of some lichens.[2]
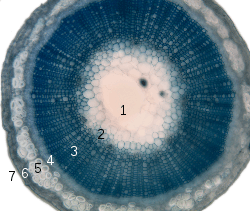
1. Pith
2. Protoxylem
3. Xylem I
4. Phloem I
5. Sclerenchyma (bast fibre)
6. Cortex
7. Epidermis
The cortex is composed mostly of large thin-walled parenchyma cells of the ground tissue system and shows little to no structural differentiation.[3] The outer cortical cells often acquire irregularly thickened cell walls, and are called collenchyma cells. Some of the outer cortical cells may contain chloroplasts.Cortex forms layer of cells that constitute cork. It is responsible for the transportation of materials into the central cylinder of the root through diffusion and may also be used for food storage in the form of starch.[4] The innermost layer of the cortex is the endodermis.[3]
On a lichen, the cortex is the "skin", or outer layer of thallus tissue that covers the undifferentiated cells of the medulla. Fruticose lichens have one cortex encircling the branches, even flattened, leaf-like forms; foliose lichens have different upper and lower cortices; crustose, placodioid and squamulose lichens have an upper cortex but no lower cortex; and leprose lichens lack any cortex.
See also
- Bast (biology)
References
- Allaby, Michael (2019). "A Dictionary of Plant Sciences". Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/acref/9780198833338.001.0001. ISBN 9780198833338. Missing or empty
|url=(help) - What is a lichen?, Australian National Botanical Garden
- Hine, Robert (18 April 2019). "A Dictionary of Biology". Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/acref/9780198821489.001.0001. ISBN 9780198821489. Missing or empty
|url=(help) - Janice Glimn-Lacy, Peter B. Kaufman (2012). Botany Illustrated: Introduction to Plants, Major Groups, Flowering Plant Families (illustrated ed.). Springer Science & Business Media. p. 13. ISBN 9789400955349.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)