Brisbane
Brisbane (/ˈbrɪzbən/ (![]()
| Brisbane Queensland | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
      Skyline from Kangaroo Point CityCat ferry passing under the Story Bridge; Brisbane City Hall South Bank Parklands; Queenslander architecture Panorama of the Queensland Cultural Centre | |||||||||
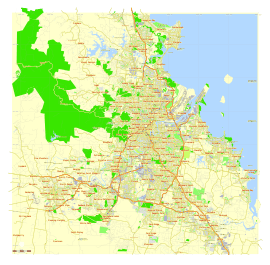 Map of the Brisbane metropolitan area | |||||||||
 Brisbane | |||||||||
| Coordinates | 27°28′04″S 153°01′41″E | ||||||||
| Population | 2,514,184 (2019)[1] (3rd) | ||||||||
| • Density | 155/km2 (400/sq mi) | ||||||||
| Established | 13 May 1825 | ||||||||
| Area | 15,842 km2 (6,116.6 sq mi)[2][3] (2016 GCCSA) | ||||||||
| Time zone | AEST (UTC+10:00) | ||||||||
| Location | |||||||||
| LGA(s) | |||||||||
| Region | South East Queensland | ||||||||
| County | Stanley, Canning, Cavendish, Churchill, Ward | ||||||||
| State electorate(s) | 41 divisions | ||||||||
| Federal Division(s) | 17 divisions | ||||||||
| |||||||||
One of the oldest cities in Australia, Brisbane was founded upon the ancient homelands of the Aboriginal Turrbal and Jagera nations. Named after the Brisbane River on which it is located—which in turn takes its name from Sir Thomas Brisbane, the Governor of New South Wales at the time of the city's founding[10]—the area was chosen as a place for secondary offenders from the Sydney Colony. The Moreton Bay penal settlement was founded in 1824 at Redcliffe, 28 kilometres (17 mi) north of the central business district, but was soon abandoned and moved to North Quay in 1825, opening to free settlement in 1842. Brisbane was chosen as the capital when Queensland was proclaimed a separate colony from New South Wales in 1859. During World War II, Brisbane played a central role in the Allied campaign and served as the South West Pacific headquarters for United States Army General Douglas MacArthur.[17]
A diverse city with 32.2% of its metropolitan population being foreign born,[18] Brisbane is classified as a global city,[19][20] and ranks highly in ratings of liveable cities.[21][22][23] Brisbane is well known for its distinct Queenslander architecture which forms much of the city's built heritage. The city is noted for its cuisine brunches, outdoor dining, and rooftop bar scene. Brisbane was also the origin of the Anzac Day tradition through the works of Canon David John Garland. A transportation hub, Brisbane is served by a large suburban rail network, popular bus and ferry networks as well as Australia's third-busiest airport and seaport.
Brisbane is a popular tourist destination, serving as a gateway to the state of Queensland, particularly to the Gold Coast and the Sunshine Coast, which are home to numerous popular surf beaches, located immediately south and north of Brisbane respectively. Major landmarks and attractions include South Bank Parklands, the Queensland Cultural Centre (including the Queensland Museum, Queensland Art Gallery, Gallery of Modern Art, Queensland Performing Arts Centre and State Library of Queensland), City Hall, the Story Bridge, the Howard Smith Wharves, ANZAC Square, St John's Cathedral, Fortitude Valley (including James Street and Chinatown), West End, the Teneriffe woolstores precinct, the Brisbane River and its Riverwalk network, the City Botanic Gardens, Roma Street Parkland, New Farm Park (including the Brisbane Powerhouse), the Kangaroo Point Cliffs and park, the Lone Pine Koala Sanctuary, the Mount Coot-tha Reserve (including Mount Coot-tha Lookout and Mount Coot-tha Botanic Gardens), the D'Aguilar Range and National Park, as well as Moreton Bay (including Moreton, North Stradbroke and Bribie islands, and coastal suburbs such as Shorncliffe, Wynnum and those on the Redcliffe Peninsula).
History
Pre-19th century
Indigenous Australians are believed to have lived in coastal South East Queensland for 22,000 years, with an estimated population between 6,000 and 10,000 individuals before white settlement.[24][25] At this time, the Brisbane area was inhabited by the Jagera people, including the Turrbal group,[26] who knew the area that is now the central business district as Mian-jin, meaning "place shaped as a spike".[27] Archaeological evidence suggests frequent habitation around the Brisbane River, and notably at the site now known as Musgrave Park.[28]
Jagara (also known as Jagera, Yagara, and Yuggera) and Yugarabul (also known as Ugarapul and Yuggerabul) are Australian Aboriginal languages of South-East Queensland. There is some uncertainty over the status of Jagara as a language, dialect or perhaps a group or clan within the local government boundaries of Ipswich City Council, Lockyer Regional Council and the Somerset Regional Council.[29][30] The languages of Greater Brisbane are related – there is uncertainty over which dialects belong to which language. The Yugarabul language region includes the landscape within the local government boundaries of Brisbane City Council, Ipswich City Council and the Scenic Rim Regional Council.[31]
19th century


The Moreton Bay area was initially explored on behalf of European colonisers by Matthew Flinders. On 17 July 1799, Flinders landed at what is now known as Woody Point, which he named "Red Cliff Point" after the red-coloured cliffs visible from the bay.[32] In 1823 Governor of New South Wales Sir Thomas Brisbane instructed that a new northern penal settlement be developed, and an exploration party led by John Oxley further explored Moreton Bay.[33]
Oxley claimed, named, and explored the Brisbane River as far as Goodna, 20 km (12 mi) upstream from the Brisbane central business district.[33] Oxley recommended Red Cliff Point for the new colony, reporting that ships could land at any tide and easily get close to the shore.[34] The party settled in Redcliffe on 13 September 1824, under the command of Lieutenant Henry Miller with 14 soldiers (some with wives and children) and 29 convicts. However, this settlement was abandoned after a year and the colony was moved to a site on the Brisbane River now known as North Quay, 28 km (17 mi) south, which offered a more reliable water supply. The newly selected Brisbane region, at the time, was plagued by mosquitos.[35]
After visiting the Redcliffe settlement, Sir Thomas Brisbane then travelled 45 km (28 mi) up the Brisbane River in December 1824. Governor Brisbane stayed overnight in a tent and often landed ashore, bestowing upon Brisbane City the distinction of being the only Australian capital city set foot upon by its namesake.[36] Chief Justice Forbes gave the new settlement the name of Edenglassie before it was named Brisbane.[37]
Non-convict European settlement of the Brisbane region commenced in 1838 and the population grew strongly thereafter, with free settlers soon far outstripping the convict population.[38] German missionaries settled at Zions Hill, Nundah as early as 1837, five years before Brisbane was officially declared a free settlement. The band consisted of ministers Christopher Eipper (1813–1894) and Carl Wilhelm Schmidt and lay missionaries Haussmann, Johann Gottried Wagner, Niquet, Hartenstein, Zillman, Franz, Rode, Doege and Schneider.[39] They were allocated 260 hectares and set about establishing the mission, which became known as the German Station.[40] Later in the 1860s many German immigrants from the Uckermark region in Prussia as well as other German regions settled in the Bethania- Beenleigh and Darling Downs areas. These immigrants were selected and assisted through immigration programs established by John Dunmore Lang and Johann Christian Heussler and were offered free passage, good wages, and selections of land.[41][42]
The penal settlement under the control of Captain Patrick Logan flourished with the numbers of convicts increasing dramatically from around 200 to over 1,000 men.[43] He created a substantial settlement of brick and stone buildings, complete with school and hospital. He formed additional outstations and made several important journeys of exploration. Logan is infamous for his extreme use of the cat o' nine tails on convicts. The maximum allowed limit of lashes was 50; however, Logan regularly applied sentences of 150 lashes.[43]
Free settlers entered the area over the following five years, and by the end of 1840, Robert Dixon began work on the first plan of Brisbane Town, in anticipation of future development.[44] Queensland was separated from New South Wales by letters patent dated 6 June 1859, proclaimed by Sir George Ferguson Bowen on 10 December 1859, whereupon he became Queensland's first governor,[45] with Brisbane chosen as its capital.
In 1893, Brisbane was affected by the Black February flood, when the Brisbane River burst its banks on three occasions in February and again in June in the same year, with the city receiving more than a year's rainfall during February 1893, leaving much of the city's population homeless.
20th century

Over 20 small municipalities and shires were amalgamated in 1925 to form the City of Brisbane, governed by the Brisbane City Council.[46][47] A significant year for Brisbane was 1930, with the completion of Brisbane City Hall, then the city's tallest building and the Shrine of Remembrance, in ANZAC Square, which has become Brisbane's main war memorial.[48] These historic buildings, along with the Story Bridge which opened in 1940, are key landmarks that help define the architectural character of the city.
During World War II, Brisbane became central to the Allied campaign when the AMP Building (now called MacArthur Central) was used as the South West Pacific headquarters for General Douglas MacArthur, chief of the Allied Pacific forces, until his headquarters were moved to Hollandia in August 1944. MacArthur had previously rejected use of the University of Queensland complex as his headquarters, as the distinctive bends in the river at St Lucia could have aided enemy bombers. Also used as a headquarters by the American troops during World War II was the T & G Building.[49] About one million US troops passed through Australia during the war, as the primary co-ordination point for the South West Pacific.[50] In 1942, Brisbane was the site of a violent clash between visiting US military personnel and Australian servicemen and civilians, which resulted in one death and hundreds of injuries. This incident became known colloquially as the Battle of Brisbane.[51]
Post-war Brisbane had developed a "big country town" stigma, an image the city's politicians and marketers were very keen to remove.[52] In the late 1950s, an anonymous poet known as The Brisbane Bard generated much attention to the city which helped shake this stigma.[53][54] Despite steady growth, Brisbane's development was punctuated by infrastructure problems. The state government under Joh Bjelke-Petersen began a major programme of change and urban renewal, beginning with the central business district and inner suburbs. Trams in Brisbane were a popular mode of public transport until the network was closed in 1969, leaving Melbourne and one line in Adelaide as the last Australian state capitals to operate trams until Sydney began operation of a new system in 1997.

The 1974 Brisbane flood was a major disaster which temporarily crippled the city. During this era, Brisbane grew and modernised, rapidly becoming a destination of interstate migration. Some of Brisbane's popular landmarks were lost to development in controversial circumstances, including the Bellevue Hotel in 1979 and Cloudland in 1982. Major public works included the Riverside Expressway, the Gateway Bridge, and later, the redevelopment of South Bank, starting with the Queensland Art Gallery.
Between 1968 and 1987, when Queensland was governed by Premier Joh Bjelke-Petersen, whose government was characterised by strong social conservatism and the use of police force against demonstrators, and which ended with the Fitzgerald Inquiry into police corruption, Brisbane developed a counterculture focussed on the University of Queensland, street marches and Brisbane punk rock music.
Brisbane hosted the 1982 Commonwealth Games and the 1988 World Exposition (known locally as World Expo 88). These events were accompanied by a scale of public expenditure, construction, and development not previously seen in the state of Queensland.[55][56] Brisbane's population growth far exceeded the national average in the last two decades of the 20th century, with a high level of interstate migration from Victoria and New South Wales.
21st century
After three decades of record population growth, Brisbane was hit again by a major flood in January 2011. The Brisbane River did not reach the same height as the previous 1974 flood, but still caused extensive damage and disruption to the city.[57][58]
Brisbane also hosted major international events including the final Goodwill Games in 2001, the Rugby League World Cup Final in 2008 and again in 2017, as well as the 2014 G20 Brisbane summit.
Population growth has continued to be among the highest of the Australian capital cities in the first two decades of the 21st century, and major infrastructure including the Howard Smith Wharves, Roma Street Parklands, Queens Wharf, the Brisbane Riverwalk, the Queen's Wharf casino and resort precinct, the Brisbane International Cruise Terminal, the Clem Jones, Airport Link, and Legacy Way road tunnels, and the Airport, Springfield, Redcliffe Peninsula and Cross River Rail railway lines have been completed or are under construction.
Geography and environment



Brisbane is in the southeast corner of Queensland. The city is centred along the Brisbane River, and its eastern suburbs line the shores of Moreton Bay, a bay of the Coral Sea in the Pacific Ocean. The greater Brisbane region is on the coastal plain east of the Great Dividing Range, with the Taylor and D'Aguilar ranges extending into the metropolitan area. Brisbane's metropolitan area sprawls along the Moreton Bay floodplain between the Gold and Sunshine coasts, approximately from Caboolture in the north to Beenleigh in the south, and across to Ipswich in the south west.
The Brisbane River is a wide tidal estuary and its waters throughout most of the metropolitan area are brackish and navigable. The river takes a winding course through the metropolitan area with many steep curves from the southwest to its mouth at Moreton Bay in the east. The metropolitan area is also traversed by several other rivers and creeks including the North Pine and South Pine rivers in the northern suburbs, which converge to form the Pine River estuary at Bramble Bay, the Caboolture River further north, the Logan and Albert rivers in the south-eastern suburbs, and tributaries of the Brisbane River including the Bremer River in the south-western suburbs, Breakfast Creek in the inner-north, Norman Creek in the inner-south, Oxley Creek in the south, Bulimba Creek in the inner south-east and Moggill Creek in the west. The city is on a low-lying floodplain,[59] with the risk of flooding increased by the many suburban creeks which criss-cross the city.
The waters of Moreton Bay are sheltered from large swells by Moreton, Stradbroke and Bribie islands, so whilst the bay can become rough in windy conditions, the waves at Moreton Bay beaches are generally not surfable. Unsheltered surf beaches lie on the eastern coasts of Moreton, Stradbroke and Bribie islands islands and on the Gold Coast and Sunshine Coast to the north and south. The southern part of Moreton Bay also contains smaller islands such as St Helena Island, Peel Island, Coochiemudlo Island, Russell Island, Lamb Island and Macleay Island.
The city of Brisbane is hilly.[60] The urban area, including the central business district, are partially elevated by spurs of the Herbert Taylor Range, such as the summit of Mount Coot-tha, reaching up to 300 m (980 ft) and the smaller Enoggera Hill. The D'Aguilar National Park, encompassing the D'Aguilar Range, bounds the north-west of Brisbane's built-up area, and contains the taller peaks of Mount Nebo, Camp Mountain, Mount Pleasant, Mount Glorious, Mount Samson and Mount Mee. Other prominent rises in Brisbane are Mount Gravatt and nearby Toohey Mountain. Mount Petrie at 170 m (560 ft) and the lower rises of Highgate Hill, Mount Ommaney, Stephens Mountain, and Whites Hill are dotted across the city.
Much of the rock upon which Brisbane is located is the characteristic Brisbane tuff, a form of welded ignimbrite,[61] which is most prominently found at the Kangaroo Point Cliffs at Kangaroo Point and the New Farm Cliffs on the Petrie Bight reach of the Brisbane River. The stone was used in the construction of historical buildings such as the Commissariat Store and Cathedral of St Stephen, and the roadside kerbs in inner areas of Brisbane are still manufactured of Brisbane tuff.
Ecology
.jpg)
Brisbane is located within the South East Queensland biogeographic region, and is home to numerous Eucalyptus varieties. Trees considered iconic to Brisbane include the Moreton Bay fig, a very large evergreen banyan with imposing buttress roots named for the region which are often lit with decorative lights in the inner city, as well as the jacaranda, a subtropical tree native to South America which line avenues and parks throughout Brisbane and bloom with purple flowers during October, referred to locally as 'jacaranda season'.[62] Other trees common to the metropolitan area include Moreton Bay chestnut, broad-leaved paperbark, poinciana, weeping lilli pilli and Bangalow palm. Some of the banks of the Brisbane River and Moreton Bay are home to mangrove wetlands.
Brisbane is home to numerous bird species, with common species including rainbow lorikeets, kookaburras, galahs, Australian white ibises, Australian brushturkeys, Torresian crows, Australian magpies and noisy miners. Common reptiles include common garden skinks, Australian water dragons, bearded dragons and blue-tongued lizards. Common ringtail possums and flying foxes are common in parks and yards throughout the city, as are common crow butterflies, blue triangle butterflies, golden orb-weaver spiders and St Andrew's Cross spiders. The Brisbane River is home to many fish species including yellowfin bream, flathead, Australasian snapper, and bull sharks. The waters of Moreton Bay are home to dugongs, humpback whales, dolphins, mud crabs, soldier crabs, Moreton Bay bugs and numerous shellfish species.
Climate
Brisbane has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification: Cfa)[63] with hot, wet summers and moderately dry, moderately warm winters.[64][65] Brisbane experiences an annual mean minimum of 16.6 °C (62 °F) and mean maximum of 26.6 °C (80 °F), making it Australia's second-hottest capital city after Darwin.[66] Seasonality is not pronounced, and average maximum temperatures of above 26 °C (79 °F) persist from October through to April.
Due to its proximity to the Coral Sea and a warm ocean current, Brisbane's overall temperature variability is somewhat less than most Australian capitals. Summers are long, hot, and wet, but temperatures only occasionally reach 35 °C (95 °F) or more. Eighty percent of summer days record a maximum temperature of 27 to 33 °C (81 to 91 °F). Winters are short and warm, with average maximums of about 22 °C (72 °F); maximum temperatures below 20 °C (68 °F) are rare.
The city's highest recorded temperature was 43.2 °C (109.8 °F) on Australia Day 1940 at the Brisbane Regional Office,[67] with the highest temperature at the current station being 41.7 °C (107.1 °F) on 22 February 2004;[68] but temperatures above 38 °C (100 °F) are uncommon. On 19 July 2007, Brisbane's temperature fell below the freezing point for the first time since records began, registering −0.1 °C (31.8 °F) at the airport station.[69] The city station has never dropped below 2 °C (36 °F),[70] with the average coldest night during winter being around 6 °C (43 °F), however locations in the west of the metropolitan area such as Ipswich have dropped as low as −5 °C (23 °F) with heavy ground frost.[71]
In 2009, Brisbane recorded its hottest winter day (from June to August) at 35.4 °C (95.7 °F) on 24 August;[72] The average July day however is around 22 °C (72 °F) with sunny skies and low humidity, occasionally as high as 27 °C (81 °F), whilst maximum temperatures below 18 °C (64 °F) are uncommon and usually associated with brief periods of cloud and winter rain.[70] The highest minimum temperature ever recorded in Brisbane was 28.0 °C (82.4 °F) on 29 January 1940 and again on 21 January 2017, whilst the lowest maximum temperature was 10.2 °C (50.4 °F) on 12 August 1954.[67]
Annual precipitation is ample. From November to March, thunderstorms are common over Brisbane, with the more severe events accompanied by large damaging hail stones, torrential rain and destructive winds. On an annual basis, Brisbane averages 124 clear days.[73] Dewpoints in the summer average at around 20 °C (68 °F); the apparent temperature exceeds 30 °C (86 °F) on almost all summer days.[70] Brisbane's wettest day occurred on 21 January 1887, when 465 millimetres (18.3 in) of rain fell on the city, the highest maximum daily rainfall of Australia's capital cities. The wettest month on record was February 1893, when 1,025.9 millimetres (40.39 in) of rain fell, although in the last 30 years the record monthly rainfall has been a much lower 479.8 millimetres (18.89 in) from December 2010. Very occasionally a whole month will pass with no recorded rainfall, the last time this happened was August 1991.[67] The city has suffered three major floods since its founding, in February 1893, January 1974 (partially a result of Cyclone Wanda), and January 2011 (partially a result of Cyclone Tasha).
Brisbane is within the southern reaches of the tropical cyclone risk zone. Full strength tropical cyclones rarely affect Brisbane, but they do occasionally. The biggest risk is ex-tropical cyclones which can cause destructive winds and flooding rains.
The average annual temperature of the sea ranges from 21.0 °C (69.8 °F) in July to 27.0 °C (80.6 °F) in February.[74]
| Climate data for Brisbane (Brisbane, 1999-2020) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 40.0 (104.0) |
41.7 (107.1) |
37.9 (100.2) |
33.7 (92.7) |
30.7 (87.3) |
29.0 (84.2) |
29.1 (84.4) |
35.4 (95.7) |
37.0 (98.6) |
38.7 (101.7) |
38.9 (102.0) |
41.2 (106.2) |
41.7 (107.1) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 30.5 (86.9) |
30.2 (86.4) |
29.1 (84.4) |
27.1 (80.8) |
24.6 (76.3) |
22.0 (71.6) |
22.1 (71.8) |
23.4 (74.1) |
25.7 (78.3) |
27.0 (80.6) |
28.3 (82.9) |
29.6 (85.3) |
26.6 (79.9) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 26.1 (79.0) |
25.8 (78.4) |
24.7 (76.5) |
22.2 (72.0) |
19.2 (66.6) |
16.9 (62.4) |
16.2 (61.2) |
17.1 (62.8) |
19.7 (67.5) |
21.7 (71.1) |
23.5 (74.3) |
25.0 (77.0) |
20.7 (69.3) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 21.7 (71.1) |
21.4 (70.5) |
20.2 (68.4) |
17.4 (63.3) |
13.8 (56.8) |
11.9 (53.4) |
10.3 (50.5) |
10.8 (51.4) |
13.8 (56.8) |
16.4 (61.5) |
18.8 (65.8) |
20.4 (68.7) |
16.4 (61.5) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 17.0 (62.6) |
16.5 (61.7) |
12.2 (54.0) |
10.0 (50.0) |
5.0 (41.0) |
5.0 (41.0) |
2.6 (36.7) |
4.1 (39.4) |
7.0 (44.6) |
8.8 (47.8) |
10.8 (51.4) |
14.0 (57.2) |
2.6 (36.7) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 140 (5.5) |
150 (5.9) |
115 (4.5) |
61 (2.4) |
62 (2.4) |
67 (2.6) |
25 (1.0) |
36 (1.4) |
28 (1.1) |
78 (3.1) |
91 (3.6) |
129 (5.1) |
1,011 (39.8) |
| Average rainy days (≥ 1 mm) | 8.2 | 9.7 | 9.7 | 7.2 | 5.7 | 6.6 | 3.6 | 3.6 | 3.8 | 6.9 | 7.8 | 8.9 | 81.7 |
| Average afternoon relative humidity (%) | 57 | 59 | 57 | 54 | 49 | 52 | 44 | 43 | 48 | 51 | 56 | 57 | 52 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 267 | 235 | 233 | 237 | 239 | 198 | 239 | 270 | 267 | 270 | 273 | 264 | 2,989 |
| Source: Bureau of Meteorology[75] | |||||||||||||
Urban structure
.jpg)

The Brisbane central business district (CBD, colloquially referred to as 'the city') lies in a curve of the Brisbane river. The CBD covers 2.2 km2 (0.8 sq mi) and is walkable. Most central streets are named after members of the House of Hanover. Queen Street (named in honour of Queen Victoria) is Brisbane's traditional main street and contains its largest pedestrian mall, the Queen Street Mall. Streets named after female members (Adelaide, Alice, Ann, Charlotte, Elizabeth, Margaret, and Mary) run parallel to Queen Street and perpendicular to streets named after male members (Albert, Edward, George, and William).
The CBD's squares include King George Square, Post Office Square and ANZAC Square (home to the city's central war memorial).
Brisbane's metropolitan area is broadly and colloquially divided into the 'northside' and the 'southside', with the dividing line being the Brisbane River,[76] as crossing one of the 15 bridges across the river is required to travel to the opposite side by land transport. This results in many areas which are south of the CBD being classified as located in the 'northside', and vice versa, as a result of the river's winding trajectory. In addition to being classified as located on the 'northside' or 'southside' there are further broad and colloquial regions such as the 'westside' for some areas to the southwest of the CBD and the 'bayside' for areas located on the coast of Moreton Bay.
Greater Brisbane had a density of 148 inhabitants per square kilometre (380/sq mi) in 2016.[77] Like most Australian and North American cities, Brisbane has a sprawling metropolitan area which takes in excess of one hour to traverse either north to south or east to west by car without traffic.
From the 1970s onwards, there has been a large increase in the construction of apartment developments, including mid-rise and high rise buildings, which has quickened in the 21st century. At the 2016 census, 76.4% of residents lived in separate houses, 12.6% lived in apartments, and 10% lived in townhouses, terrace houses, or semidetached houses.[78]
Parklands
Brisbane's major parklands include the riverside City Botanic Gardens at Gardens Point, Roma Street Parkland, the 27-hectare Victoria Park at Spring Hill and Herston, South Bank Parklands along the river at South Bank, the Brisbane Botanic Gardens at Mount Coot-tha and the riverside New Farm Park at New Farm.
There are many national parks surrounding the Brisbane metropolitan area. The D'Aguilar National Park is a major national park along the northwest of the metropolitan area in the D'Aguilar Range. The Glass House Mountains National Park is located to the north of the metropolitan area in the Glass House Mountains and provides green space between the Brisbane metropolitan area and the Sunshine Coast. The Tamborine National Park at Tamborine Mountain is located in the Gold Coast hinterland to the south of the metropolitan area.
The eastern metropolitan area is built along the Moreton Bay Marine Park, encompassing Moreton Bay. Significant areas of Moreton, North Stradbroke and Bribie islands also covered by the Moreton Island National Park, Naree Budjong Djara National Park and the Bribie Island National Park respectively. The Boondall Wetlands in the suburb of Boondall include 1,100 hectares of wetlands which are home to mangroves and shorebirds as well as walking tracks.
Architecture

Brisbane has retained many heritage buildings, some of which date back to the 1820s, including The Old Windmill in Wickham Park, built by convict labour in 1824,[79][80] which is the oldest surviving building in Brisbane, and the Commissariat Store on William Street, built by convict labour in 1828, was originally used as a grainhouse, and is now the home of the Royal Historical Society of Brisbane and contains a museum.[81][82][83] Other 19th and early 20th-century buildings of architectural significance include the Treasury Building, City Hall, Customs House and the Land Administration Building.
Brisbane is the origin of a distinctive architectural style known as Queenslander architecture, which developed in the 1840s and characterises the majority of pre-war homes built in the metropolitan area. Queenslander homes typically feature timber construction with large verandahs, gabled corrugated iron roofs, high ceilings. Most of these houses are elevated on stumps (also called "stilts"), traditionally built of timber, which allow for a void under the houses which aid in cooling. Queenslander houses are considered iconic to Brisbane and are typically sold at a significant premium to equivalent modern houses.The relatively low cost of timber in south-east Queensland meant that until recently, most residences were constructed of timber, rather than brick or stone. Early legislation decreed a minimum size for residential blocks leading to few terrace houses being constructed in Brisbane. The high-density housing that historically existed came in the form of miniature Queenslander-style houses which resemble the much larger traditional styles, but are sometimes only one-quarter the size. These houses are most common in the inner-city suburbs.
Brisbane is home to several of Australia's tallest buildings and it is ranked among world cities with the most skyscrapers. All of Brisbane's skyscrapers (buildings with a height greater than 150 metres) are located within the CBD, with large numbers of high-rise buildings also proliferating in the inner suburbs of South Brisbane, Kangaroo Point, Fortitude Valley, Newstead, Teneriffe, New Farm, Bowen Hills, Spring Hill, Milton, Auchenflower, Toowong, Taringa, St Lucia, West End and Woolloongabba. Brisbane's 91-metre City Hall was the city's tallest building for decades after its completion in 1930 and was finally surpassed in 1970, which marked the beginning of the widespread construction of high-rise buildings. Brisbane's tallest building is currently Brisbane Skytower, which has a height of 270 metres.[84]
Demographics

Brisbane's Greater Capital City Statistical Area includes the Local Government Areas of City of Brisbane, City of Ipswich, Moreton Bay Region, Logan City and Redland City, as well as parts of Lockyer Valley Region, Scenic Rim Region and Somerset Region, which form a continuous metropolitan area. The Australian Bureau of Statistics estimates that the population of Greater Brisbane is 2,514,184 as of June 2019,[1] making it the third largest city in Australia.
Ancestry and immigration
| Country of birth (2016)[85] | |
|---|---|
| Birthplace[N 1] | Population |
| Australia | 1,538,813 |
| New Zealand | 106,053 |
| England | 90,086 |
| Mainland China | 36,175 |
| India | 35,335 |
| South Africa | 22,068 |
| Philippines | 20,797 |
| Vietnam | 16,731 |
| South Korea | 12,202 |
| Taiwan | 11,976 |
| Scotland | 11,691 |
| Malaysia | 10,765 |
At the 2016 census, the most commonly nominated ancestries were:[N 2][86]
- English (39.7%)
- Australian (34.6%)[N 3]
- Irish (13.2%)
- Scottish (11%)
- German (6.4%)
- Chinese (4.7%)
- Italian (2.8%)
- Indian (2.6%)
- Indigenous (2.4%)[N 4]
- Dutch (1.7%)
- New Zealander (1.7%)
- Maori (1.5%)
- Filipino (1.3%)
- Vietnamese (1.2%)
- Samoan (1.1%)
The 2016 census showed that 32.2% of Brisbane's inhabitants were born overseas[78] and 50.9% of inhabitants had at least one parent born overseas.[78] Brisbane has the 26th largest immigrant population among world metropolitan areas. Of inhabitants born outside of Australia, the four most prevalent countries of birth were New Zealand, England, Mainland China, and India.[78] Brisbane has the largest New Zealand and Taiwanese-born populations of any city in Australia.[85]
The areas of Sunnybank,[88] Sunnybank Hills,[89] Stretton,[90] Robertson,[91] Calamvale,[92] Macgregor,[93] Eight Mile Plains,[94] Runcorn[95] and Rochedale,[96] are home to a large proportion of Brisbane's Mainland China, Taiwan and Hong Kong-born population, with Chinese being the most commonly-reported ancestry in each of these areas. The Vietnamese-born are the largest immigrant group in Inala,[97] Darra,[98] Durack,[99] Willawong,[100] Richlands[101] and Doolandella.[102] The Indian-born are the largest immigrant group in Chermside.[103]
2.4% of the population, or 54,158 people, identified as Indigenous Australians (Aboriginal Australians and Torres Strait Islanders) in 2016.[N 5][86]
Language

At the 2016 census, 78% of inhabitants spoke only English at home,[78] with the next most common languages being Mandarin (2.4%), Vietnamese (1.0%), Cantonese (0.9%), Spanish (0.7%), Hindi (0.6%), Samoan (0.6%), Korean (0.6%) and Punjabi (0.6%).[104]
Religion
At the 2016 census, the most commonly cited religious affiliations was 'No religion' (30.6%).[86]
Brisbane's most popular religion at the 2016 census was Christianity, and the most popular denomonations were Catholicism (21.5%) and Anglicanism (13.3%). Other Christian denominations including Uniting Church, Baptists, Pentecostalism, Lutheranism and Eastern Orthodox made up 18.8% of the population.[86] All Christian demoninations totalled 53.6% of the population. Brisbane's CBD is home to two cathedrals – St John's (Anglican) and St Stephen's (Catholic).
The most popular non-Christian religions at the 2016 census were Buddhist (2%), Muslim (1.5%) and Hindu (1.5%).[86]
Economy

Categorised as a global city, Brisbane is among Asia-Pacific cities with largest GDPs and is one of the major business hubs in Australia, with strengths in mining, banking, insurance, transportation, information technology, real estate and food.[105]
Some of the largest companies headquartered in Brisbane, all among Australia's largest, include Suncorp Group, Virgin Australia, Aurizon, Bank of Queensland, Flight Centre, CUA, Sunsuper, QSuper, Domino's Pizza Enterprises, Star Entertainment Group, ALS, TechnologyOne, NEXTDC, Super Retail Group, New Hope Coal, Jumbo Interactive, National Storage, Collins Foods and Boeing Australia.[106] Most major Australian companies, as well as numerous international companies, have contact offices in Brisbane.
Brisbane throughout its history has been one of Australia's most important seaport cities. The Port of Brisbane located at the Brisbane River's mouth on Moreton Bay and on the adjacent Fisherman's Island, created by means of land reclamation. It is the 3rd busiest port in Australia for value of goods.[107] Container freight, sugar, grain, coal and bulk liquids are the major exports. Most of the port facilities are less than three decades old and some are built on reclaimed mangroves and wetlands. The Port is a part of the Australia TradeCoast, which includes the Brisbane Airport along with large industrial estates located along both banks at the mouth of the Brisbane River.[108]
White-collar industries include information technology, financial services, higher education and public sector administration generally concentrated in and around the central business district and satellite hubs located in the inner suburbs such as South Brisbane, Fortitude Valley, Spring Hill, Milton and Toowong.
Blue-collar industries, including petroleum refining, stevedoring, paper milling, metalworking and QR railway workshops, tend to be located on the lower reaches of the Brisbane River proximal to the Port of Brisbane and in new industrial zones on the urban fringe.
Tourism is an important part of the Brisbane economy, both in its own right and as a gateway to other areas of Queensland,[109] as international education, with over 95,000 international students enrolled in universities and other tertiary education institutions in the central Brisbane City Council local government area alone in 2018.[110]
Retail

Retail in the CBD is centred around the Queen Street Mall, which is Queensland's largest pedestrian mall. Shopping centres in the CBD include the Myer Centre, the Wintergarden, MacArthur Central and QueensPlaza, with the last of these along with Edward Street forming the city's focus for luxury brands. There are historical shopping arcades at Brisbane Arcade and Tattersalls Arcade. Suburbs adjacent to the CBD such as Fortitude Valley (particularly James Street), South Brisbane and West End are also a major inner-city retail hubs.
Outside of the inner-city, retail is focused on indoor shopping centres, including numerous regional shopping centres along with six super regional shopping centres, all of which are among Australia's largest, namely: Westfield Chermside in the north; Westfield Garden City in the south; Westfield Carindale in the east; Indooroopilly Shopping Centre in the west; Westfield North Lakes in the outer-north; and Logan Hyperdome in the outer-south. Brisbane's major factory outlet centres are the Direct Factory Outlets at Skygate and Jindalee.
The 100 hectare Brisbane Markets at Rocklea are Brisbane's largest wholesale markets, whilst smaller markets operate at numerous locations throughout the city including South Bank Parklands, Davies Park in West End, Queensland and the Eat Street Markets at Hamilton.
Culture and sport
Brisbane is home to several art galleries, the largest of which are the Queensland Art Gallery and the Queensland Gallery of Modern Art (GOMA), which is the largest modern art gallery in Australia. GOMA holds the Asia Pacific Triennial (APT) which focuses on contemporary art from the Asia and Pacific in a variety of media from painting to video work. In Addition, its size enables the gallery to exhibit particularly large shows.
Dramatic and musical theatre performances are held at the multiple large theatres located at Queensland Performing Arts Centre (QPAC). The Brisbane Powerhouse in New Farm and the Judith Wright Centre of Contemporary Arts in Fortitude Valley also feature diverse programmes featuring exhibitions and festivals of visual art, music and dance. Brisbane is also home to numerous small theatres including the Brisbane Arts Theatre in Petrie Terrace, the La Boite Theatre Company which performs at the Roundhouse Theatre at Kelvin Grove, the Twelfth Night Theatre at Bowen Hills, the Metro Arts Theatre in Edward Street, and the Queensland Theatre Company's Bille Brown Theatre in West End.
The Queensland Performing Arts Centre (QPAC) at South Bank, consists of the Lyric Theatre, the Concert Hall, the Cremorne Theatre and the Playhouse Theatre and is home to the Queensland Ballet, Opera Queensland, the Queensland Theatre Company, and the Queensland Symphony Orchestra. The Queensland Conservatorium, a musical conservatorium in which professional music companies and conservatorium students also stage performances, is located within the South Bank Parklands. Numerous choirs present performances across the city annually. These choirs include the Brisbane Chorale, Queensland Choir, Brisbane Chamber Choir, Canticum Chamber Choir, Brisbane Concert Choir, Imogen Children's Chorale and Brisbane Birralee Voices.
Brisbane has maintained a constantly evolving live music scene, producing acts spanning genres including punk (see Brisbane punk rock), indie rock, electronic music, experimental music, noise rock, metal and post-punk. Brisbane's live music history is often intertwined with social unrest and authoritarian politics, as retold by journalist Andrew Stafford in Pig City: From The Saints to Savage Garden, Radical Brisbane: An Unruly History, edited by academics Raymond Evans and Carole Ferrier, and BNE – The Definitive Archive: Brisbane Independent Electronic Music Production 1979–2014, produced by record label director Dennis Remmer.[111][112] There are also popular entertainment pubs and clubs within both the City and Fortitude Valley.[113][114] The Brisbane Entertainment Centre at Boondall is an arena which hosts many musical concerts, with some of the largest being held at Lang Park.
Musicians from Brisbane include the Bee Gees (raised in Redcliffe and Cribb Island), Powderfinger (who met at Brisbane Grammar School and the University of Queensland), The Go-Betweens (after whom Brisbane's Go Between Bridge is named, and whose songs and albums, such as Spring Hill Fair, reflect the attitude of 1980s Brisbane), The Veronicas (born and raised in Albany Creek), The Saints (based in Brisbane since 1974, one of the first punk rock bands), Savage Garden, Sheppard, Pete Murray, Ball Park Music, and Twoset Violin. The city is featured in music including The Saints' "Brisbane (Security City)" (1978); The Stranglers' "Nuclear Device" (1979) about Joh Bjelke-Petersen; Midnight Oil's single "Dreamworld" (1987); and Powderfinger's album Vulture Street (2003).
Prominent writers from Brisbane include David Malouf (whose 1975 novel Johnno is set in Brisbane and at Brisbane Grammar School during World War II), Nick Earls (whose 1996 novel Zigzag Street is set at Zigzag Street in Red Hill), and Li Cunxin, author of Mao's Last Dancer and artistic director of the Queensland Ballet. The State Library of Queensland, the state's largest library, is located at the Queensland Cultural Centre.
Brisbane is home to over 6,000 restaurants and dining establishments,[115] with outdoor dining featuring prominently. The most popular cuisines by number of dining establishments are Japanese,[116] Chinese,[117] Modern Australian,[118] Italian,[119] American,[120] Indian,[121] and Vietnamese.[122] Moreton Bay bugs, less commonly known as flathead lobsters, are an ingredient named for the Brisbane region and which feature commonly in the city's cuisine, along with macadamia nuts, also native to the region.
Annual events

The Royal Queensland Exhibition (known locally as the Ekka), an agricultural exhibition held each August at the Brisbane Showgrounds in Bowen Hills is the longest-running major annual event held in Brisbane, during which there is a public holiday for each local government area across Brisbane so as to enable widespread public attendance.
The Brisbane Festival, which includes one of the nation's largest annual fireworks displays called 'Riverfire', and which is held each September at South Bank Parklands, the CBD and surrounding areas is the second of Brisbane's major annual events, with the 'Riverfire' fireworks displays attended by hundreds of thousands of residents annually.
The Brisbane International Film Festival (BIFF) is held in July/August each year in a variety of venues around Brisbane. BIFF features new films and retrospectives by domestic and international filmmakers along with seminars and awards.
The Buddha Birth Day festival at South Bank parklands attracts over 200,000 visitors each year,[123][124] and is the largest event of its type in Australia.
There are also many smaller community events such as the Paniyiri festival (a Greek cultural festival held over two days in May), the Brisbane Medieval Fayre and Tournament (held each June), the Bridge to Brisbane charity fun run and the Caxton Street Seafood and Wine Festival.
Major events are often held at the 171,000 square metre Brisbane Convention & Exhibition Centre in South Brisbane.
Sport

Brisbane has hosted several major sporting events including the 1982 Commonwealth Games and the 2001 Goodwill Games, as well as events during the 1987 Rugby World Cup, 1992 Cricket World Cup, 2000 Sydney Olympics, 2003 Rugby World Cup, 2008 Rugby League World Cup, 2017 Rugby League World Cup and the 2018 Commonwealth Games. It holds the Brisbane International tennis competition every year.
Rugby league is popular in Brisbane and the city hosts the Brisbane Broncos, who play in the National Rugby League competition and the Queensland Maroons who play in the State of Origin series.
In rugby union the city hosts the Queensland Reds who play in the Super Rugby competition.
Cricket is popular in the Brisbane and the city hosts the Brisbane Heat who play in the Big Bash League and the Queensland Bulls who play in the Sheffield Shield and the Ryobi One Day Cup.
Brisbane also hosts an A-League soccer team, the Brisbane Roar FC; an Australian Football League team, the Brisbane Lions; a basketball team, the Brisbane Bullets; a baseball team, the Brisbane Bandits; a netball team, the Queensland Firebirds; a field hockey team, the Brisbane Blaze; and water polo teams the Brisbane Barracudas and Queensland Breakers.
The city's major stadiums and sporting venues include the Gabba (a 42,000 seat round stadium at Woolloongabba), Lang Park (a 52,500 seat rectangular stadium at Milton also known by its corporate name Suncorp Stadium), Ballymore Stadium, the Queensland Sport and Athletics Centre, the Sleeman Centre (swimming), the State Tennis Centre, the Eagle Farm Racecourse and the Doomben Racecourse. The city is also home to numerous golf courses, with the largest being the Indooroopilly Golf Club at Indooroopilly, Queensland, the Brookwater Golf and Country Club at Brookwater, the Keperra Country Golf Club at Keperra and the Royal Queensland Golf Club at Eagle Farm.
In addition to its flagship sport franchises, Brisbane and its regions and suburbs have numerous teams in secondary leagues including the Intrust Super Cup, National Rugby Championship, Queensland Premier Rugby, National Premier League Queensland, North East Australian Football League, National Basketball League, ANZ Championship, Australian Baseball League, Hockey One, National Water Polo League and F-league.
Tourism and recreation


Tourism plays a major role in Brisbane's economy, being the third-most popular destination for international tourists after Sydney and Melbourne.[125] Popular tourist and recreation areas in Brisbane include the South Bank Parklands (including the Wheel of Brisbane), the City Botanic Gardens, Roma Street Parkland, New Farm Park, the Howard Smith Wharves, the Lone Pine Koala Sanctuary, the Teneriffe woolstores precinct, Fortitude Valley (including James Street and Chinatown), West End, City Hall (including the Museum of Brisbane), the Parliament of Queensland, the Story Bridge and bridge climb; St John's Cathedral, ANZAC Square and the Queensland Cultural Centre (including the Queensland Museum, Queensland Performing Arts Centre, Queensland Art Gallery, the Gallery of Modern Art and the State Library of Queensland), the Kangaroo Point Cliffs and park, and the Queensland Maritime Museum.
Brisbane is notable for its Brisbane Riverwalk network, which runs along much of the Brisbane River foreshore throughout the inner-city area, with the longest span running between Newstead and Toowong. Another popular stretch runs beneath the Kangaroo Point Cliffs between South Brisbane and Kangaroo Point. Several spans of the Riverwalk are built out over the Brisbane River. Brisbane also has over 27 km (17 mi) of bicycle pathways, mostly surrounding the Brisbane River and city centre. Other popular recreation activities include the Story Bridge adventure climb and rock climbing at the Kangaroo Point Cliffs.
Moreton Bay and its marine park is also a major attraction, and its three primary islands Moreton Island, North Stradbroke Island and Bribie Island, accessible by ferry, contain popular surf beaches and resorts. Tangalooma resort on Moreton Island is popular for its nightly wild dolphin feeding attraction, and for operating Australia's longest running whale watching cruises. The Fort Lytton National Park including a colonial defence fort and museum is also a historical bayside attraction. Beachside suburbs such as those on the Redcliffe Peninsula, as well as Shorncliffe, Sandgate, Wynnum, Manly and Wellington Point are also popular attractions for their bayside beaches, piers, and infrastrure cture for boating, sailing, fishing and kitesurfing.
The Mount Coot-tha Reserve, including Mount Coot-tha, the Mount Coot-tha Lookout, the Mount Coot-tha Botanic Gardens and the Sir Thomas Brisbane Planetarium is a popular recreational attraction for hiking and bushwalking.
There are many national parks surrounding the Brisbane metropolitan area which are popular recreational attractions for hiking and bushwalking. The D'Aguilar National Park runs along the northwest of the metropolitan area in the D'Aguilar Range, and contains popular bushwalking and hiking peaks at Mount Nebo, Camp Mountain, Mount Pleasant, Mount Glorious, Mount Samson and Mount Mee. The Glass House Mountains National Park is located to the north of the metropolitan area in the Glass House Mountains between it and that of the Sunshine Coast. The Tamborine National Park at Tamborine Mountain is located in the Gold Coast hinterland to the south of the metropolitan area. Moreton, North Stradbroke and Bribie islands are substantially covered by the Moreton Island National Park, Naree Budjong Djara National Park and the Bribie Island National Park respectively. The Boondall Wetlands in the suburb of Boondall are protected mangrove wetlands with floating walking trails.
Immediately to the south and north of Brisbane are the Gold Coast and Sunshine Coast respectively, which are home to several of Australia's most popular swimming and surfing beaches, and are popular day and weekend destinations for Brisbanites.
In 2015, a competition by travel guidebook Rough Guides saw Brisbane elected as one of the top ten most beautiful cities in the world, citing reasons such as "its winning combination of high-rise modern architecture, lush green spaces and the enormous Brisbane River that snakes its way through the centre before emptying itself into the azure Moreton Bay".[126]
Governance
Unlike other Australian capital cities, a large portion of the greater metropolitan area, or Greater Capital City Statistical Area (GCCSA) of Brisbane is controlled by a single local government area, the City of Brisbane. Since the creation of the City of Brisbane in 1925 the urban areas of Brisbane have expanded considerably past the council boundaries.[127] The City of Brisbane local government area is by far the largest local government area (in terms of population and budget) in Australia, serving more than 40% of the GCCSA's population. It was formed by the merger of twenty smaller LGAs in 1925, and covers an area of 1,367 km2 (528 sq mi). There is a directly-elected Lord Mayor, and a council composed of councillors representing 26 wards. City Hall is the seat of the Brisbane City Council, whilst the bulk of its executive offices are located at the Brisbane Square skyscraper.
The remainder of the metropolitan area falls into the LGAs of Logan City to the south, Moreton Bay Region in the northern suburbs, the City of Ipswich to the south west, Redland City to the south east on the bayside, with a small strip to the far west in the Scenic Rim Region. All LGAs within the metropolitan area have a similar structure to the City of Brisbane LGA.


As the capital city of Queensland, Brisbane is home to the Parliament of Queensland at Parliament House at Gardens Point in the CBD, adjacent to Old Government House. Queensland's current Government House is located in Paddington. The bulk of the state government's executive offices are located at the 1 William Street skyscraper. The Queensland Supreme and District courts are located at the Queen Elizabeth II Courts of Law in George Street, while the Magistrates court is located at the adjacent Brisbane Magistrates Court building. The various federal courts are loced at the Commonwealth Law Courts building on North Quay.
The Australian Army's Enoggera Barracks is located in Enoggera, while the historic Victoria Barracks in Petrie Terrace now hosts a military museum. The Royal Australian Navy's HMAS Moreton base is located at Bulimba. The Royal Australian Air Force's RAAF Base Amberley is located in Amberley in the outer south-west of the metropolitan area.
Brisbane's largest prisons and correctional facilities, the Brisbane Correctional Centre, Brisbane Women's Correctional Centre, Arthur Gorrie Correctional Centre and Wolston Correctional Centre are located at Wacol, while the city's main historical prison, the Boggo Road Gaol, is now a museum.
Education


There are five major multi-campus universities with campuses in Brisbane's metropolitan area, namely:
- The University of Queensland (UQ), which is Queensland's oldest university and frequently ranks among the world's top 50,[128][129][130] with campuses in St Lucia, Herston and Gatton
- Queensland University of Technology (QUT), with campuses in the central business district (Gardens Point) and Kelvin Grove
- Griffith University (GU), with campuses in Nathan, Mount Gravatt, South Bank and Meadowbrook
- The University of Southern Queensland (USQ), with campuses in Springfield and Ipswich
- The University of the Sunshine Coast (USC), with campuses in Petrie and Caboolture
Other universities which have campuses in Brisbane include the Australian Catholic University, Central Queensland University, James Cook University and the University of the Sunshine Coast.
Brisbane is a major destination for international students, who constitute a large proportion of enrolments in Brisbane's universities and are important to the city's economy and real estate market. In 2018, there were over 95,000 international students enrolled in universities and other tertiary education institutions in the central Brisbane City Council local government area alone.[110] The majority of Brisbane's international students originate from China, India and other countries in the Asia-Pacific region.[131]
There are biotechnology and research facilities at several universities in Brisbane, including the Institute for Molecular Bioscience and CSIRO at the University of Queensland and the Institute of Health and Biomedical Innovation at Queensland University of Technology.[132]
There are three major TAFE colleges in Brisbane; the Brisbane North Institute of TAFE, the Metropolitan South Institute of TAFE, and the Southbank Institute of TAFE.[133] Brisbane is also home to numerous other independent tertiary providers, including the Australian College of Natural Medicine, the Queensland Theological College, the Brisbane College of Theology, SAE Institute), Jschool: Journalism Education & Training, JMC Academy, and American College and the Aboriginal Centre for the Performing Arts.
Many of Brisbane's pre-school, primary, and secondary schools are under the jurisdiction of Education Queensland, a branch of the Queensland Government.[134] Independent (private), Roman Catholic and other religious schools also constitute a large share of Brisbane's primary and secondary schooling sectors, with the oldest such independent schools composing the memberships of the Great Public Schools Association of Queensland (GPS) for boys' schools and Queensland Girls' Secondary Schools Sports Association (QGSSSA) for girls' schools.
Infrastructure
.jpg)
Transport
Brisbane has an extensive transportation network within the city, as well as connections to regional centres, interstate and to overseas destinations. Like all Australian cities, the most popular mode of transport is private car.[135] Public transport is provided by rail, bus and ferry services and is co-ordinated by TransLink, which provides a unified ticketing and electronic payment system (known as 'go card') for South East Queensland. The region is divided into seven fare zones radiating outwards from the Brisbane central business district (CBD), with Brisbane's built-up area falling within zones 1–3. Bus services are operated by public and private operators whereas trains and ferries are operated by public agencies. The CBD is the central hub for all public transport services with services focusing on Roma Street, Central and Fortitude Valley railway stations; King George Square, Queen Street and Roma Street busway stations; and North Quay, Riverside and QUT Gardens Point ferry wharves.
Roads
Brisbane is served by a large network of urban and inter-urban motorways. The Pacific Motorway (M3/M1) connects the inner-city with the southern suburbs, Gold Coast and New South Wales. The Ipswich Motorway (M7/M2) connects the inner-city with the outer south-western suburbs. The Western Freeway and Centenary Motorway (M5) connect the city's inner-west and outer south-west. The Bruce Highway and Gympie Arterial Road (M1/M3) connect the city's northern suburbs with the Sunshine Coast and northern Queensland. The Logan Motorway (M2/M6) connects the southern and south-western suburbs. The Gateway Motorway is a toll road which connects the Gold and Sunshine Coast. The Port of Brisbane Motorway links the Gateway Motorway to the Port of Brisbane. The Inner City Bypass and Riverside Expressway serve as an inner ring freeway system to prevent motorists from travelling through the city's congested centre.[136]
Brisbane also has a large network of major road tunnels under the metropolitan area, known as the TransApex network, which include the Clem Jones Tunnel between the inner-north and inner-south, the Airport Link tunnel in the north-east and the Legacy Way tunnel in the south-west. They are the three longest road tunnels in Australia.
Bridges

The Brisbane River creates a barrier to road transport routes. In total there are sixteen bridges over the river, mostly concentrated in the inner city area. The road bridges (which usually also include provision for pedestrians and cyclists) by distance from the river mouth are the Sir Leo Hielscher Bridges, the Story Bridge, the Captain Cook Bridge, the Victoria Bridge, the William Jolly Bridge, the Go Between Bridge, the Eleanor Schonell Bridge, the Walter Taylor Bridge the Centenary Bridge and Colleges Crossing. There are three railway bridges, namely the Merivale Bridge, the Albert Bridge and the Indooroopilly Railway Bridge. There are also three pedestrian only bridges: the Goodwill Bridge, the Kurilpa Bridge and the Jack Pesch Bridge.
The Houghton Highway (northbound) and Ted Smout Memorial Bridge (southbound) bridges, over Bramble Bay between Brighton and the Redcliffe Peninsula, are the longest bridges in the state. The abutment arches of the original crossing The Hornibrook Bridge still remain in place.
Rail

The Queensland Rail City network consists of 152 train stations along 13 suburban rail lines and across the metropolitan area, namely: the Airport line; the Beenleigh line; the Caboolture line; the Cleveland line; the Doomben line; the Exhibition line; the Ferny Grove line; the Ipswich/Rosewood line; the Redcliffe Peninsula line; the Shorncliffe line; and the Springfield line. The network extends to the Gold and Sunshine coasts, which are fully integrated into the network on the Gold Coast line and Sunshine Coast line. The Airtrain service which runs on the Airport line is jointly operated between the City of Brisbane and Brisbane Airport.
55 million passenger trips were taken across the network in 2018–19.[137]
Construction of the network began in 1865[138] and has been progressively expanded in the subsequent centuries. Electrification of the network was completed between 1979 and 1988. The Cross River Rail project includes a twin rail tunnel (5.9 kilometres (3.7 mi) long) which will pass under the Brisbane River to link two new railway stations at Albert Street in the CBD and Wooloongabba is under construction and scheduled to be completed in 2024.[139]
Bus
Brisbane has a large dedicated bus rapid transit network, the Brisbane busway network. The network comprises the South East Busway, the Northern Busway and the Eastern Busway. The main network hubs are the King George Square, Queen Street, and Roma Street busway stations.
There are also numerous suburban bus routes operating throughout the metropolitan area, including the high-frequency Blue and Maroon CityGlider routes which run between Newstead and West End (Blue), and Ashgrove and Stones Corner (Maroon) respectively.
Ferry
_in_January_2019_in_Brisbane.jpg)
Transdev Brisbane Ferries operates three ferry services along the Brisbane River, CityCat, CityFerry and CityHopper. Brisbane's ferries, and particularly its catamaran CityCats, are considered iconic to the city.[140]
The CityCat high-speed catamaran ferry service, popular with tourists and commuters, operates services along the Brisbane River between the University of Queensland and Northshore Hamilton, with wharves at UQ St Lucia, West End, Guyatt Park, Regatta, Milton, North Quay, South Bank, QUT Gardens Point, Riverside, Sydney Street, Mowbray Park, New Farm Park, Hawthorne, Bulimba, Teneriffe, Bretts Wharf, Apollo Road and Northshore Hamilton.
The CityFerry service operates smaller vessels for popular cross-river routes, namely: Bulimba–Teneriffe, New Farm Park–Norman Park, and Holman Street–Eagle Street Pier–Thornton Street.
The free CityHopper service operates smaller vessels along a route between North Quay and Sydney Street, stopping at South Bank, Maritime Museum, Thornton Street, Eagle Street Pier, Holman Street and Dockside.
Pedestrian
An extensive network of pedestrian and cyclist pathways span the banks of the Brisbane River in the inner suburbs to form the Riverwalk network.[141] In some segments, the Riverwalk is built over the river. The longest span of the Riverwalk connects Newstead in the east with Toowong in the west.
Airports

Brisbane Airport (IATA code: BNE) is the city's main airport, the third busiest in Australia after Sydney Airport and Melbourne Airport. It is located north-east of the city centre on Moreton Bay and provides domestic and international passenger services. In the 2017, Brisbane Airport handled over 23 million passengers.[142] The airport is an airline hub for Qantas, Virgin Australia and Jetstar as well as a number of minor and freight airlines. The airport is served by the Airtrain service which runs on the Airport line, providing a direct service to the CBD.
Archerfield Airport in Brisbane's southern suburbs, Redcliffe Airport on the Redcliffe Peninsula and Caboolture Airfield in the far north of the metropolitan area serve Brisbane as general aviation airports.
Brisbane is also served by other major airports in South East Queensland, including Gold Coast Airport at Coolangatta, Sunshine Coast Airport at Marcoola and Toowoomba Wellcamp Airport at Wellcamp.
Seaport

The Port of Brisbane is located at the mouth of the Brisbane River on Moreton Bay and on the adjacent Fisherman's Island, an artificial island created by land reclamation. It is the third busiest port in Australia for value of goods.[107] The port is the endpoint of the main shipping channel across Moreton Bay which extends 90 kilometres north near Mooloolaba. The port has 29 operating berths including nine deep-water container berths and three deep-water bulk berths as well as 17 bulk and general cargo berths.
There are two cruise ship terminals in Brisbane. Portside Wharf at Hamilton is an international standard facility for cruise liners. Due to the height of the Gateway Bridge which must be passed to reacch the terminal, the wharf services small and medium-sized cruise ships. The Brisbane International Cruise Terminal at Luggage Point in Pinkenba is able to accommodate the largest cruise vessels in the world, and will be opened in 2020.[143]
Healthcare
Brisbane is covered by Queensland Health's "Metro North" and "Metro South" Health Service Networks.[144] Within the greater Brisbane area there are eight major public hospitals, four major private hospitals, and numerous smaller public and private facilities. The Royal Brisbane and Women's Hospital and the Princess Alexandra Hospital are two of Queensland's three major trauma centres. The Royal Brisbane and Women's Hospital includes a specialist burns unit, and is one of the largest hospitals in the Southern Hemisphere.[145] Other major public hospitals include the Mater Hospital, the Queen Elizabeth II Jubilee Hospital, and the Queensland Children's Hospital.
Specialist and general medical practices are located in the CBD, and most suburbs and localities.
Brisbane is also home to the headquarters of the Queensland Ambulance Service central executive, located at the Emergency Services Complex Kedron Park, along with the headquarters of the Queensland Fire and Emergency Services and the Queensland Emergency Operations Centre.
Other utilities

Water storage, treatment and delivery for Brisbane is handled by SEQ Water, which sells on to Queensland Urban Utilities (previously Brisbane Water) for distribution to the greater Brisbane area. Water for the area is stored in three major dams to the north-west of the metropolitan area: Wivenhoe, Somerset and North Pine.
There is an open market in relation to the supply of electricity and gas in Brisbane with the largest providers being Energex (electricity) and Origin Energy (gas).
Metropolitan Brisbane is serviced by all major and most minor telecommunications companies and their networks, including Telstra, Optus and Vodafone Australia.
Brisbane is home to numerous cemeteries including the following large 19th-centry historical cemeteries: the 44-hectare Toowong Cemetery (the largest cemetery in Queensland, which is a popular destination for walkers and joggers), Balmoral Cemetery, Lutwyche Cemetery, Nudgee Cemetery, Nundah Cemetery and South Brisbane Cemetery.
Media
Print
The main local print newspapers of Brisbane are The Courier-Mail and its sibling The Sunday Mail, both owned by News Corporation. Brisbane also receives the national daily, The Australian, its sibling the Weekend Australian, as well as The Australian Financial Review. Sydney's The Sydney Morning Herald and Melbourne's The Age also sell in Brisbane in smaller numbers.
The Brisbane Times is Brisbane's second major local news source, owned by Nine, and is online only.
There are community and suburban newspapers throughout the metropolitan area, including Brisbane News and City News, many of which are produced by Quest Community Newspapers.
Television

Brisbane is served by all five major television networks in Australia, which broadcast from prominent television transmission towers on the summit of Mount Coot-tha. The three commercial stations, Seven, Nine, and Ten, are accompanied by two government networks, ABC and SBS. Channels provided by these networks include 10 Bold, 10 Peach, TVSN, Spree TV, ABC HD (ABC broadcast in HD), ABC COMEDY/KIDS, ABC ME, ABC News, SBS HD (SBS broadcast in HD), SBS Viceland, SBS Viceland HD (SBS Viceland broadcast in HD), Food Network, NITV, 7HD (Seven broadcast in HD), 7Two, 7mate, 7flix, TV4ME, RACING.COM, 9HD (Nine broadcast in HD), 9Gem, 9Go!, 9Life and 9Rush. 31, a community station, also broadcasts in Brisbane. Optus and Foxtel operate PayTV services in Brisbane, via cable and satellite means.
Radio
Brisbane is serviced by five major public radio stations including major commercial radio stations, including 612 ABC Brisbane (local news, current affairs and talk); ABC Radio National (national news and current affairs); ABC NewsRadio (national news); ABC Classic FM (classical music); Triple J (alternative music); and SBS Radio (multicultural broadcasting).
Brisbane is serviced by numerous major commercial and community radio stations including 4BC (local and national talk, news and current affairs); 4KQ (oldies); Magic 882 (oldies); 4BH; 97.3 (pop); HIT 105 (pop); Nova 106.9 (pop); Triple M (rock); 96five Family FM (pop); Radio TAB (betting) and 4MBS (classical).
Brisbane is also serviced by community radio stations such as VAC Radio (Mandarin); Radio Brisvaani (Hindi); Radio Arabic (Arabic); 4EB (multiple languages); 98.9 FM (indigenous); 4RPH (vision impaired); Switch 1197 (youth broadcasting); 4ZZZ (community radio); and Vision Christian Radio (Christian).[146] Additional channels are also available via DAB digital radio.
Notable people
See also
Notes
- In accordance with the Australian Bureau of Statistics source, England, Scotland, Mainland China and the Special Administrative Regions of Hong Kong and Macau are listed separately
- As a percentage of 2,122,578 persons who nominated their ancestry at the 2016 census.
- The Australian Bureau of Statistics has stated that most who nominate "Australian" as their ancestry are part of the Anglo-Celtic group.[87]
- Of any ancestry. Includes those identifying as Aboriginal Australians or Torres Strait Islanders. Indigenous identification is separate to the ancestry question on the Australian Census and persons identifying as Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander may identify any ancestry.
- Of any ancestry. Includes those identifying as Aboriginal Australians or Torres Strait Islanders. Indigenous identification is separate to the ancestry question on the Australian Census and persons identifying as Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander may identify any ancestry.
References
- https://www.abs.gov.au/ausstats/abs@.nsf/Latestproducts/3218.0Main%20Features12018-19?opendocument&tabname=Summary&prodno=3218.0&issue=2018-19&num=&view=
- "2016 Census Community Profile – Greater Brisbane (3GBRI – GCCSA)". Australian Bureau of Statistics. Archived from the original on 14 July 2017.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 14 July 2017. Retrieved 2 July 2017.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link), ZIPed Excel spreadsheet. Cover
- "Great Circle Distance between Brisbane and Sydney". Geoscience Australia. March 2004. Archived from the original on 7 February 2016. Retrieved 17 January 2016.
- "Great Circle Distance between Brisbane and Canberra". Geoscience Australia. March 2004. Archived from the original on 7 February 2016. Retrieved 17 January 2016.
- "Great Circle Distance between Brisbane and Melbourne". Geoscience Australia. March 2004. Archived from the original on 7 February 2016. Retrieved 17 January 2016.
- "Great Circle Distance between Brisbane and Adelaide". Geoscience Australia. March 2004. Archived from the original on 7 February 2016. Retrieved 17 January 2016.
- "Great Circle Distance between Brisbane and Perth". Geoscience Australia. March 2004. Archived from the original on 7 February 2016. Retrieved 17 January 2016.
- Macquarie Dictionary. The Macquarie Library. 2003. p. 121. ISBN 1-876429-37-2.
- "Brisbane (entry 4555)". Queensland Place Names. Queensland Government. Retrieved 14 March 2014.
- "3218.0 – Regional Population Growth, Australia, 2018-19". Australian Bureau of Statistics. 25 March 2020. Retrieved 1 April 2020.
- "Brisbane and Greater Brisbane". Queensland Places. Archived from the original on 27 January 2014.
- Kent, Lucinda (21 March 2014). "Is this the average Brisbanite?". ABC Radio Brisbane. Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Archived from the original on 31 August 2014. Retrieved 20 April 2019.
- "Names for where we're from". ABC Radio National. Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 13 October 2012. Retrieved 20 April 2019.
- Scott, Noel; Clark, Stephen (2006). "The Development and Tracking of a Branding Campaign for Brisbane". In Prideaux, Bruce; Moscardo, Gianna; Laws, Eric (eds.). Managing Tourism and Hospitality Services: Theory and International Applications. CABI. ISBN 9781845930158.
- "Viva BrisVegas". The Sydney Morning Herald. 19 July 2002. Retrieved 1 April 2020.
- "South West Pacific campaign". www.ww2places.qld.gov.au. Queensland Government. Archived from the original on 5 February 2016. Retrieved 22 January 2016.
- "2016 Census Community Profiles: Greater Brisbane". Australian Bureau of Statistics. 23 October 2017. Retrieved 1 April 2020.
- "The World According to GaWC 2018". www.lboro.ac.uk. Archived from the original on 3 May 2017. Retrieved 24 May 2017.
- Schroders Global Cities Index – Schroders, 2019
- "Australia falls from top 10 Quality of Living ranking". Mercer. 13 March 2019. Retrieved 1 April 2020.
- "Announced: Melbourne Remains the World's Second Most Liveable City". Broadsheet. 4 September 2019. Retrieved 1 April 2020.
- https://amp.couriermail.com.au/news/queensland/brisbane-moves-up-liveability-index-but-trails-other-aussie-cities/news-story/61fc6ced3c92d6c85af1a7e98f084acc&ved=2ahUKEwi594jPh7zlAhWkmOYKHQMgAa0QFjAKegQIBxAL&usg=AOvVaw1i12Wvljn4Qt4CpWlyUk_h&cf=1
- Archibald Meston. "Aboriginal Indigeneous Tribes of Brisbane and Moreton Bay". Archived from the original on 12 July 2017. Retrieved 17 July 2017.
- Tony Moore (17 May 2012). "The indigenous history of Musgrave Park". Brisbane Times. Archived from the original on 30 July 2017. Retrieved 17 July 2017.
- "Tom Petrie's Early Reminiscences of Early Queensland". Archived from the original on 1 September 2013. Retrieved 24 November 2008.
- Our Brisbane – Our shared vision – Brisbane City Council Page 2 Archived 27 January 2014 at the Wayback Machine
- Ros Kidd. "Aboriginal History of the Princess Alexandra Hospital Site". Diamantina Health Care Museum Association Inc. Archived from the original on 2 August 2017. Retrieved 17 July 2017.
-

-

-

- "Redcliffe". The Sydney Morning Herald. 8 February 2004. Archived from the original on 23 May 2008. Retrieved 17 May 2008.
- "John Oxley Governor Report". Archived from the original on 1 September 2013. Retrieved 1 February 2010.
- Potter, Ron. "Place Names of South East Queensland". Piula Publications. Archived from the original on 23 May 2008. Retrieved 17 May 2008.
- Irving, Robert (1998). Reader's Digest Book of Historic Australian Towns. p. 70. ISBN 0-86449-271-5.
- "Sir Thomas 28 miles up the Brisbane River". MOST Brisbane. Archived from the original on 1 July 2016. Retrieved 24 June 2016.
- compiled by Royal Automobile Club of Queensland. (1980). Seeing South-East Queensland (2 ed.). RACQ. p. 7. ISBN 0-909518-07-6.
- "About Redcliffe". Redcliffe City Council. Archived from the original on 17 November 2007. Retrieved 1 December 2007.
- Lybaek, Lena; Konrad Raiser; Stefanie Schardien (2004). Gemeinschaft der Kirchen und gesellschaftliche Verantwortung. Münster: LIT. p. 114. ISBN 978-3-8258-7061-4.
- "Christopher Eipper (1813–1894)". Street Signs — And What They Mean. Pelican Waters Shire Council. Archived from the original on 18 November 2007. Retrieved 20 December 2007.
- "Frank Henry Vogler | German Immigrant | Johann Cesar 1863". mcnamarafamily.id.au. Archived from the original on 27 February 2016. Retrieved 10 March 2016.
- "German Settlement in Queensland in the 19th Century". www.germanaustralia.com. Archived from the original on 15 December 2016. Retrieved 10 March 2016.
- "Patrick Logan" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 5 February 2016.
- de Strzelecki, Paul Edmond (1845). Physical Description of New South Wales and Van Diemen's Land: Accompanied by a Geological Map, Sections, and Diagrams. London, United Kingdom: Longman, Brown, Green, and Longmans.
- "The Queensland Proclamation" (PDF). Queensland Government Archives. Archived (PDF) from the original on 29 June 2014. Retrieved 2 October 2014.
- "Organisation chart". Brisbane City Council. Retrieved 20 December 2007.
- "Jolly, William Alfred (1881–1955)". Australian Dictionary of Biography. Archived from the original on 26 May 2008. Retrieved 20 December 2007.
- "Brisbane". ANZAC Day Commemoration Committee (Qld) Incorporated. 1998. Archived from the original on 12 October 2007. Retrieved 28 December 2007.
- Peter Dunn (2 March 2005). "Hirings Section". Australia @ War. Archived from the original on 12 October 2007. Retrieved 7 January 2008.
- "QM Supply in the Pacific during WWII". Quartermaster Professional Bulletin. Spring 1999. Archived from the original on 21 February 2004. Retrieved 7 January 2008.
- Peter Dunn (27 August 2005). "The Battle of Brisbane — 26 & 27 November 1942". Australia @ War. Archived from the original on 10 January 2008. Retrieved 7 January 2008.
- Brisbane's last in but best-dressed, Brooke Falvey, City news, 11 July 2008. Archived 15 December 2013 at the Wayback Machine
- Swanwick, Tristan (12 December 2010). "Filmmakers on trail of Brisbane Bard". The Courier-Mail. Archived from the original on 8 February 2012. Retrieved 10 February 2012.
- She picked me up at a dance one night, Joan and Bill Bentson, Queensland Government. Archived 18 June 2009 at the Wayback Machine
- "ACGA Past Games 1982". Commonwealth Games Australia. Archived from the original on 17 September 2007. Retrieved 28 December 2007.
- Rebecca Bell. "Expo 88 / Brisbane". OZ Culture. Archived from the original on 28 January 1999. Retrieved 28 December 2007.
- Berry, Petrina (13 January 2011). "Brisbane braces for flood peak as Queensland's flood crisis continues". The Courier-Mail. Archived from the original on 16 August 2011. Retrieved 14 January 2011.
- "Before and after photos of the floods in Brisbane". Abc.net.au. Archived from the original on 12 July 2011. Retrieved 4 November 2012.
- "Flood-proof road destroyed in deluge". ABC News. Archived from the original on 6 July 2014.
- Gregory, Helen (2007). Brisbane Then and Now. Wingfield, South Australia: Salamander Books. p. 60. ISBN 978-1-74173-011-1.
- "Brisbane Tuff". Windsor and Districts Historical Society. Retrieved 2 June 2014.
- "Get out and explore Brisbane's top jacaranda trees hotspots". Visit Brisbane. Retrieved 18 April 2020.
- "Climate: Brisbane – Climate graph, Temperature graph, Climate table". Climate-Data.org. Archived from the original on 15 December 2013. Retrieved 28 August 2013.
- Tapper, Andrew; Tapper, Nigel (2006). "Sub-Synoptic-Scale Processes and Phenomena". In Gray, Kathleen (ed.). The weather and climate of Australia and New Zealand (Second ed.). Melbourne, Australia: Oxford University Press. p. 346. ISBN 978-0-19-558466-0.
- Linacre, Edward; Geerts, Bart (1997). "Southern Climates". Climates and Weather Explained. London: Routledge. p. 379. ISBN 0-415-12519-7.
- "Climate statistics for Australian stations – Brisbane". Bureau of Meteorology. Archived from the original on 13 August 2017. Retrieved 12 February 2018.
- "Brisbane Regional Office". Climate statistics for Australian locations. Bureau of Meteorology. Retrieved 15 January 2017.
- http://www.bom.gov.au/jsp/ncc/cdio/weatherData/av?p_nccObsCode=122&p_display_type=dailyDataFile&p_startYear=&p_c=&p_stn_num=040913
- Daniel Sankey and Tony Moore (19 July 2007). "Coldest day on record for Brisbane". The Brisbane Times. Archived from the original on 12 October 2007. Retrieved 5 January 2008.
- "Brisbane". Climate statistics for Australian locations. Bureau of Meteorology. Retrieved 16 June 2013.
- "Amberley AMO". Climate statistics for Australian locations. Bureau of Meteorology. February 2014. Retrieved 9 February 2014.
- Unknown (24 August 2009). "Hot August day as Records Fall". The Brisbane Times. Archived from the original on 27 August 2009. Retrieved 31 August 2010.
- "Brisbane Aero". Climate statistics for Australian locations. Bureau of Meteorology. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- "Brisbane Climate Guide". Archived from the original on 5 October 2011. Retrieved 9 October 2011.
- Bureau of Meteorology. "Brisbane". Archived from the original on 11 April 2020. Retrieved 13 April 2020.
- "North v South: Brisbane's Watery Divide". Brisbane Times. Retrieved 18 April 2020.
- "2016 Census Community Profile – Greater Brisbane (3GBRI – GCCSA)". Australian Bureau of Statistics. Archived from the original on 14 July 2017.; "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 14 July 2017. Retrieved 2 July 2017.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link), ZIPed Excel spreadsheet. Cover & G01a
- "2016 Census QuickStats". Australian Bureau of Statistics. Archived from the original on 14 July 2017. Retrieved 4 August 2017.
- Campbell Newman, "bmag", 3 November 2009
- "TimeWalks Brisbane — Windmill". Queensland Government. 24 March 2008. Archived from the original on 19 December 2007. Retrieved 10 April 2008.
- Statham-Drew, Pamela (1990). The Origin of Australia's Capital Cities. Cambridge University Press. p. 257. ISBN 978-0-521-40832-5.
- Pike, Jeffrey (2002). Australia. Insight. ISBN 978-981-234-799-2.
- "The Commissariat Stores". Archived from the original on 23 May 2008. Retrieved 24 February 2008.
- CTBUH. "CTBUH Tall Building Database – The Skyscraper Center". Skyscrapercenter.
- "2016 Census Community Profile – Greater Brisbane (3GBRI – GCCSA)". Australian Bureau of Statistics. Archived from the original on 14 July 2017.; "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 14 July 2017. Retrieved 2 July 2017.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link), ZIPed Excel spreadsheet. Table G09e & G09f
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 14 July 2017. Retrieved 1 July 2017.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Feature Article – Ethnic and Cultural Diversity in Australia". Australian Bureau of Statistics. Archived from the original on 20 April 2016. Retrieved 15 June 2019.
- "2016 Census QuickStats: Sunnybank". Censusdata.abs.gov.au. Archived from the original on 14 July 2017. Retrieved 19 September 2017.
- "2016 Census QuickStats: Sunnybank Hills". Censusdata.abs.gov.au. Archived from the original on 14 July 2017. Retrieved 19 September 2017.
- "2016 Census QuickStats: Stretton". Censusdata.abs.gov.au. Archived from the original on 14 July 2017. Retrieved 19 September 2017.
- "2016 Census QuickStats: Robertson (Qld)". Censusdata.abs.gov.au. Archived from the original on 14 July 2017. Retrieved 19 September 2017.
- "2016 Census QuickStats: Calamvale". Censusdata.abs.gov.au. Archived from the original on 14 July 2017. Retrieved 19 September 2017.
- "2016 Census QuickStats: Macgregor (Qld)". Censusdata.abs.gov.au. Archived from the original on 14 July 2017. Retrieved 19 September 2017.
- "2016 Census QuickStats: Eight Mile Plains". Censusdata.abs.gov.au. Archived from the original on 14 July 2017. Retrieved 19 September 2017.
- "2016 Census QuickStats: Runcorn". Censusdata.abs.gov.au. Archived from the original on 14 July 2017. Retrieved 19 September 2017.
- "2016 Census QuickStats: Rochedale". Censusdata.abs.gov.au. Archived from the original on 14 July 2017. Retrieved 19 September 2017.
- "2016 Census QuickStats: Inala". Censusdata.abs.gov.au. Archived from the original on 14 July 2017. Retrieved 19 September 2017.
- Australian Bureau of Statistics (27 June 2017). "Darra (SSC)". 2016 Census QuickStats. Retrieved 1 April 2020.

- "2016 Census QuickStats: Durack (Qld)". Censusdata.abs.gov.au. Archived from the original on 14 July 2017. Retrieved 19 September 2017.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 18 May 2019. Retrieved 18 May 2019.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 18 May 2019. Retrieved 18 May 2019.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 18 May 2019. Retrieved 18 May 2019.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 29 July 2018. Retrieved 18 May 2019.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "2016 Census Community Profile – Greater Brisbane (3GBRI – GCCSA)". Australian Bureau of Statistics. Archived from the original on 14 July 2017.; "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 14 July 2017. Retrieved 2 July 2017.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link), ZIPed Excel spreadsheet. Table G13e & G13f
- "Brisbane business visitor numbers skyrocket". Brisbane Marketing Convention Bureau. e-Travel Blackboard. 3 January 2008. Archived from the original on 20 January 2011. Retrieved 13 January 2008.
- "Brisbane Top Companies". Business News Australia. 11 October 2019. Retrieved 19 April 2020.
- "Brisbane Container Terminal, Australia". Port Technology. Archived from the original on 23 January 2008. Retrieved 29 December 2007.
- "About Us". Australia TradeCoast. Archived from the original on 8 January 2008. Retrieved 13 January 2008.
- Department of Tourism, Regional Development and Industry (14 December 2007). "Brisbane's business visitors drive $412 million domestic tourism increase". Brisbane Marketing. Archived from the original on 9 May 2008. Retrieved 29 December 2007.
- https://www.choosebrisbane.com.au/study/news-and-events/news/brisbane-doubles-international-student-enrolments-in-a-decade?sc_lang=en-au
- Remmer, Dennis (2014). BNE – The Definitive Archive: Brisbane Independent Electronic Music Production 1979–2014. Transmission Communications. p. 41. ISBN 9780646921501.
- Project BNE: Brisbane Independent Electronic Music Production 1979-2014
- "Billboard Loves Brisbane". Music News. Triple J. Archived from the original on 12 October 2007. Retrieved 15 November 2007.
- "Beijing, Berlin among music hot spots in 2007". Music News. Reuters. 1 January 2007. Archived from the original on 21 May 2008. Retrieved 29 December 2007.
- "Brisbane restaurants". Zomato. Retrieved 2 May 2020.
- "Japanese restaurants in Brisbane". Zomato. Retrieved 2 May 2020.
- "Chinese restaurants in Brisbane". Zomato. Retrieved 2 May 2020.
- "Modern Australian restaurants in Brisbane". Zomato. Retrieved 2 May 2020.
- "Italian restaurants in Brisbane". Zomato. Retrieved 2 May 2020.
- "American restaurants in Brisbane". Zomato. Retrieved 2 May 2020.
- "Indian restaurants in Brisbane". Zomato. Retrieved 2 May 2020.
- "Vietnamese restaurants in Brisbane". Zomato. Retrieved 2 May 2020.
- "2015 Buddha Birth Day Festival". Archived from the original on 17 October 2015. Retrieved 26 June 2015.
- "Buddha Birth Day Festival". Visit Brisbane. Archived from the original on 12 March 2018. Retrieved 12 March 2018.
- "International Market Tourism Facts" (PDF). Tourism Australia. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 March 2008.
- "Brisbane voted one of most beautiful cities". Brisbane Times. Archived from the original on 18 February 2015.
- "Brisbane City Council". NetCat. Archived from the original on 29 August 2007. Retrieved 28 December 2007.
- https://www.topuniversities.com/university-rankings/world-university-rankings/2020
- https://www.usnews.com/education/best-global-universities/rankings
- http://www.leidenranking.com/ranking/2017/list
- https://internationaleducation.gov.au/_layouts/download.aspx?SourceUrl=/research/International-Student-Data/Documents/INTERNATIONAL%20STUDENT%20DATA/2019/Pivot_Basic_Latest.xlsm
- Peter Beattie (4 December 2007). "Brain power drives Smart State". The Courier-Mail. Archived from the original on 2 July 2012. Retrieved 29 December 2007.
- "TAFE Queensland". Queensland Government. Archived from the original on 29 August 2007. Retrieved 2 December 2007.
- "Education Queensland". Queensland Government. Archived from the original on 17 November 2007. Retrieved 2 December 2007.
- "Year Book Australia, 2005". ABS. Archived from the original on 14 December 2007. Retrieved 19 February 2008.
- "The upgrade". Gateway Upgrade Project. Archived from the original on 6 July 2011. Retrieved 5 January 2008.
- "Queensland Rail Annual and Financial Report 2018-19" (PDF). Queensland Rail. Retrieved 25 April 2020.
- "QR Corporate - QR History - Beginnings". www.corporate.qr.com.au. Archived from the original on 15 January 2010. Retrieved 16 August 2008.
- "Cross River Rail to dominate Queensland election". The Courier Mail. News Corp. 17 June 2017. Retrieved 19 June 2017.
- "Brisbane city council to sell iconic CityCats". The Courier Mail. News Corp. 20 April 2009. Retrieved 25 April 2020.
- "About RiverWalk". Brisbane City Council. Archived from the original on 22 May 2008. Retrieved 5 January 2008.
- Airport traffic data Archived 28 August 2017 at the Wayback Machine – Bureau of Infrastructure, Transport and Regional Economics, 2017
- "Brisbane International Cruise Terminal". Port of Brisbane. Archived from the original on 4 January 2020. Retrieved 4 January 2020.
- "Hospital and Health Service maps". Queensland Health. Archived from the original on 9 November 2017. Retrieved 8 November 2017.
- https://www.rbwhfoundation.com.au/2020/05/06/urgent-funding-release-for-covid-19-grants/?fbclid=IwAR2xVQkVVl5RTLYbLkAw-iZfEn5hDbYwp2P9KJYGvErXJ_ZK8P8pUEfw1Ww. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - "The Australian Radio Guide – AM (Mediumwave) Stations – Queensland". www.radioheritage.net. Archived from the original on 30 November 2018. Retrieved 30 November 2018.
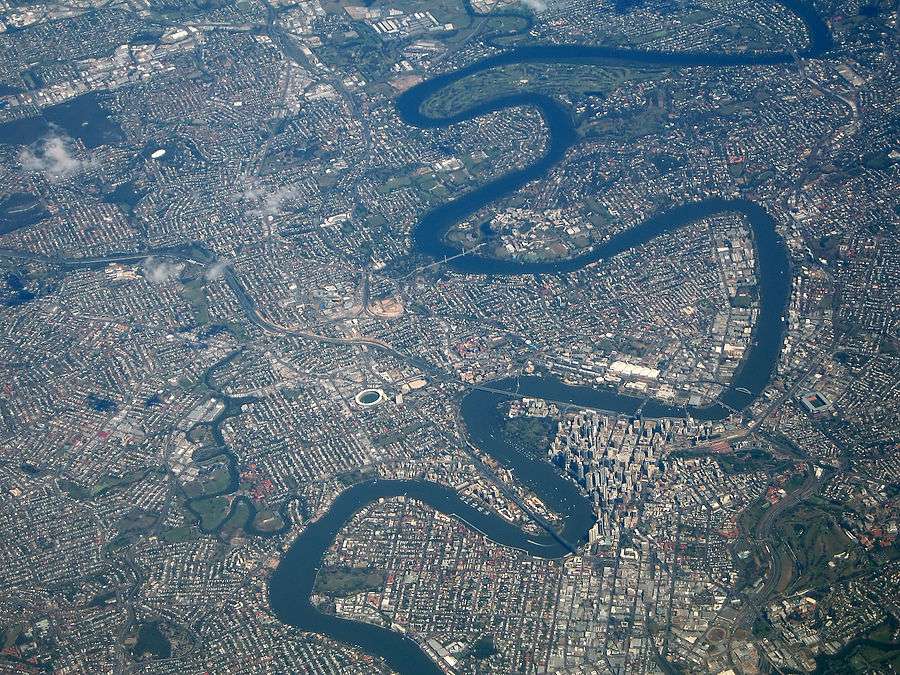





.jpg)


