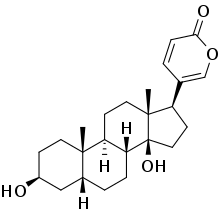
Bufalin
Bufalin, is a cardiotonic steroid originally isolated from the Chinese toad venom. It is a component found in many Chinese traditional medicine.[1][2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(3β,5β)-3,14-Dihydroxybufa-20,22-dienolide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.150.073 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C24H34O4 | |
| Molar mass | 386.532 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  |
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
GHS hazard statements |
H300 |
| P264, P270, P301+310, P321, P330, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Usage
Bufalin has a in vitro antitumor effects against various malignancies, including hepatocellular[3] and lung carcinoma.[4] However, as with other bufadienolides, its use is hampered by its cardiotoxicity.[5]
References
- "Datasheet: Bufotalin sc-sc-200136" Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc.https://datasheets.scbt.com/sc-200136.pdf
- Okada, Masahiro; Suga, Toshiro; et al. (April 1960). "Pharmacology of the priniciples isolated from Senso (Ch'an Su) the dried venom of the Chinese toad (IV)" (PDF). Asian Medical Journal. 3 (4): 155–160. Retrieved April 27, 2017.
- Zhang ZJ (Feb 2014). "Bufalin attenuates the stage and metastatic potential of hepatocellular carcinoma in nude mice". J Transl Med. 12: 57. doi:10.1186/1479-5876-12-57. PMC 4015709. PMID 24581171.
- Wu SH (2014). "Bufalin induces cell death in human lung cancer cells through disruption of DNA damage response pathways". Am J Chin Med. 42 (3): 729–42. doi:10.1142/S0192415X14500475. PMID 24871662.
- Ma H (Jul 2012). "The novel antidote Bezoar Bovis prevents the cardiotoxicity of Toad (Bufo bufo gargarizans Canto) Venom in mice". Exp Toxicol Pathol. 64 (5): 417–23. doi:10.1016/j.etp.2010.10.007. PMID 21084181.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.