Cephaeline
Cephaeline is an alkaloid that is found in Cephaelis ipecacuanha and other plant species including Psychotria acuminata.[1] Cephaeline induces vomiting by stimulating the stomach lining and is found in commercial products such as syrup of ipecac.[2] Chemically, it is closely related to emetine.
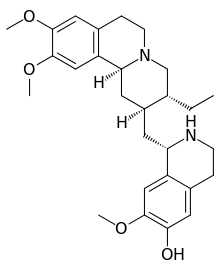 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(1R)-1-[[(2S,3R,11bS)-3-ethyl-9,10-dimethoxy-2,3,4,6,7,11b-hexahydro-1H-pyrido[2,1-a]isoquinolin-2-yl]methyl]-7-methoxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolin-6-ol | |
| Other names
Cepheline; Desmethylemetine; Dihydropsychotrine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.902 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C28H38N2O4 | |
| Molar mass | 466.622 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White silky crystals |
| Solubility in ethanol | Soluble |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Emetic / poisonous |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Poison treatment
Cephaeline in the form of syrup of ipecac was once commonly recommended as an emergency treatment for accidental poisoning, but its use has been phased out due to its ineffectiveness.[3]
References
- Lara, Alfonso; Valverde, Roberto; Gomez, Luis; Hidalgo, Nancy (July 1, 2003). "Micropropagacion de la planta medicinal psychotria acuminata". Agronomía Costarricense. Retrieved 26 December 2009.
- "Pharma Japan: Approval of 4 drugs including Seroquel recommended: CPAC panel". Chemical Business Newsbase. November 14, 2000. Retrieved 26 December 2009.
- "Policy statement: Poison treatment in the home". Pediatrics. 112 (5): 1182–1185. November 2003. doi:10.1542/peds.112.5.1182. PMID 14595067. Archived from the original on 2010-07-06. Retrieved 31 December 2009.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.