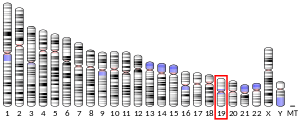
CLC (gene)
Eosinophil lysophospholipase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CLC gene.[3][4]
Lysophospholipases are enzymes that act on biological membranes to regulate the multifunctional lysophospholipids. The protein encoded by this gene is a lysophospholipase expressed in eosinophils and basophils. It hydrolyzes lysophosphatidylcholine to glycerophosphocholine and a free fatty acid. This protein may possess carbohydrate or IgE-binding activities. It is both structurally and functionally related to the galectin family of beta-galactoside binding proteins. It may be associated with inflammation and some myeloid leukemias.[4]
See also
- Charcot-Leyden crystals
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000105205 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Mastrianni DM, Eddy RL, Rosenberg HF, Corrette SE, Shows TB, Tenen DG, Ackerman SJ (Jun 1992). "Localization of the human eosinophil Charcot-Leyden crystal protein (lysophospholipase) gene (CLC) to chromosome 19 and the human ribonuclease 2 (eosinophil-derived neurotoxin) and ribonuclease 3 (eosinophil cationic protein) genes (RNS2 and RNS3) to chromosome 14". Genomics. 13 (1): 240–2. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(92)90237-M. PMID 1577491.
- "Entrez Gene: CLC Charcot-Leyden crystal protein".
External links
- Human CLC genome location and CLC gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
Further reading
- Gleich GJ, Loegering DA, Mann KG, Maldonado JE (1976). "Comparative properties of the Charcot-Leyden crystal protein and the major basic protein from human eosinophils". J. Clin. Invest. 57 (3): 633–40. doi:10.1172/JCI108319. PMC 436696. PMID 942977.
- Golightly LM, Thomas LL, Dvorak AM, Ackerman SJ (1992). "Charcot-Leyden crystal protein in the degranulation and recovery of activated basophils". J. Leukoc. Biol. 51 (4): 386–92. doi:10.1002/jlb.51.4.386. PMID 1373430.
- Dvorak AM, Weller PF, Monahan-Earley RA, et al. (1990). "Ultrastructural localization of Charcot-Leyden crystal protein (lysophospholipase) and peroxidase in macrophages, eosinophils, and extracellular matrix of the skin in the hypereosinophilic syndrome". Lab. Invest. 62 (5): 590–607. PMID 2160562.
- Dvorak AM, Letourneau L, Weller PF, Ackerman SJ (1990). "Ultrastructural localization of Charcot-Leyden crystal protein (lysophospholipase) to intracytoplasmic crystals in tumor cells of primary solid and papillary epithelial neoplasm of the pancreas". Lab. Invest. 62 (5): 608–15. PMID 2160563.
- Dvorak AM, Ackerman SJ (1989). "Ultrastructural localization of the Charcot-Leyden crystal protein (lysophospholipase) to granules and intragranular crystals in mature human basophils". Lab. Invest. 60 (4): 557–67. doi:10.1111/1523-1747.ep12703656. PMID 2709814.
- Sieker LC, Turley S, Le Trong I, et al. (1989). "Crystallographic characterization of human eosinophil Charcot-Leyden crystals". J. Mol. Biol. 204 (2): 489–91. doi:10.1016/0022-2836(88)90590-6. PMID 3221396.
- Weller PF, Bach D, Austen KF (1982). "Human eosinophil lysophospholipase: the sole protein component of Charcot-Leyden crystals". J. Immunol. 128 (3): 1346–9. PMID 6173432.
- Weller PF, Bach DS, Austen KF (1985). "Biochemical characterization of human eosinophil Charcot-Leyden crystal protein (lysophospholipase)". J. Biol. Chem. 259 (24): 15100–5. PMID 6511787.
- Gomolin HI, Yamaguchi Y, Paulpillai AV, et al. (1993). "Human eosinophil Charcot-Leyden crystal protein: cloning and characterization of a lysophospholipase gene promoter". Blood. 82 (6): 1868–74. doi:10.1182/blood.V82.6.1868.1868. PMID 8400237.
- Ackerman SJ, Corrette SE, Rosenberg HF, et al. (1993). "Molecular cloning and characterization of human eosinophil Charcot-Leyden crystal protein (lysophospholipase). Similarities to IgE binding proteins and the S-type animal lectin superfamily". J. Immunol. 150 (2): 456–68. PMID 8419478.
- Leonidas DD, Elbert BL, Zhou Z, et al. (1996). "Crystal structure of human Charcot-Leyden crystal protein, an eosinophil lysophospholipase, identifies it as a new member of the carbohydrate-binding family of galectins". Structure. 3 (12): 1379–93. doi:10.1016/S0969-2126(01)00275-1. PMID 8747464.
- Dyer KD, Handen JS, Rosenberg HF (1997). "The genomic structure of the human Charcot-Leyden crystal protein gene is analogous to those of the galectin genes". Genomics. 40 (2): 217–21. doi:10.1006/geno.1996.4590. PMID 9119387.
- Swaminathan GJ, Leonidas DD, Savage MP, et al. (1999). "Selective recognition of mannose by the human eosinophil Charcot-Leyden crystal protein (galectin-10): a crystallographic study at 1.8 A resolution". Biochemistry. 38 (42): 13837–43. doi:10.1021/bi990756e. PMID 10529229.
- Larramendy ML, Niini T, Elonen E, et al. (2003). "Overexpression of translocation-associated fusion genes of FGFRI, MYC, NPMI, and DEK, but absence of the translocations in acute myeloid leukemia. A microarray analysis". Haematologica. 87 (6): 569–77. PMID 12031912.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Abedin MJ, Kashio Y, Seki M, et al. (2003). "Potential roles of galectins in myeloid differentiation into three different lineages". J. Leukoc. Biol. 73 (5): 650–6. doi:10.1189/jlb.0402163. PMID 12714580.
- Grimwood J, Gordon LA, Olsen A, et al. (2004). "The DNA sequence and biology of human chromosome 19". Nature. 428 (6982): 529–35. doi:10.1038/nature02399. PMID 15057824.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The Status, Quality, and Expansion of the NIH Full-Length cDNA Project: The Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Nielsen K, Heegaard S, Vorum H, et al. (2005). "Altered expression of CLC, DSG3, EMP3, S100A2, and SLPI in corneal epithelium from keratoconus patients". Cornea. 24 (6): 661–8. doi:10.1097/01.ico.0000153556.59407.69. PMID 16015083.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.