CDK5R2
Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activator 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CDK5R2 gene.[5][6]
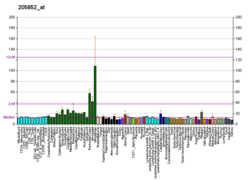
The protein encoded by this gene is a neuron-specific activator of CDK5 kinase. It associates with CDK5 to form an active kinase. This protein and neuron-specific CDK5 activator CDK5R1/p39NCK5A both share limited similarity to cyclins, and thus may define a distinct family of cyclin-dependent kinase activating proteins.[6]
Interactions
CDK5R2 has been shown to interact with Actinin, alpha 1.[7]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000171450 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000090071 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Tang D, Yeung J, Lee KY, Matsushita M, Matsui H, Tomizawa K, Hatase O, Wang JH (November 1995). "An isoform of the neuronal cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (Cdk5) activator". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 270 (45): 26897–903. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.45.26897. PMID 7592934.
- "Entrez Gene: CDK5R2 cyclin-dependent kinase 5, regulatory subunit 2 (p39)".
- Dhavan R, Greer PL, Morabito MA, Orlando LR, Tsai LH (September 2002). "The cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activators p35 and p39 interact with the alpha-subunit of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II and alpha-actinin-1 in a calcium-dependent manner". The Journal of Neuroscience. 22 (18): 7879–91. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-18-07879.2002. PMID 12223541.
External links
- Human CDK5R2 genome location and CDK5R2 gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
Further reading
- Humbert S, Dhavan R, Tsai L (March 2000). "p39 activates cdk5 in neurons, and is associated with the actin cytoskeleton". Journal of Cell Science. 113 ( Pt 6) (6): 975–83. PMID 10683146.
- Humbert S, Lanier LM, Tsai LH (July 2000). "Synaptic localization of p39, a neuronal activator of cdk5". NeuroReport. 11 (10): 2213–6. doi:10.1097/00001756-200007140-00030. PMID 10923673.
- Muravenko OV, Gizatullin RZ, Protopopov AI, Kashuba VI, Zabarovsky ER, Zelenin AV (2000). "Assignment of CDK5R2 coding for the cyclin-dependent kinase 5, regulatory subunit 2 (NCK5AI protein) to human chromosome band 2q35 by fluorescent in situ hybridization". Cytogenetics and Cell Genetics. 89 (3–4): 160–1. doi:10.1159/000015602. PMID 10965112.
- Agarwal-Mawal A, Paudel HK (June 2001). "Neuronal Cdc2-like protein kinase (Cdk5/p25) is associated with protein phosphatase 1 and phosphorylates inhibitor-2". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 276 (26): 23712–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M010002200. PMID 11320080.
- Patzke H, Tsai LH (March 2002). "Calpain-mediated cleavage of the cyclin-dependent kinase-5 activator p39 to p29". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 277 (10): 8054–60. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109645200. PMID 11784720.
- Dhavan R, Greer PL, Morabito MA, Orlando LR, Tsai LH (September 2002). "The cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activators p35 and p39 interact with the alpha-subunit of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II and alpha-actinin-1 in a calcium-dependent manner". The Journal of Neuroscience. 22 (18): 7879–91. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-18-07879.2002. PMID 12223541.
- Sakashita G, Shima H, Komatsu M, Urano T, Kikuchi A, Kikuchi K (February 2003). "Regulation of type 1 protein phosphatase/inhibitor-2 complex by glycogen synthase kinase-3beta in intact cells". Journal of Biochemistry. 133 (2): 165–71. doi:10.1093/jb/mvg020. PMID 12761178.
- Rademakers R, Sleegers K, Theuns J, Van den Broeck M, Bel Kacem S, Nilsson LG, Adolfsson R, van Duijn CM, Van Broeckhoven C, Cruts M (2005). "Association of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 and neuronal activators p35 and p39 complex in early-onset Alzheimer's disease". Neurobiology of Aging. 26 (8): 1145–51. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2004.10.003. PMID 15917097.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.