Catharism
Catharism (/ˈkæθərɪzəm/; from the Greek: καθαροί, katharoi, "the pure [ones]")[1][2] was a Christian dualist or Gnostic revival movement between the 12th and 14th centuries which thrived in Southern Europe, particularly what is now northern Italy and southern France. Followers were known as Cathars, or Good Christians, and are now mainly remembered for a prolonged period of persecution by the Catholic Church, which did not recognise their belief as being Christian. Catharism appeared in Europe in the Languedoc region of France in the 11th century, when the name first appeared. The adherents were sometimes known as Albigensians, after the city Albi in southern France where the movement first took hold.[3] The belief may have originated in the Byzantine Empire. Catharism was initially taught by ascetic leaders who set few guidelines and so some Catharist practices and beliefs varied by region and over time. The Catholic Church denounced its practices, including the consolamentum ritual by which Cathar individuals were baptised and raised to the status of "perfect".[4]
Catharism may have had its roots in the Paulician movement in Armenia and eastern Byzantine Anatolia and certainly in the Bogomils of the First Bulgarian Empire,[5] who were influenced by the Paulicians resettled in Thrace (Philipopolis) by the Byzantines. Though the term Cathar (/ˈkæθɑːr/) has been used for centuries to identify the movement, whether it identified itself with the name is debated.[6] In Cathar texts, the terms Good Men (Bons Hommes), Good Women (Bonnes Femmes), or Good Christians (Bons Chrétiens) are the common terms of self-identification.[7]
The idea of two gods or deistic principles, one good and the other evil, was central to Cathar beliefs. This was antithetical to the monotheistic Catholic Church, whose fundamental principle was that there was only one God, who created all things visible and invisible.[8] Cathars believed that the good God was the God of the New Testament, creator of the spiritual realm, whereas the evil God was the God of the Old Testament, creator of the physical world whom many Cathars identified as Satan. Cathars believed human spirits were the sexless spirits of angels trapped in the material realm of the evil god, destined to be reincarnated until they achieved salvation through the consolamentum, when they would return to the good god.[9]
From the beginning of his reign, Pope Innocent III attempted to end Catharism by sending missionaries and by persuading the local authorities to act against them. In 1208, Pierre de Castelnau, Innocent's papal legate, was murdered while returning to Rome after excommunicating Count Raymond VI of Toulouse, who, in his view, was too lenient with the Cathars.[10] Pope Innocent III then abandoned the option of sending Catholic missionaries and jurists, declared Pierre de Castelnau a martyr and launched the Albigensian Crusade in 1209. The Crusade ended in 1229 with the defeat of the Cathars. Catharism underwent persecution by the Medieval Inquisition, which succeeded in eradicating it by 1350.
Origins
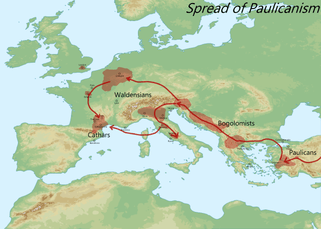
The origins of the Cathars' beliefs are unclear, but most theories agree they came from the Byzantine Empire, mostly by the trade routes and spread from the First Bulgarian Empire to the Netherlands. The name of Bulgarians (Bougres) was also applied to the Albigensians, and they maintained an association with the similar Christian movement of the Bogomils ("Friends of God") of Thrace. "That there was a substantial transmission of ritual and ideas from Bogomilism to Catharism is beyond reasonable doubt."[11] Their doctrines have numerous resemblances to those of the Bogomils and the Paulicians, who influenced them,[12] as well as the earlier Marcionites, who were found in the same areas as the Paulicians, the Manicheans and the Christian Gnostics of the first few centuries AD, although, as many scholars, most notably Mark Pegg, have pointed out, it would be erroneous to extrapolate direct, historical connections based on theoretical similarities perceived by modern scholars.
John Damascene, writing in the 8th century AD, also notes of an earlier sect called the "Cathari", in his book On Heresies, taken from the epitome provided by Epiphanius of Salamis in his Panarion. He says of them: "They absolutely reject those who marry a second time, and reject the possibility of penance [that is, forgiveness of sins after baptism]".[13] These are probably the same Cathari (actually Novations) who are mentioned in Canon 8 of the First Ecumenical Council of Nicaea in the year 325, which states "... [I]f those called Cathari come over [to the faith], let them first make profession that they are willing to communicate [share full communion] with the twice-married, and grant pardon to those who have lapsed ..."[14]

The writings of the Cathars were mostly destroyed because of the doctrine´s threat perceived by the Papacy;[15] thus, the historical record of the Cathars is derived primarily from their opponents. Cathar ideology continues to be debated, with commentators regularly accusing opposing perspectives of speculation, distortion and bias. Only a few texts of the Cathars remain, as preserved by their opponents (such as the Rituel Cathare de Lyon) which give a glimpse into the ideologies of their faith.[12] One large text has survived, The Book of Two Principles (Liber de duobus principiis),[16] which elaborates the principles of dualistic theology from the point of view of some Albanenses Cathars.[17]
It is now generally agreed by most scholars that identifiable historical Catharism did not emerge until at least 1143, when the first confirmed report of a group espousing similar beliefs is reported being active at Cologne by the cleric Eberwin of Steinfeld.[18] A landmark in the "institutional history" of the Cathars was the Council, held in 1167 at Saint-Félix-Lauragais, attended by many local figures and also by the Bogomil papa Nicetas, the Cathar bishop of (northern) France and a leader of the Cathars of Lombardy.
The Cathars were largely local, Western European/Latin Christian phenomena, springing up in the Rhineland cities (particularly Cologne) in the mid-12th century, northern France around the same time, and particularly the Languedoc—and the northern Italian cities in the mid-late 12th century. In the Languedoc and northern Italy, the Cathars attained their greatest popularity, surviving in the Languedoc, in much reduced form, up to around 1325 and in the Italian cities until the Inquisitions of the 14th century finally extirpated them.[19]
General beliefs
Theology

Cathar cosmology identified two twin, opposing deities. The first was a good God, portrayed in the New Testament and creator of the spirit, while the second was an evil God, depicted in the Old Testament and creator of matter and the physical world.[20] The latter, often called Rex Mundi ("King of the World"),[21] was identified as the God of Judaism,[20] and was also either conflated with Satan or considered Satan's father, creator or seducer.[5] They solved the problem of evil by stating that the good God's power to do good was limited by the evil God's works and vice versa.[22] All visible matter, including the human body, was created by this Rex Mundi; matter was therefore tainted with sin. Under this view, humans were actually angels seduced by Satan before a war in heaven against the army of Michael, after which they would have been forced to spend an eternity trapped in the evil God's material realm.[5] The Cathars taught that to regain angelic status one had to renounce the material self completely. Until one was prepared to do so, they would be stuck in a cycle of reincarnation, condemned to live on the corrupt Earth.[23] Zoé Oldenbourg compared the Cathars to "Western Buddhists" because she considered that their view of the doctrine of "resurrection" taught by Christ was similar to the Buddhist doctrine of rebirth.[24]
Cathars venerated Jesus Christ and followed what they considered to be His true teachings, labelling themselves as "Good Christians."[7] However, they denied His physical incarnation.[25] Authors believe that their conception of Jesus resembled docetism, believing Him the human form of an angel,[26] whose physical body was only an appearance.[27] This illusory form would have possibly been given by the Virgin Mary, another angel in human form.[22] Most did not accept the normative Trinitarian understanding of Jesus, instead resembling nontrinitarian modalistic monarchianism (Sabellianism) in the West and adoptionism in the East, which might or might not be combined with the mentioned docetism.[28] Bernard of Clairvaux's biographer and other sources accuse some Cathars of Arianism,[29][30] and some scholars see Cathar Christology as having traces of earlier Arian roots.[31][32] In any case, Cathars firmly rejected the Resurrection of Jesus, seeing it as representing reincarnation, and the Christian symbol of the cross, considering it to be not more than a material instrument of torture and evil. They also saw John the Baptist, identified also with Elijah, as an evil being sent to hinder Jesus's teaching through the false sacrament of baptism.[5]

However, those beliefs were far from unanimous. Some Cathar communities believed in a mitigated dualism similar to their Bogomil predecessors, stating that the evil god, Satan, had previously been the true God's servant before rebelling against him.[22] Others, likely a majority given the influence reflected on the Book of the Two Principles, believed in an absolute dualism, where the two gods were twin entities of the same power and importance.[22] In the same line, some communities might have believed in the existence of a spirit realm created by the good God, the "Land of the Living", whose history and geography would have served as the basis for the evil god's corrupt creation. Under this view, the history of Jesus would have happened roughly as told, only in the spirit realm.[20] The physical Jesus from the material world would have been evil, a false messiah and a lustful lover of the material Mary Magdalene. However, the true Jesus would have influenced the physical world in a way similar to the Harrowing of Hell, only by inhabiting the body of Paul.[20] Cathars also possibly believed in a Day of Judgement that would come when the number of just equated that of angels who fell, in which the believers would ascend to the spirit realm while the sinners would be thrown to everlasting fire along with Satan.[22] 13th century chronicler Pierre des Vaux-de-Cernay recorded those views.[20]
The alleged sacred texts of the Cathars, besides the New Testament, included the previously Bogomil text The Gospel of the Secret Supper (also called John's Interrogation) and the Cathar original work The Book of the Two Principles.[33] They regarded the Old Testament as written by Satan except for a few books which they accepted.[5]
Sacraments
Cathars, in general, formed an anti-sacerdotal party in opposition to the pre-Reformation Catholic Church, protesting against what they perceived to be the moral, spiritual and political corruption of the Church.[12] In contrast, the Cathars had but one central rite, the Consolamentum, or Consolation. This involved a brief spiritual ceremony to remove all sin from the believer and to induct him into the next higher level as a perfect.[34]
Many believers would receive the Consolamentum as death drew near, performing the ritual of liberation at a moment when the heavy obligations of purity required of Perfecti would be temporally short. Some of those who received the sacrament of the consolamentum upon their death-beds may thereafter have shunned further food or drink and, more often and in addition, expose themselves to extreme cold, in order to speed death. This has been termed the endura.[35] It was claimed by some of the church writers that when a Cathar, after receiving the Consolamentum, began to show signs of recovery he or she would be smothered in order to ensure his or her entry into paradise. Other than at such moments of extremis, little evidence exists to suggest this was a common Cathar practice.[36]

The Cathars also refused the sacrament of the eucharist saying that it could not possibly be the body of Christ. They also refused to partake in the practice of Baptism by water. The following two quotes are taken from the Inquisitor Bernard Gui's experiences with the Cathar practices and beliefs:
Then they attack and vituperate, in turn, all the sacraments of the Church, especially the sacrament of the eucharist, saying that it cannot contain the body of Christ, for had this been as great as the largest mountain Christians would have entirely consumed it before this. They assert that the host comes from straw, that it passes through the tails of horses, to wit, when the flour is cleaned by a sieve (of horse hair); that, moreover, it passes through the body and comes to a vile end, which, they say, could not happen if God were in it.[37] Of baptism, they assert that the water is material and corruptible and is therefore the creation of the evil power, and cannot sanctify the spirit, but that the churchmen sell this water out of avarice, just as they sell earth for the burial of the dead, and oil to the sick when they anoint them, and as they sell the confession of sins as made to the priests.[37]
Social relationships
Killing was abhorrent to the Cathars. Consequently, abstention from all animal food (sometimes exempting fish) was enjoined of the Perfecti. The Perfecti avoided eating anything considered to be a by-product of sexual reproduction.[34] War and capital punishment were also condemned—an abnormality in Medieval Europe. In a world where few could read, their rejection of oath-taking marked them as rebels against social order.
To the Cathars, reproduction was a moral evil to be avoided, as it continued the chain of reincarnation and suffering in the material world. It was claimed by their opponents that, given this loathing for procreation, they generally resorted to sodomy. Such was the situation that a charge of heresy leveled against a suspected Cathar was usually dismissed if the accused could show he was legally married.
When Bishop Fulk of Toulouse, a key leader of the anti-Cathar persecutions, excoriated the Languedoc Knights for not pursuing the heretics more diligently, he received the reply, "We cannot. We have been reared in their midst. We have relatives among them and we see them living lives of perfection."[38]
Organization
It has been alleged that the Cathar Church of the Languedoc had a relatively flat structure, distinguishing between the baptised perfecti (a term they did not use; instead, bonhommes) and ordinary unbaptised believers (credentes).[34] By about 1140, liturgy and a system of doctrine had been established.[39] They created a number of bishoprics, first at Albi around 1165 [40] and after the 1167 Council at Saint-Félix-Lauragais sites at Toulouse, Carcassonne, and Agen, so that four bishoprics were in existence by 1200.[34][39][41][42] In about 1225, during a lull in the Albigensian Crusade, the bishopric of Razès was added. Bishops were supported by their two assistants: a filius maior (typically the successor) and a filius minor, who were further assisted by deacons.[43] The perfecti were the spiritual elite, highly respected by many of the local people, leading a life of austerity and charity.[34] In the apostolic fashion they ministered to the people and travelled in pairs.[34]
Role of women and gender
Catharism has been seen as giving women the greatest opportunities for independent action since women were found as being believers as well as Perfecti, who were able to administer the sacrament of the consolamentum.[44]
Cathars believed that one would be repeatedly reincarnated until one commits to the self-denial of the material world. A man could be reincarnated as a woman and vice versa.[45] The spirit was of utmost importance to the Cathars and was described as being immaterial and sexless.[45] Because of this belief, the Cathars saw women as equally capable of being spiritual leaders.[46]
Women accused of being heretics in early medieval Christianity included those labeled Gnostics, Cathars, and, later, the Beguines, as well as several other groups that were sometimes "tortured and executed".[47] Cathars, like the Gnostics who preceded them, assigned more importance to the role of Mary Magdalene in the spread of early Christianity than the church previously did. Her vital role as a teacher contributed to the Cathar belief that women could serve as spiritual leaders. Women were found to be included in the Perfecti in significant numbers, with numerous receiving the consolamentum after being widowed.[44] Having reverence for the Gospel of John, the Cathars saw Mary Magdalene as perhaps even more important than Saint Peter, the founder of the church.[48]
Catharism attracted numerous women with the promise of a leadership role that the Catholic Church did not allow.[9] Catharism let women become a perfect.[49] These female perfects were required to adhere to a strict and ascetic lifestyle, but were still able to have their own houses.[50] Although many women found something attractive in Catharism, not all found its teachings convincing. A notable example is Hildegard of Bingen, who in 1163 gave a widely renowned sermon against the Cathars in Cologne. During this sermon, Hildegard announced a state of eternal punishment and damnation to all who accepted Cathar beliefs.[51]
While women perfects rarely traveled to preach the faith, they still played a vital role in the spreading of the Catharism by establishing group homes for women.[52] Though it was extremely uncommon, there were isolated cases of female Cathars leaving their homes to spread the faith.[53] In Cathar communal homes (ostals), women were educated in the faith, and these women would go on to bear children who would then also become believers. Through this pattern the faith grew exponentially through the efforts of women as each generation passed.[52]
Despite women having a role in the growing of the faith, Catharism was not completely equal, for example the belief that one's last incarnation had to be experienced as a man to break the cycle.[38] This belief was inspired by later French Cathars, who taught that women must be reborn as men in order to achieve salvation.[9] Another example was that the sexual allure of women impeded man's ability to reject the material world.[38] Toward the end of the Cathar movement, Catharism became less equal and started the practice of excluding women perfects.[9] However, this trend remained limited (Later Italian perfects still included women.[9])
Suppression

In 1147, Pope Eugene III sent a legate to the Cathar district in order to arrest the progress of the Cathars. The few isolated successes of Bernard of Clairvaux could not obscure the poor results of this mission, which clearly showed the power of the sect in the Languedoc at that period. The missions of Cardinal Peter of Saint Chrysogonus to Toulouse and the Toulousain in 1178, and of Henry of Marcy, cardinal-bishop of Albano, in 1180–81, obtained merely momentary successes.[12] Henry's armed expedition, which took the stronghold at Lavaur, did not extinguish the movement.
Decisions of Catholic Church councils—in particular, those of the Council of Tours (1163) and of the Third Council of the Lateran (1179)—had scarcely more effect upon the Cathars. When Pope Innocent III came to power in 1198, he was resolved to deal with them.[54]
At first Innocent tried peaceful conversion, and sent a number of legates into the Cathar regions. They had to contend not only with the Cathars, the nobles who protected them, and the people who respected them, but also with many of the bishops of the region, who resented the considerable authority the Pope had conferred upon his legates. In 1204, Innocent III suspended a number of bishops in Occitania;[55] in 1205 he appointed a new and vigorous bishop of Toulouse, the former troubadour Foulques. In 1206 Diego of Osma and his canon, the future Saint Dominic, began a programme of conversion in Languedoc; as part of this, Catholic-Cathar public debates were held at Verfeil, Servian, Pamiers, Montréal and elsewhere.
Dominic met and debated with the Cathars in 1203 during his mission to the Languedoc. He concluded that only preachers who displayed real sanctity, humility and asceticism could win over convinced Cathar believers. The institutional Church as a general rule did not possess these spiritual warrants.[56] His conviction led eventually to the establishment of the Dominican Order in 1216. The order was to live up to the terms of his famous rebuke, "Zeal must be met by zeal, humility by humility, false sanctity by real sanctity, preaching falsehood by preaching truth." However, even Dominic managed only a few converts among the Cathari.
Albigensian Crusade

In January 1208 the papal legate, Pierre de Castelnau—a Cistercian monk, theologian and canon lawyer—was sent to meet the ruler of the area, Raymond VI, Count of Toulouse.[57] Known for excommunicating noblemen who protected the Cathars, Castelnau excommunicated Raymond for abetting heresy following an allegedly fierce argument during which Raymond supposedly threatened Castelnau with violence.[58] Shortly thereafter, Castelnau was murdered as he returned to Rome, allegedly by a knight in the service of Count Raymond. His body was returned and laid to rest in the Abbey at Saint Gilles.
As soon as he heard of the murder, the Pope ordered the legates to preach a crusade against the Cathars and wrote a letter to Philip Augustus, King of France, appealing for his intervention—or an intervention led by his son, Louis. This was not the first appeal but some see the murder of the legate as a turning point in papal policy. The chronicler of the crusade which followed, Peter of Vaux de Cernay, portrays the sequence of events in such a way that, having failed in his effort to peaceably demonstrate the errors of Catharism, the Pope then called a formal crusade, appointing a series of leaders to head the assault.
The French King refused to lead the crusade himself, and could not spare his son to do so either—despite his victory against John, King of England, there were still pressing issues with Flanders and the empire and the threat of an Angevin revival. Philip did sanction the participation of some of his barons, notably Simon de Montfort and Bouchard de Marly. There followed twenty years of war against the Cathars and their allies in the Languedoc: the Albigensian Crusade.

This war pitted the nobles of France against those of the Languedoc. The widespread northern enthusiasm for the Crusade was partially inspired by a papal decree permitting the confiscation of lands owned by Cathars and their supporters. This angered not only the lords of the south but also the French King, who was at least nominally the suzerain of the lords whose lands were now open to seizure. Philip Augustus wrote to Pope Innocent in strong terms to point this out—but the Pope did not change his policy. As the Languedoc was supposedly teeming with Cathars and Cathar sympathisers, this made the region a target for northern French noblemen looking to acquire new fiefs. The barons of the north headed south to do battle.
Their first target was the lands of the Trencavel, powerful lords of Carcassonne, Béziers, Albi and the Razes. Little was done to form a regional coalition and the crusading army was able to take Carcassonne, the Trencavel capital, incarcerating Raymond Roger Trencavel in his own citadel where he died within three months; champions of the Occitan cause claimed that he was murdered. Simon de Montfort was granted the Trencavel lands by the Pope and did homage for them to the King of France, thus incurring the enmity of Peter II of Aragon who had held aloof from the conflict, even acting as a mediator at the time of the siege of Carcassonne. The remainder of the first of the two Cathar wars now focused on Simon's attempt to hold on to his gains through winters where he was faced, with only a small force of confederates operating from the main winter camp at Fanjeaux, with the desertion of local lords who had sworn fealty to him out of necessity—and attempts to enlarge his newfound domains in the summer when his forces were greatly augmented by reinforcements from France, Germany and elsewhere.
Summer campaigns saw him not only retake what he had lost in the "close" season, but also seek to widen his sphere of operation—and we see him in action in the Aveyron at St. Antonin and on the banks of the Rhône at Beaucaire. Simon's greatest triumph was the victory against superior numbers at the Battle of Muret—a battle which saw not only the defeat of Raymond of Toulouse and his Occitan allies—but also the death of Peter of Aragon—and the effective end of the ambitions of the house of Aragon/Barcelona in the Languedoc. This was in the medium and longer term of much greater significance to the royal house of France than it was to de Montfort—and with the Battle of Bouvines was to secure the position of Philip Augustus vis a vis England and the Empire. The Battle of Muret was a massive step in the creation of the unified French kingdom and the country we know today—although Edward III, Edward the Black Prince and Henry V would threaten later to shake these foundations.
Massacre

The crusader army came under the command, both spiritually and militarily, of the papal legate Arnaud-Amaury, Abbot of Cîteaux. In the first significant engagement of the war, the town of Béziers was besieged on 22 July 1209. The Catholic inhabitants of the city were granted the freedom to leave unharmed, but many refused and opted to stay and fight alongside the Cathars.
The Cathars spent much of 1209 fending off the crusaders. The Béziers army attempted a sortie but was quickly defeated, then pursued by the crusaders back through the gates and into the city. Arnaud-Amaury, the Cistercian abbot-commander, is supposed to have been asked how to tell Cathars from Catholics. His reply, recalled by Caesarius of Heisterbach, a fellow Cistercian, thirty years later was "Caedite eos. Novit enim Dominus qui sunt eius"—"Kill them all, the Lord will recognise His own".[59][60] The doors of the church of St Mary Magdalene were broken down and the refugees dragged out and slaughtered. Reportedly at least 7,000 men, women and children were killed there by Catholic forces. Elsewhere in the town, many more thousands were mutilated and killed. Prisoners were blinded, dragged behind horses, and used for target practice.[61] What remained of the city was razed by fire. Arnaud-Amaury wrote to Pope Innocent III, "Today your Holiness, twenty thousand heretics were put to the sword, regardless of rank, age, or sex."[62][63] "The permanent population of Béziers at that time was then probably no more than 5,000, but local refugees seeking shelter within the city walls could conceivably have increased the number to 20,000."
After the success of his siege of Carcassonne, which followed the Massacre at Béziers in 1209, Simon de Montfort was designated as leader of the Crusader army. Prominent opponents of the Crusaders were Raymond Roger Trencavel, viscount of Carcassonne, and his feudal overlord Peter II of Aragon, who held fiefdoms and had a number of vassals in the region. Peter died fighting against the crusade on 12 September 1213 at the Battle of Muret. Simon de Montfort was killed on 25 June 1218 after maintaining a siege of Toulouse for nine months.[64]
Treaty and persecution

The official war ended in the Treaty of Paris (1229), by which the king of France dispossessed the house of Toulouse of the greater part of its fiefs, and that of the Trencavels (Viscounts of Béziers and Carcassonne) of the whole of their fiefs. The independence of the princes of the Languedoc was at an end. But in spite of the wholesale massacre of Cathars during the war, Catharism was not yet extinguished and Catholic forces would continue to pursue Cathars.[55]
In 1215, the bishops of the Catholic Church met at the Fourth Council of the Lateran under Pope Innocent III; part of the agenda was combating the Cathar heresy.[65]
The Inquisition was established in 1233 to uproot the remaining Cathars.[66] Operating in the south at Toulouse, Albi, Carcassonne and other towns during the whole of the 13th century, and a great part of the 14th, it succeeded in crushing Catharism as a popular movement and driving its remaining adherents underground.[66] Cathars who refused to recant were hanged, or burnt at the stake.[67]
On Friday, 13 May 1239, 183 men and women convinced of Catharism were burned at the stake on the orders of Robert le Bougre. Mount Guimar was already denounced as a place of heresy by the letter of the bishop of Liège to Pope Lucius II in 1144. Augustine, bishop of Hippo Regius, had expelled from the city a Fortunatus who had fled Africa in 392; he is a Fortunatus who is reported as a monk from Africa and protected by the lord of Widomarum.[68][69][70]
From May 1243 to March 1244, the Cathar fortress of Montségur was besieged by the troops of the seneschal of Carcassonne and the archbishop of Narbonne.[71] On 16 March 1244, a large and symbolically important massacre took place, where over 200 Cathar Perfects were burnt in an enormous pyre at the prat dels cremats ("field of the burned") near the foot of the castle.[71] Moreover, the church decreed lesser chastisements against laymen suspected of sympathy with Cathars, at the 1235 Council of Narbonne.[72]

A popular though as yet unsubstantiated theory holds that a small party of Cathar Perfects escaped from the fortress before the massacre at prat dels cremats. It is widely held in the Cathar region to this day that the escapees took with them le trésor cathar. What this treasure consisted of has been a matter of considerable speculation: claims range from sacred Gnostic texts to the Cathars' accumulated wealth, which might have included the Holy Grail (see the Section on Historical Scholarship, below).
Hunted by the Inquisition and deserted by the nobles of their districts, the Cathars became more and more scattered fugitives: meeting surreptitiously in forests and mountain wilds. Later insurrections broke out under the leadership of Roger-Bernard II, Count of Foix, Aimery III of Narbonne, and Bernard Délicieux, a Franciscan friar later prosecuted for his adherence to another heretical movement, that of the Spiritual Franciscans at the beginning of the 14th century. But by this time the Inquisition had grown very powerful. Consequently, many presumed to be Cathars were summoned to appear before it. Precise indications of this are found in the registers of the Inquisitors, Bernard of Caux, Jean de St Pierre, Geoffroy d'Ablis, and others.[55] The parfaits it was said only rarely recanted, and hundreds were burnt. Repentant lay believers were punished, but their lives were spared as long as they did not relapse. Having recanted, they were obliged to sew yellow crosses onto their outdoor clothing and to live apart from other Catholics, at least for a while.
Annihilation
After several decades of harassment and re-proselytising, and, perhaps even more important, the systematic destruction of their religious texts, the sect was exhausted and could find no more adepts. The leader of a Cathar revival in the Pyrenean foothills, Peire Autier, was captured and executed in April 1310 in Toulouse.[74][75] After 1330, the records of the Inquisition contain very few proceedings against Cathars.[55] The last known Cathar perfectus in the Languedoc, Guillaume Bélibaste, was executed in the autumn of 1321.[76][75]
From the mid-12th century onwards, Italian Catharism came under increasing pressure from the Pope and the Inquisition, "spelling the beginning of the end".[77] Other movements, such as the Waldensians and the pantheistic Brethren of the Free Spirit, which suffered persecution in the same area, survived in remote areas and in small numbers into the 14th and 15th centuries. Some Waldensian ideas were absorbed into other proto-Protestant sects, such as the Hussites, Lollards, and the Moravian Church (Herrnhuters of Germany). Cathars were in no way Protestant, and very few if any Protestants consider them as their forerunners (as opposed to groups like Waldensians, Hussites, Lollards and Arnoldists).
Later history
After the suppression of Catharism, the descendants of Cathars were discriminated against and at times required to live outside towns and their defences. They retained their Cathar identity, despite their reintegration into Catholicism. As such, any use of the term "Cathar" to refer to people after the suppression of Catharism in the 14th century is a cultural or ancestral reference and has no religious implication. Nevertheless, interest in the Cathars and their history, legacy and beliefs continues.
Pays cathare

The term Pays cathare, French meaning "Cathar Country", is used to highlight the Cathar heritage and history of the region in which Catharism was traditionally strongest. The area is centred around fortresses such as Montségur and Carcassonne; also, the French département of the Aude uses the title Pays cathare in tourist brochures.[78] The areas have ruins from the wars against the Cathars that are still visible today.
Some criticise the promotion of the identity of Pays cathare as an exaggeration for tourism purposes. Many of the promoted Cathar castles were not built by Cathars but by local lords, and many of them were layer rebuilt and extended for strategic purposes. Good examples are the magnificent castles of Queribus and Peyrepertuse, which are both perched on the side of precipitous drops on the last folds of the Corbieres mountains. They were for several hundred years frontier fortresses belonging to the French crown, and most of what is still there dates from a post-Cathar era. Many consider the County of Foix to be the actual historical centre of Catharism.
Interrogation of heretics
In an effort to find the few remaining heretics in and around the village of Montaillou, Jacques Fournier, Bishop of Pamiers, future Pope Benedict XII, had those suspected of heresy interrogated in the presence of scribes who recorded their conversations. The late 13th- to early-14th-century document, discovered in the Vatican archives in the 1960s and edited by Jean Duvernoy, is the basis for Emmanuel Le Roy Ladurie's work Montaillou: The Promised Land of Error.[19]
Historical scholarship
The publication of the early scholarly book Crusade Against the Grail by the young German Otto Rahn in the 1930s rekindled interest in the connection between the Cathars and the Holy Grail, especially in Germany. Rahn was convinced that the 13th-century work Parzival by Wolfram von Eschenbach was a veiled account of the Cathars. The philosopher and Nazi government official Alfred Rosenberg speaks favourably of the Cathars in The Myth of the Twentieth Century.[79]
Academic books in English first appeared at the beginning of the millennium: for example, Malcolm Lambert's The Cathars[80] and Malcolm Barber's The Cathars.[22]
Starting in the 1990s and continuing to the present day, historians like R. I. Moore have radically challenged the extent to which Catharism, as an institutionalized religion, actually existed. Building on the work of French historians such as Monique Zerner and Uwe Brunn, Moore's The War on Heresy[81] argues that Catharism was "contrived from the resources of [the] well-stocked imaginations" of churchmen, "with occasional reinforcement from miscellaneous and independent manifestations of local anticlericalism or apostolic enthusiasm".[82] In short, Moore claims that the men and women persecuted as Cathars were not the followers of a secret religion imported from the East, instead they were part of a broader spiritual revival taking place in the later twelfth and early thirteenth century. Moore's work is indicative of a larger historiographical trend towards examination of how heresy was constructed by the church.[83]
In art and music
The principal legacy of the Cathar movement is in the poems and songs of the Cathar troubadors, though this artistic legacy is only a smaller part of the wider Occitan linguistic and artistic heritage. The Occitan song Lo Boièr is particularly associated to Catharism.[84]
Recent artistic projects concentrating on the Cathar element in Provençal and troubador art include commercial recording projects by Thomas Binkley, electric hurdy-gurdy artist Valentin Clastrier and his CD Heresie dedicated to the church at Cathars,[85] La Nef,[86] and Jordi Savall.[87]
The Cathars are depicted in Jacques Tissinier's cement sculpture Les Chevaliers Cathares, along l'autoroute des Deux Mers in Narbonne.[88]
In recent popular culture, Catharism has been linked with the Knights Templar, an active sect of monks founded during the First Crusade (1095–1099). This link has caused fringe theories about the Cathars and the possibility of their possession of the Holy Grail such as the pseudohistorical The Holy Blood and the Holy Grail.
See also
- Antonin Gadal
- Crusades
- Edmund Hamer Broadbent—The Pilgrim Church
References
Notes
- OED (1989), "Cathar".
- καθαροί. Liddell, Henry George; Scott, Robert; A Greek–English Lexicon at the Perseus Project.
- Le Roy Ladurie, Emmanuel (1990). Montaillou: Cathars and Catholics in a French Village. London: Penguin. pp. vii. ISBN 978-0-14-013700-2.
- Lambert, Malcolm (1998). The Cathars. Oxford: Blackwell. p. 21. ISBN 0-631-14343-2.
- Peters, Edward, ed. (1980). "The Cathars". Heresy and Authority in Medieval Europe. University of Pennsylvania Press. p. 108.
- Pegg (2001a), pp. 181 ff.
- Théry (2002), pp. 75–117.
- See: Nicene Creed
- Schaus (2006), p. 114.
- Sumption (1999), pp. 15–16.
- Lambert (1998), p. 31.
- Alphandéry (1911), p. 505.
- John of Damascus (2012), p. 125.
- Schaff & Wace (1994), p. 20.
- Murphy (2012), pp. 26–27.
- Dondaine (1939).
- Wakefield & Evans (1991), pp. 511–515.
- See especially R. I. Moore's The Origins of European Dissent, and the collection of essays Heresy and the Persecuting Society in the Middle Ages: Essays on the Work of R.I. Moore for a consideration of the origins of the Cathars, and proof against identifying earlier heretics in the West, such as those identified in 1025 at Monforte, outside Milan, as being Cathars. Also see Heresies of the High Middle Ages, a collection of pertinent documents on Western heresies of the High Middle Ages, edited by Walter Wakefield and Austin P. Evans.
- See Emmanuel LeRoy Ladurie's Montaillou: the Promised Land of Error for an analysis of the social context of these last Languedoc Cathars, and Power and Purity by Carol Lansing for a consideration of 13th-century Catharism in Orvieto.
- Sibly, W. A.; Sibly, M. D. (2002). The History of the Albigensian Crusade. Boydell Press. pp. 10–11. ISBN 9780851158075.
- Jeffrey J., Butz (2009). The Secret Legacy of Jesus: The Judaic Teachings That Passed from James the Just to the Founding Fathers. Simon and Schuster. ISBN 9781594779213.
- Barber (2000).
- O'Shea (2000), p. 11.
- Maseko (2008), p. 482: "In the book 'Massacre at Montsegur' (a book widely regarded by medievalists as having a pronounced, pro-Cathar bias) the Cathars are referred to as 'Western Buddhists' because of their belief that the Doctrine of 'resurrection' taught."
- Butz (2009).
- Townsend (2008), p. 9: "The Cathars did not accept the Church doctrine of Jesus being the 'Son of God'. Cathars believed that Jesus was not embodied in the human form but an angel (Docetic Christology), which echoed back to the Arian controversy."
- "Albigensians", Encyclopaedia 2, The Free dictionary
- "Cathari", Columbia Encyclopedia, Columbia University Press, 2007.
- Lambert (1998), p. 41: "Bernard's biographer identifies another group in Toulouse which he calls Arians, who have sometimes been identified as Cathars though the evidence is scant. It is most likely that the first Cathars to penetrate Languedoc appealed..."
- Luscombe & Riley-Smith (2004), p. 522: "Even though his biographer does not describe their beliefs, Arians would have been an appropriate label for moderate dualists with an unorthodox Christology, and the term was certainly later used in Languedoc to describe Cathars."
- Johnston (2011), p. 115: "However, they became converts to Arian Christianity, which later developed into Catharism. Arian and Cathar doctrines were sufficiently different from Catholic doctrine that the two branches were incompatible."
- Kienzle (2001), p. 92: "The term 'Arian' is often joined with 'Manichean' to designate Cathars. Geoffrey's comment implies that he and others called those heretics 'weavers', whereas they called themselves 'Arians'."
- The Gnostic Bible, Google Books.
- Johnston (2000), p. 252.
- Murray, Alexander (1998). Suicide in the Middle Ages. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-820539-2.
- Barber (2000), pp. 103–104.
- Burr (1996).
- O'Shea (2000), p. 42.
- Sumption (1999), pp. 49–50.
- O'Shea (2000), pp. 2–4.
- Lambert (1998), p. 70.
- Lambert (2002), p. 140.
- Moore (1995), p. 137.
- Ward (2002), pp. 241–42.
- O'Shea (2000), pp. 10–12.
- O'Shea (2000), pp. 25–26.
- Clark (2001), p. 412.
- O'Shea (2000), pp. 80–81.
- O'Shea (2000), pp. 40–43.
- Kaelber (1997), p. 120.
- Newman (1998), pp. 753–755.
- O'Shea (2000), p. 41.
- Weis (2001), p. 122.
- Alphandéry (1911), pp. 505–506.
- Alphandéry (1911), p. 506.
- Johnson (1976), p. 251.
- Sumption (1999), pp. 68–69.
- Sumption (1999), pp. 72–73.
- of Heisterbach, Caesarius (1851), Strange, J (ed.), Caesarius Heiserbacencis monachi ordinis Cisterciensis, Dialogus miraculorum, 2, Cologne: JM Heberle, pp. 296–8,
Caedite eos. Novit enim Dominus qui sunt eis
. Caesarius (c) was a Cistercian Master of Novices. - Moore (2003), p. 180.
- Johnson (1976), p. 252.
- Innocent III (1855), Vol. 216.
- Sibly & Sibly (2003), p. 128.
- Chanson de la Croisade Albigeoise laisse 205.
- Sumption (1999), pp. 179–81.
- Sumption (1999), pp. 230–232.
- Martin (2005), pp. 105–121.
- fr:Mont Aimé
- «Ce lieu est terrible, le Mont-Aimé en Champagne », père Albert Mathieu
- "Albert Mathieu". BnF. Retrieved 16 September 2019.
- Sumption (1999), pp. 238–40.
- Innocent IV (1252), Ad extirpanda (Bull).
- Weis (2001), pp. 11–12.
- O'Shea (2000), pp. 237–38.
- Sumption (1999), pp. 242–43.
- O'Shea (2000), pp. 239–46.
- O'Shea (2000), p. 230.
- "Pays Cathare".
- Rosenberg, Alfred (c. 1980). "Myth of the 20th century". p. 93. Retrieved 25 January 2017.
- Lambert (1998).
- R. I. Moore, War on Heresy. New York: Belknap Press, 2012.
- Moore, R. I. (2012). "L. J. Sackville. Heresy and Heretics in the Thirteenth Century: The Textual Representations" (PDF). H-France Review. 12 (44). Retrieved 11 June 2018.
- Biller, Peter. "review of The War on Heresy: Faith and Power in Medieval Europe, (review no. 1546)". Reviews in History. Retrieved 9 October 2015, with R. I. Moore's response.
- Jean Blum (2007). Cátaros: Su misterio y su mensaje (in Spanish). EDAF. ISBN 978-84-414113-7-1.
- L'Agonie du Languedoc: Claude Marti / Studio der frühen Musik – Thomas Binkley, dir. EMI "Reflexe" 1C 063-30 132 [LP-Stereo]1975
- La Nef. Montségur: La tragédie cathare. Dorian Recordings.DOR-90243
- Savall The Forgotten Kingdom: The Cathar Tragedy – The Albigensian Crusade AVSA9873 A+C Alia Vox 2009
- "Narbonne: les chevaliers cathares de Pech Loubat dans le top 15 des aires autoroutières 'immanquables'!". L'Indépendant (in French). Pyrénées-Orientales. 3 May 2016. Retrieved 19 February 2019.
Bibliography
- Alphandéry, Paul Daniel (1911). . In Chisholm, Hugh (ed.). Encyclopædia Britannica. 1 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 505–506.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Arnold, John H (24 August 2001), Inquisition and Power, Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press, ISBN 0-8122-3618-1. Deals with Catharism in the context of the Inquisition's evolution and analyses Inquisitorial practice as the construction of the "confessing subject".
- Barber, Malcolm (2000), The Cathars: Dualist heretics in Languedoc in the High Middle Ages, Harlow: Longman, ISBN 978-0582256620CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Berlioz, Jacques (1994), Tuez-les tous Dieu reconnaîtra les siens. Le massacre de Béziers et la croisade des Albigeois vus par Césaire de Heisterbach (in French), Loubatières. A discussion of the command "Kill them all, God will know his own." recorded by a contemporary Cistercian Chronicler.
- (in French) Biget, Jean-Louis (2007), Hérésie et inquisition dans le midi de la France, Paris: Picard (Les médiévistes français), 2007.
- (in French) Biget, Jean-Louis (2020), Eglise, dissidences et société dans l'Occitanie médiévale, with a foreword by Julien Théry, Lyon, Avignon : CIHAM Editions, 2020 (collection Mondes médiévaux), 2020.
- (in French) Brunn, Uwe (2006), Des contestataires aux "cathares" : Discours de réforme et propagande antihérétique dans les pays du Rhin et de la Meuse avant l'Inquisition, Paris, Institut d'études augustiniennes
- Burr, David (1996), Bernard Gui: Inquisitor's Manual, Internet History Sourcebooks Project, New York City: Fordham University, retrieved 25 May 2013CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Caernaii, Petrus Vallis, Historia Albigensium et Sacri Belli in Eos, Migne Patrologia Latina (in Latin), 213, 0543–0711. An history of the Albigensian war told by a contemporary.
- Chesterton, G. K. (1910), What's Wrong with the WorldCS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Clark, Elizabeth A. (2001), "Women, Gender, and the Study of Christian History", Church History, 70, Cambridge University Press, pp. 395–426, doi:10.2307/3654496, JSTOR 3654496CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Conybeare, Frederick Cornwallis (1911). . In Chisholm, Hugh (ed.). Encyclopædia Britannica. 5 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 515–517.
- Jean Duvernoy, Jean: transcriptions of inquisitorial manuscripts, many hitherto unpublished
- Dondaine, Antoine OP (1939), Un traité neo-manichéen du XIIIe siècle: Le Liber de duobus principiis, suivi d'un fragment de rituel Cathare (in French), Rome: Institutum Historicum Fratrum PraedicatorumCS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Frassatto, Michael, ed. (1996) [1975]. Heresy and the Persecuting Society in the Middle Ages: Essays on the Work of R.I. Moore. Medieval Academy of America. ISBN 978-9004150980.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Given, James (1992). Inquisition and Medieval Society: Power, Discipline, and Resistance in Languedoc. Cornell University Press. ISBN 978-0801487590.
- Godlike Productions (2010), Web Forum: Before the Catholics, The Cathars taught of Jesus, Power of Love, Godlike Productions, Zero Point Ltd.
- Gui, Bernard; Shirley, Janet (2006), The Inquisitor's Guide: A Medieval Manual on Heretics, Welwyn Garden City: Ravenhall Books, ISBN 978-1905043095CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Henry, William (2002), Secrets of The Cathars: Why the Dark Age Church Was Out to Destroy Them, Biblioteca Pleyades and Atlantis Rising
- Innocent III (1855), Volume 216, Patrologia Cursus Completus, Paris: Jacques Paul Migne.
- John of Damascus (2012) [1958], Writings: The Fount of Knowledge: The Philosophical Chapters, On Heresies, The Orthodox Faith, The Fathers of the Church, Translator: Frederic H Chase (Reprint ed.), CreateSpace, ISBN 978-1470149246CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Johnson, Paul (1976), A History of Christianity, Atheneum, ISBN 0-689-70591-3
- Johnston, Ruth A (2011), All Things Medieval: An Encyclopedia of the Medieval World, Greenwood Press, p. 115, ISBN 978-0313364624CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Johnston, William M (2000). Encyclopedia of Monasticism. Fitzroy Dearborn Publishers. ISBN 1-57958-090-4.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Kaelber, Lutz (1997). "Weavers into Heretics? The Social Organization of Early-Thirteenth-Century Catharism in Comparative Perspective". Social Science History. 21 (1): 111–137. doi:10.1017/S0145553200017661.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Kienzle, Beverly Mayne (2001), Cistercians, heresy, and Crusade in Occitania, 1145–1229, York Medieval Press, ISBN 978-1903153000CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Lambert, Malcolm (1998). The Cathars. Oxford, UK: Blackwell. ISBN 978-0631143437.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Lambert, Malcolm (2002). Medieval Heresy: Popular Movements from the Gregorian Reform to the Reformation. Oxford: Blackwell. ISBN 978-0631222767.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Lansing, Carol (1998). Power and Purity: Cathar Heresy in Medieval Italy. Oxford University Press (USA). ISBN 978-0195149807.
- Le Roy Ladurie, Emmanuel (1979). Montaillou: The Promised Land of Error, Barbara Bray translator. Vintage Books. ISBN 978-0807615980.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Luscombe, David; Riley-Smith, Jonathan (2004), The new Cambridge medieval history: c. 1024 – c. 1198, p. 522CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Madaule, Jacques (1967). The Albigensian Crusade: An Historical Essay. New York: Fordham UP.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Magee, M D (12 December 2002), Heresy and the Inquisition II Persecution of Heretics.
- Mann, Judith (2002), The Trail of Gnosis, Gnosis Traditions Press
- Markale, Jean (2003), Montségur and the Mystery of the Cathars, Inner Traditions, ISBN 978-0892810901, archived from the original on 4 December 2003
- Martin, Sean (2005), The Cathars: The Most Successful Heresy of the Middle Ages, Pocket Essentials, ISBN 1-904048-33-1, archived from the original on 22 February 2014, retrieved 29 May 2006CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Maris, Yves (2006), Cathars – Memories of an initiate, AdA.
- Maseko, Achim N. (2008), Church Schism & Corruption, South Africa: Lulu.com, p. 482, ISBN 9781409221869CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Mathieu, Albert, "Ce lieu est terrible, le Mont-Aimé en Champagne" Vendredi 13 mai 1239 Réf : Bibliothèque Nationale de France
- Moore, John Clare (2003), Pope Innocent III (1160/61–1216): To Root Up and to Plant, Brill, p. 180, ISBN 90-04-12925-1CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Moore, R. I. (1985). The Origins of European Dissent. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell. ISBN 978-0631144045.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Moore, R. I. (1995). The Birth of Heresy. Medieval Academy of America. ISBN 0-8020-7659-9.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Moore, R. I. (2006) [1992]. The Formation of a Persecuting Society. Oxford: Blackwell. ISBN 978-1405129640.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Moore, R. I. (2012). The War on Heresy. London: Profile Books. ISBN 9781846682001.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Moreland, Miles (1992), Miles Away: A Walk Across France, New York: Random House, ISBN 0-679-42527-6
- Murphy, Cullen (2012), God's Jury: The Inquisition and the Making of the Modern World, Houhton Mifflin Harcourt, ISBN 978-0-618-09156-0CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Newman, Barbara (1998). "Possessed by the Spirit: Devout Women, Demoniacs, and the Apostolic Life in the Thirteenth Century". Speculum. 73 (3): 733–770. doi:10.2307/2887496. JSTOR 2887496.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- O'Shea, Stephen (2000). The Perfect Heresy: The Revolutionary Life and Death of the Medieval Cathars. New York: Walker & Company. ISBN 978-1861972705.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Pegg, Mark (2001a), "On Cathars, Albigenses, and good men of Languedoc", Journal of Medieval History, 27 (2): 181–190, doi:10.1016/s0304-4181(01)00008-2CS1 maint: ref=harv (link).
- Pegg, Mark (2001b), The Corruption of Angels: The Great Inquisition of 1245–1245, Princeton University Press, ISBN 978-0691006567CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Pegg, Mark (2006), "Heresy, good men, and nomenclature", in Frassetto, Michael (ed.), Heresy and the Persecuting Society in the Middle Ages, Studies in the History of Christian Traditions, Leiden: Brill, pp. 227–39.
- Pegg, Mark (2008). A Most Holy War: The Albigensian Crusade and the Battle for Christendom. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780195171310.
- Pegg, Mark (2015). "Innocent III, les 'pestilentiels Provençaux' et le paradigme épuisé du catharisme/Innocent III, 'Pestilential Provençals' and the Obsolete Paradigm of Catharism" (Privat (English and French abstracts)). Innocent III et le Midi. Cahiers de Fanjeaux, 50. Toulouse: Presses Universitaires de Rennes. pp. 277–207. ISBN 9782708934542.
- Peters, Edward, ed. (1980), Heresy and Authority in Medieval Europe, University of Pennsylvania Press. A collection of primary sources, some on Catharism.
- Riparelli, Enrico (2008), Il volto del Cristo dualista. Da Marcione ai catari (in Italian), Bern: Peter Lang, ISBN 978-303911490-0
- Roach, Andrew P (2005), The Devil's World: Heresy and Society 1100–1320, Harlow: Pearson Longman
- Schaff, Philip; Wace, Henry, eds. (1994) [1900], Nicene and Post-Nicene Fathers, Second Series, Volume 14: I Nice AD 325 (Canons of the Council of Nicaea), Trans. Henry R. Percival (Reprint ed.), Hendrickson, ISBN 978-1565631168CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Schaus, Margaret (2006), Women And Gender in Medieval Europe: An Encyclopedia, New York: Taylor and Francis Group, ISBN 978-0415969444CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Sennis, Antonio, Cathars in Question, York: York Medieval Press, 2016
- Sibly, W A; Sibly, M D (2003), The Chronicle of William of Puylaurens: The Albigensian Crusade and Its Aftermath, Boydell Press, p. 128, ISBN 978-0851159256CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Simpson, John, ed. (1989), Oxford English Dictionary (Second ed.), Oxford: Oxford University Press
- Stork, Nancy P., The Inquisition Record of Jacques Fournier, Bishop of Pamiers 1318–1325, California: San Jose State University
- Sumption, Jonathan (1999) [1978]. The Albigensian Crusade (New ed.). London: Faber and Faber. ISBN 978-0571200023.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Théry, Julien (2002), L'Hérésie des bons hommes (XIIe-début du XIVe s.). Comment nommer la dissidence religieuse non-vaudoise ni béguine en Languedoc?, Heresis (in French), 36–37, pp. 75–117CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Théry, Julien (2010), "Les Hérésies, du XIIe au début du XIVe s.", in de Cevins, Marie-Madeleine; Matz, Jean-Michel (eds.), Structures et dynamiques de la vie religieuse en Occident (1179–1449) (in French), Rennes: Presses Universitaires de Rennes, pp. 373–386CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Townsend, Anne Bradford (2008), The Cathars of Languedoc as heretics: From the perspectives of Five Contemporary Scholars (Dissertation ed.), Union Institute and University, p. 9, ISBN 978-1243491602CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Wakefield, Walter Leggett; Evans, Austin P (1991). Heresies of the High Middle Ages. Columbia University Press. ISBN 978-0231096324.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Walther, Daniel (1965), "A Survey of Recent Research on the Albigensian Cathari", Church History, 34, Cambridge University Press, pp. 146–177, doi:10.2307/3162901, JSTOR 3162901CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Ward, Jennifer (2002). Women in Medieval Europe, 1200–1500. London: Longman. ISBN 978-0582288270.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Weber, Nicholas (1908a), "Albigenses", Catholic Encyclopedia, New AdventCS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Weber, Nicholas (1908b), "Cathari", Catholic Encyclopedia, New AdventCS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Weis, René (2001). The Yellow Cross: The Story of the Last Cathars 1290–1329. New York: Random House.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Zerner, Monique (1998), Inventer l'hérésie ? Discours polémiques et pouvoirs avant l'Inquisition, Nice: Centre d'études médiévales
- Zerner, Monique (2001), L'histoire du catharisme en discussion : le "concile" de Saint-Félix (1167), Nice : Centre d'études médiévales
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Cathars. |
- Ce lieu est terrible [Texte imprimé] : le Mont-Aimé en Champagne [Forgotten Story of France: Northern Cathar in Champagne]
- Cathar texts, The Gnostic Society Library, including the Lyon Ritual.
- Cathars Today: Official website of the Cathar Temple
- Catharism on In Our Time at the BBC
- "Catharism and the Cathars of the Languedoc", Castles & Manor Houses, archived from the original on 7 June 2011: History, origins, theology and extirpation.
- Cathar castles, catharcastles.info: details, histories, photographs, plans and maps of 30 Cathar castles.
- Cathar castles (interactive map), Aude‐Aude.
- Perrottet, Tony (9 May 2010), "The Besieged and the Beautiful in Languedoc", The New York Times
- Des hérétiques dans les Pyrénées catalanes à la fin du XIe siècle? [Heretics in the Catalan Pyrenees at the end of the 11th century?] (article), Paratge, 2013.
- Pegg, Mark Gregory (2008), A Most Holy War: The Albigensian Crusade and the Battle for Christendom (book), Oxford, ISBN 9780199721511 – via Google Books.
- Cathars, cathar.info: Cathar history & theology
- Mark, Joshua J. (2 April 2019), "Cathars", Ancient History Encyclopedia
