CENTD1
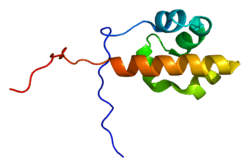
Arf-GAP with Rho-GAP domain, ANK repeat and PH domain-containing protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ARAP2 gene.[5]
Function
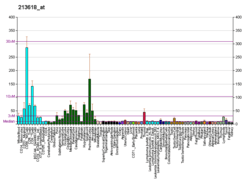
The protein encoded by this gene contains ARF-GAP, RHO-GAP, ankyrin repeat, RAS-associating, and pleckstrin homology domains. This protein lacks the predicted catalytic arginine in the RHO-GAP domain and is therefore unlikely to have RHO-GAP activity. While the encoded protein does contain a sterile alpha motif (SAM) commonly found in some signaling molecules, the function of the protein has not been determined. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.[5]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000047365 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000037999 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Entrez Gene: CENTD1 centaurin, delta 1".
External links
- Human ARAP2 genome location and ARAP2 gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
Further reading
- Olsen JV, Blagoev B, Gnad F, Macek B, Kumar C, Mortensen P, Mann M (November 2006). "Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks". Cell. 127 (3): 635–48. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.026. PMID 17081983.
- Yoon HY, Miura K, Cuthbert EJ, Davis KK, Ahvazi B, Casanova JE, Randazzo PA (November 2006). "ARAP2 effects on the actin cytoskeleton are dependent on Arf6-specific GTPase-activating-protein activity and binding to RhoA-GTP". Journal of Cell Science. 119 (Pt 22): 4650–66. doi:10.1242/jcs.03237. PMID 17077126.
- Miura K, Jacques KM, Stauffer S, Kubosaki A, Zhu K, Hirsch DS, Resau J, Zheng Y, Randazzo PA (January 2002). "ARAP1: a point of convergence for Arf and Rho signaling". Molecular Cell. 9 (1): 109–19. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(02)00428-8. PMID 11804590.
- Krugmann S, Anderson KE, Ridley SH, Risso N, McGregor A, Coadwell J, Davidson K, Eguinoa A, Ellson CD, Lipp P, Manifava M, Ktistakis N, Painter G, Thuring JW, Cooper MA, Lim ZY, Holmes AB, Dove SK, Michell RH, Grewal A, Nazarian A, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Stephens LR, Hawkins PT (January 2002). "Identification of ARAP3, a novel PI3K effector regulating both Arf and Rho GTPases, by selective capture on phosphoinositide affinity matrices". Molecular Cell. 9 (1): 95–108. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(02)00434-3. PMID 11804589.
- "Toward a complete human genome sequence". Genome Research. 8 (11): 1097–108. November 1998. doi:10.1101/gr.8.11.1097. PMID 9847074.
- Nagase T, Ishikawa K, Miyajima N, Tanaka A, Kotani H, Nomura N, Ohara O (February 1998). "Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. IX. The complete sequences of 100 new cDNA clones from brain which can code for large proteins in vitro". DNA Research. 5 (1): 31–9. doi:10.1093/dnares/5.1.31. PMID 9628581.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.