Brazilian Air Force
The Brazilian Air Force (Portuguese: Força Aérea Brasileira, FAB) is the air branch of the Brazilian Armed Forces and one of the three national uniformed services. The FAB was formed when the Army and Navy air branch were merged into a single military force initially called "National Air Forces" in 1941. Both air branches transferred their equipment, installations and personnel to the new force.
| Brazilian Air Force | |
|---|---|
| Força Aérea Brasileira | |
 Brazilian Air Force COA | |
| Founded | 20 January 1941 |
| Country | |
| Type | Air force |
| Role | Aerial warfare |
| Size | 80,937 personnel (2018) 566 aircraft |
| Part of | Ministry of Defence |
| Command headquarters | Brasília, Federal District, Brazil |
| Nickname(s) | FAB |
| Patron | Alberto Santos-Dumont[1] Eduardo Gomes[1] |
| Motto(s) | Asas que protegem o País (English: "Wings that protect the country!") |
| March | Hino dos Aviadores |
| Anniversaries | May 22 (anniversary) April 22 (fighter aviation day) |
| Engagements | Contestado War (1912–16) Lieutenants Revolts (1922–27) Constitutionalist War (1932) World War II (1942–45) Lobster War (1961–63) Araguaia guerrilla (1966–74) Operation Traira (1991) |
| Commanders | |
| Commander-in-Chief | |
| Minister of Defence | |
| Commander | |
| Insignia | |
| Roundel |   |
| Fin flash |  |
| Aircraft flown | |
| Attack | A-1M, A-29, AH-2 |
| Electronic warfare | R-99, E-99 |
| Fighter | F-5EM, F-39E |
| Interceptor | F-39E |
| Patrol | P-3AM, P-95 |
| Reconnaissance | R-95, RA-1M, R-35, RQ-450, RQ-900, IAI Heron |
| Trainer | F-5FM, F-39F, AMX-T, AT-27, AT-29B, T-25, H-50 |
| Transport | C-130, C-767, KC-390, C-98, C-105, H-34, H-1, C-95, C-99, H-60, H-36 |
According to the Flight International (Flightglobal.com) and the International Institute for Strategic Studies, the Brazilian Air Force has an active strength of 80,937 military personnel and operates around 566 aircraft.[2] The Brazilian Air Force is the largest air force in the Southern Hemisphere and the second largest in the Americas after the United States Air Force.[3]
History
Contestado Campaign
The Contestado War was the first conflict in which Brazilian military aviation was employed. On September 19, 1914, taking advantage of a special train driving troops, three aircraft were boarded: a Morane-Saulnier biplace, a Morane-Saulnier monoplace and a Blitzer SIT biplace. The train continued from Rio de Janeiro passing through São Paulo where it would reach the São Paulo – Rio Grande railway to the station of União da Vitória.
Along the way, sparks shot through the locomotive, hitting a gallon of gasoline in one of the wagons carrying the dismantled aircraft. The fire spread, much like the planes. After the crash, Morane-Saulnier remained in flying condition.
In the conflict zone, he coordinated the construction of runways and hangars to be used in União da Vitória, Canoinhas and Rio Negro. Then, two Morane-Saulnier and special ammunition were brought from Rio de Janeiro, as well as a mechanic.
The first aerial activity occurred only on January 4, 1915, when a training flight followed the course of the Iguaçú River to the Timbo River. The first official mission took place on January 19 and the duration of the flight was just over an hour.
The following week, on February 25, 1915, a Morane-Saulnier had an accident. During a test flight in the vicinity of the field, the engine stopped and aircraft crashed with total loss, pilot survived.
March 1, 1915 was the scheduled date for a heavy attack on the rebels. The mission was to fly over the Valley of Santa Maria, to launch bombs on the rebels' stronghold, and to observe and direct the shots of the artillery and the advance of the infantry. Two Morane-Saulnier aircraft took off, but the attack was canceled due to adverse weather conditions, aircraft piloted by then lieutenant-aviator Ricardo Kirk suffered a crash and fell victim to fatally.
Ricardo Kirk was the first Brazilian Military Aviator. In 1891 he entered the Military Academy and he was promoted to ensign in November, 1893 and to first-lieutenant in March, 1898 and posthumously to captain in 1915.
Paulista War
Aviation had its important role in the war, although the two sides in struggle had few airplanes. The federal government had approximately 58 aircraft divided between the Navy and the Army.
On the other hand, the Paulistas had only two Potez and two Waco planes, in addition to a small number of tourist planes. At the end of July, the rebel government obtained another device, brought by Lieutenant Artur Mota Lima, who defected from Campo dos Afonsos in Rio de Janeiro. The "reds", as the federal government planes were known, not only acted on the lines of combat, but also were used to bombard several cities of São Paulo, among them Campinas, where they caused great damage. They also served as a propaganda weapon, dropping leaflets on enemy cities and into rebel concentration camps.
For the use of aerial means, General Góis Monteiro had in his Staff of two advisers, Captains Vasco Alves Secco and Carlos Pfaltzgraff Brazil.

Major Eduardo Gomes, commander of the Joint Aviation Group, who since the outbreak of hostilities had coordinated the employment of his unit and the reinforcements of the Military Aviation School, was designated, on September 16, Commander of the Air Units of the Army Detachment of the East.
On September 6, Major Ajalmar Vieira Mascarenhas was appointed Commander of the Air Units of the Detachment of the Southern Army.
The Navy's aircraft were under the direct operational control of the naval authorities, operating in support of the surface ships deployed near the port of Santos, to effect a naval blockade and also in support of the Naval Flotilla of Mato Grosso, based in Ladário. They also participated in operations with Military Aviation in the Paraíba Valley and on the southern front, in escort and observation missions.
The Air Force of São Paulo was bundled into the hands of Major Ivo Borges, Commander of the Aviation Units of the Constitutionalist Aviation, and Major Lysias A. Rodrigues, Commander of the Constitutionalist Aviation Group.
Establishment
The establishment of the United Kingdom's Royal Air Force in April 1918, and the creation of the Italian Air Force (Regia Aeronautica) and the French Air Force during the 1920s drove the idea of uniting Brazilian air power under the same organization. Together with these events the Brazilian strategists were also influenced by the theories of Giulio Douhet, Billy Mitchell and Hugh Montague Trenchard.

The first public manifest[4] to create an integrated military air service came up in 1928 when an army Major called Lysias Rodrigues wrote an article called "An urgent need: The Ministry of the Air" ("Uma premente necessidade: o Ministério do Ar"). Two years later the French Military Mission, working for the Brazilian Army, made the first steps to organize a national air arm. The idea got more support when a group of Brazilian airmen came from Italy in 1934 and explained the advantages of having a military aviation unified. Also, the Spanish Revolution and the first movements of World War II at the end of the thirties showed the importance of Air power for military strategies.
One of the main supporters of the plan to create an independent air arm was the then-president Getúlio Vargas. He organized a study group early in 1940 and the whole structure of the Ministry of Aeronautics (Ministério da Aeronáutica) was established the end of that year. This new governmental agency was responsible for the all aspects of the civil and military aviation including infrastructure, regulation and organization.[5]
Formally, the Ministry of Aeronautics was founded on January 20, 1941 and so its military branch called "National Air Forces", changed to "Brazilian Air Force" (Força Aérea Brasileira – FAB) on May, 22. The Army ("Aviação Militar") and Navy ("Aviação Naval") air branches were extinguished and all personnel, aircraft, installations and other related equipment were transferred to FAB.[5]
World War II
The Brazilian Air force made important contributions to the Allied war effort in World War II, especially as part of the Brazilian Expeditionary Force on the Italian front.[6][7][8]

From mid-1942 until the end of the war, the FAB also patrolled the Atlantic. On 31 July 1943 it claimed the German submarine U-199, which was located on the surface, off Rio de Janeiro, at 23°54′S 42°54′W. Two Brazilian aircraft, a PBY Catalina and a Lockheed Hudson, and an American PBM Mariner attacked the U-boat.[9] The Catalina, named Ärará, was captained by 2º Ten.-Av. (2nd Lt.) Alberto M. Torres,[10] and hit U-199 with depth charges, sinking her. Forty-nine of the crew were killed, although twelve Germans managed to escape, including the captain. This was possible due to the Catalina's crew, who threw a lifeboat to the survivors.

1º Grupo de Aviação de Caça (1º GAVCA; "1st Fighter Group"), which saw action in Italy, was formed on December 18, 1943. Its commanding officer was Ten.-Cel.-Av. (Aviation Lieutenant Colonel) Nero Moura.
The group had 350 men, including 43 pilots. The group was divided into four flights: Red ("A"), Yellow ("B"), Blue ("C"), and Green ("D"). The CO of the group and some officers were not attached to any specific flight. Unlike the BEF's Army component, the 1º GAVCA had personnel who were experienced Brazilian Air Force pilots. One of them was Alberto M. Torres, who had piloted a PBY Catalina that had sunk U-199, operating off the Brazilian coast.
The group trained for combat in Panama, where 2º Ten.-Av. (Aviation Second Lieutenant) Dante Isidoro Gastaldoni was killed in a training accident. On May 11, 1944, the group was declared operational and became active in the air defense of the Panama Canal Zone. On June 22, the 1º GAVCA traveled to the US to convert to the Republic P-47D Thunderbolt.
On September 19, 1944 the 1º GAVCA left for Italy, arriving at Livorno on October 6. It became part of the 350th Fighter Group of the USAAF, which in turn was part of the 62nd Fighter Wing, XXII Tactical Air Command, of the 12th Air Force.

The Brazilian pilots initially flew from 31 October 1944, as individual elements of flights attached to 350th FG squadrons, at first in affiliation flights and progressively taking part in more dangerous missions. Less than two weeks later, on November 11, the group started its own operations flying from its base at Tarquinia, using its tactical callsign Jambock. Brazilian Air Force stars replaced the white U.S. star in the roundel on the FAB Thunderbolts. The 1oGAVCA started its fighting career as a fighter-bomber unit, its missions being armed reconnaissance and interdiction, in support of the US Fifth Army, to which the FEB was attached. On April 16, 1945, the U.S. Fifth Army started its offensive along the Po Valley. By then, the strength of the Group had fallen to 25 pilots, some having been killed and others shot down and captured. Some others had been relieved from operations on medical grounds due to combat fatigue. The Group disbanded the Yellow flight and distributed the surviving pilots among the other flights. Each pilot flew on average two missions a day.
On 22 April 1945, the three remaining flights took off at 5-minute intervals, starting at 8:30 AM, to destroy bridges, barges, and motorized vehicles in the San Benedetto region. At 10:00 AM, a flight took off for an armed reconnaissance mission south of Mantua. They destroyed more than 80 tanks, trucks, and vehicles. By the end of the day, the group had flown 44 individual missions and destroyed hundreds of vehicles and barges. On this day the group flew the most sorties of the war; consequently, Brazil commemorates April 22 Brazilian Fighter Arm Day.
In all, the 1oGAVCA flew a total of 445 missions, 2,550 individual sorties, and 5,465 combat flight hours, from 11 November 1944 to 6 May 1945. The XXII Tactical Air Command acknowledged the efficiency of the Group by noting that although it flew only 5% of the total of missions carried out by all squadrons under its control, it accomplished a much higher percentage of the total destruction wrought:
_during_the_1963_Lobster_War.jpg)
- 85% of the ammunition depots
- 36% of the fuel depots
- 28% of the bridges (19% damaged)
- 15% of motor vehicles (13% damaged)
- 10% of horse-drawn vehicles (10% damaged)[11]
Post World War II
After the war, the FAB began flying the British Gloster Meteor jet fighter. The jets were purchased from the British for 15,000 tons of crude cotton, as Brazil had no foreign currency reserves to spare. The jet was operated by the FAB until the mid-1960s, when it was replaced by the F-80C and TF-33A, which were later replaced by the MB-326, Mirage III and Northrop F-5 jets.
Having been given authority over all national military aircraft since 1941, from her commissioning in 1961 to 1999 the Brazilian Air Force flew the S-2 Trackers of the aircraft carrier Minas Gerais while from 1965 naval aviation flew its own helicopters. Now naval aviation is also authorized to fly its own fixed wing carrier based aircraft.
Cold War
_RSC.jpg)
During the Cold War, the then Brazilian military government was aligned with the United States and NATO. This meant that the Northrop F-5 could be bought cheaply from the United States, which called this jet the "Freedom Fighter". Many other countries, such as Mexico, also benefited from this policy. But Brazil did not buy the F-5A Freedom Fighter, instead buying the F-5 Tiger II years later.
In 1977 the Brazilian Air Force conducted Operação Prato regarding alleged UFO sightings in the city of Colares.
The Embraer (Empresa Brasileira de Aeronáutica, Brazilian Aeronautic Co.) company has its origins as an enterprise directly managed and sponsored by the FAB. Working with Italian corporations, it developed the new AMX attack aircraft (known locally as the A-1) which makes up the backbone of the FAB's attack force. The successful Tucano T-27 trainer and the new A-29 light attack aircraft are also Embraer types used extensively by the FAB.
During Operation Traira, in February 1991, six Tucanos were used for close air support against a group of 40 rebels from the Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia (Fuerzas Armadas Revolucionarias de Colombia, FARC), which had seized a Brazilian military detachment.
Inventory
Aircraft
Weapons
Developments
.jpg)
In the early 2000s, with renewed economic stability, the FAB underwent an extensive renewal of its inventory through several acquisition programs, the most ambitious of which was the acquisition of 36 new front-line interceptor aircraft to replace its aging Mirage III. Known in the late 1990s as the F-X Project, the program was postponed during the presidential mandate of Fernando Henrique Cardoso, who in the end of 2002 left the decision for his successor Luís Inácio ‘Lula’ da Silva, who postponed it again in 2003 and 2004.[12] It was postponed indefinitely in 2005.
On July 15, 2005 one agreement was set with the French government for the transfer of twelve Dassault Mirage 2000s (ten "C" and two "B" versions) second-hand ex-Armée de L'Air. Known as F-2000s in Brazil, the first two aircraft arrived at Anápolis Air Base on September 4, 2006.
In 2007, Brazilian Air Force's Institute for Advanced Studies started the 14-X development, a hypersonic scramjet demonstrator envisaged to fly at 30 km of altitude at 3 km/s, corresponding to Mach number 10. In March 2012 a Mach 7 variation has been suggested, named as 14-X S.[13]
.jpg)
On November 4, 2007 the F-X Project was restarted.[14] Known as Project F-X2 from the start of 2008, and with a bigger budget, the competitors for acquisition were the Eurofighter Typhoon, Sukhoi Su-35, Gripen NG, Dassault Rafale, Boeing F/A-18E/F Super Hornet and, although information on Lockheed Martin's F-35 Lightning II was requested, Lockheed Martin presented an F-16 Fighting Falcon variant (designated F-16BR).[15] In October 2008, FAB released a shortlist of 3 aircraft: Saab Gripen NG, Dassault Rafale and Boeing F/A-18E/F Super Hornet. In February 2009, the three companies provided their final bids.[16] In September 2009, following a surprise French visit to Brazil, Brazilian President Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva and Nicolas Sarkozy, from France, made a new military cooperation agreement. Lula, on an interview at TV5 Monde, said French Rafale was a step forward, as technology transfer would be effective.[17]

On September 7, 2009, Brazilian Independence Day, it was announced Brazil would negotiate 36 Dassault Rafale.[18] But the Defence Minister did not confirm the final decision.
On January 5, 2010, after lobbying by Air Force Officers and Commanders, it was reported that the final evaluation report by the Brazilian Air Force placed the Saab Gripen NG ahead of the other contenders. The decisive factor was apparently the overall cost of the new fighters, both in terms of unit cost, and operating and maintenance costs, and the personal preference of the test pilots. Rafale was reported not to be even the second choice.[19] It was announced in February 2011 that the decision would be further delayed due to budget cuts.[20] And that July the decision was put off for yet another six-month extension.[21]
However, in 2013, yet another six-month delay was announced.[22] In early June 2013, after a visit from US Vice President Joe Biden with Brazilian President Dilma Rouseff; Biden assured President Rouseff that the US Congress would approve technology transfer for Boeing's F-18s.[23][24] In a move apparently following the NSA spying scandal,[25][26] Russia has also offered Brazil a stake in the development of the Sukhoi PAK-FA 5th generation jet fighter[27] with complete stealth technology transfer.[28]
.jpg)
Saab won the competition on 18 December 2013.[29][30] The change away from the American jet was due to the 2013 Global surveillance disclosure, according to Reuters reporting;[31] other sources agree with the official rationale that the decision was due to cost and technological transfer.[32] As of January 2014, Brazil is in negotiations with Saab to lease current model Gripens while they wait four years for the next generation jets on order to be developed and built.[33]

On July 28, 2015, the Brazilian government met with a Swedish trading commission to revisit the contract and request a low of 2.58% in interest rates to 1.98% per annum, generating a savings of 1 billion dollars in 25 years. Sweden rejected the application and signing the contract is seriously threatened with limit until October 2015.[34] On July 29, 2015, the Brazilian government confirmed that it had reached an agreement with Sweden to finance the purchase of a batch of 36 Gripen NG.[35]
In September 2015 Brazil finalized the US$4.68 billion purchase of 36 Saab Gripen E fighters to be delivered between 2019 and 2024. An assembly line is being established in Brazil to build 15 of the aircraft with engineers and technicians from Brazil traveling to Sweden to begin training.[36] Saab officials have said they believe this is just an initial order, with potential for additional sales to other Latin American countries.[37]
Command structure
.jpg)
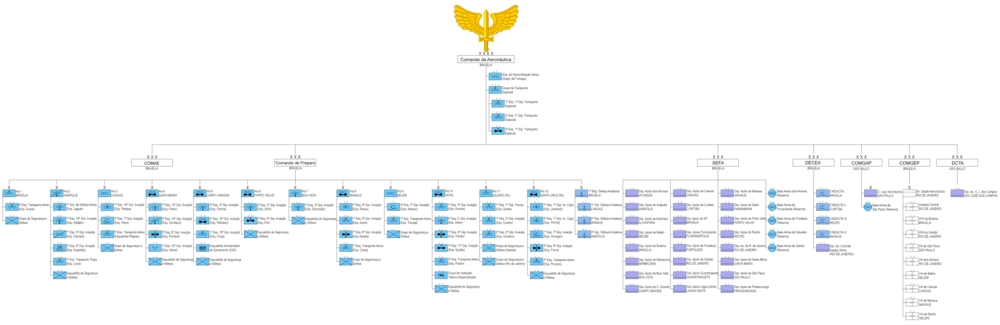
The Brazilian Air Force is the aerospace branch of the Brazilian armed forces and is managed by the "Aeronautics Command" (Comando da Aeronáutica – COMAer). The COMAer was created in 1999[38] and replaced the Ministry of Aeronautics. Now, the COMAer is one of the three armed forces assigned to the Ministry of Defense (Ministério da Defesa).
The COMAer is led by the "Aeronautics Commander" (Comandante da Aeronáutica). The Commander is a "Tenente-Brigadeiro-do-Ar" (the most senior Air Force rank), is appointed by the President, and reports directly to the Minister of Defense.
COMAer comprises six major components, four "General Commands" (Comandos-Gerais) and two "Departaments" (Departamentos). The "General Command of Air Operations" (Comando-Geral de Operações Aéreas – COMGAR), with headquarters in Brasília, supervises most of the flying operations. As the main flying element, COMGAR administers several sub-formations in the form of four "Air Forces" (Forças Aéreas) and seven "Regional Air Commands" (Comandos Aéreos Regionais – COMAR).
Besides COMGAR, other major parallel organizations, which also report directly to the COMAer, are the "General Command of Support" (Comando-Geral de Apoio – COMGAP), "General Command of Personnel" (Comando-Geral de Pessoal – COMGEP), "General Command of Aerospatial Technology" (Comando-Geral de Tecnologia Aeroespacial – CTA), "Aeronautics Departament of Teaching" (Departamento de Ensino da Aeronáutica – DEPENS), "Departament of Civil Aviation" (Departamento de Aviação Civil – DAC) and "Departament of Airspace Control" (Departamento de Controle do Espaço Aéreo – DECEA).
Operations
.jpg)
A recent operation of the FAB was the bombing of illegal landing sites in the Amazon Forest, used by drug dealers to transport drugs into and out of Brazil (see SIVAM). The operation also had support from the Brazilian Army and Brazilian Federal Police with many drug dealers being arrested as a result. The AMX Bomber/Fighter was the primary plane used.
The FAB is currently working on the United Nations Stabilization Mission in Haiti (MINUSTAH) supporting the United Nations force (a joint Brazilian, Uruguayan, Chilean and Argentine force) deployed there.
In 2010, the FAB worked on the Search & Rescue mission of Air France Flight 447. The Brazilian Air Force has started a search and rescue from the Brazilian archipelago of Fernando de Noronha, sending eight planes to search a stretch bounded by the coastal cities of Recife, Natal and the archipelago of Fernando de Noronha.
_faz_treinamento_de_intercepta%C3%A7%C3%A3o_a%C3%A9rea_para_os_Jogos_Ol%C3%ADmpicos_de_2016.jpg)
In 2011–2013, Operation Agatha marks the start of a new decade of the twenty-first century with the consolidation of the Amazon Surveillance System (SIVAM), an intricate network of radars, meteorological sensors, digital satellite communications, and advanced air-traffic-control software, among other technological advances available to Brazilian Military personnel. The Brazilian Air Force (FAB), which deployed new tactics and methods of fighting using RQ-450 remote-controlled aircraft. Operating in conjunction with sophisticated E-99 Guardian planes, they will locate objectives for A-29 Super Tucano fighters flying in darkness. Northrop F-5EM fighters, responsible for providing air superiority. In July 2016, Defense Aerospace Brazilian command displays participation of Brazilian Air Force at the Olympic Games Rio 2016, there will be over 15,000 military and 80 aircraft involved in the Olympics. To defense missions and aerial patrol 32 fighters (Northrop F-5M and A-29 Super Tucano), for aerial warning missions 2 radar aircraft (Embraer R-99), surveillance missions 3 Unmanned aircraft (Hermes 450 and Hermes 900), for maritime patrol missions 1 (P-3 Orion), for logistical support missions (Boeing C-767, C-130 and C-295), 15 helicopters (Mil Mi-35, UH-60 Black Hawk and EC-725).[39]
Exercises
The Cruzex air force exercises are the most important of its type in South America. They are hosted every 2 years by the Brazilian Air Force. Issues and participants:
- Cruzex I 2002: South Region – Argentina, Brazil, France, Chile – participation of 90 aircraft
- Cruzex II 2004: Northeast Region – Argentina, Brazil, France, Venezuela – participation of 92 aircraft
- Cruzex III 2006: Central-West Region – Argentina, Brazil, France, Chile, Uruguay, Venezuela – participation of 104 aircraft
- Cruzex IV 2008: Northeast Region – Brazil, Chile, France, Uruguay, Venezuela – participation of 100 aircraft
- Cruzex V 2010: Northeast Region – Brazil, Chile, France, Uruguay, United States – participation of 97 aircraft
- Cruzex VI 2012: Northeast Region – Argentina, Brazil, Canada, Chile, Ecuador, France, Peru, Uruguay, Venezuela, Sweden, United Kingdom, United States – personnel only, no aircraft
- Cruzex Flight 2013: Northeast Region – Brazil, Canada, Colombia, Chile, Ecuador, Uruguay, Venezuela, United States – participation of 96 aircraft
- Cruzex Flight 2018: Northeast Region – Brazil, Canada, Chile, France, Peru, Uruguay, United States – participation of 100 aircraft
Air units organization
At unit levels, "Groups" (Grupos) usually consist of one to sixteen consecutively numbered "Squadrons" (Esquadrões), each with varying numbers of aircraft, usually from six to 12. Smaller formations are known as "Flights" (Esquadrilhas). According to its tasks, a group has one of the following designations:
- Air Defense Group: Grupo de Defesa Aérea (GDA): Air defense fighters. (Fighter Jets)
- Transport Group: Grupo de Transporte (GT): Transport, Flight refueling
- Aviation Group: Grupo de Aviação (GAv): Fighter, attack, reconnaissance, SAR, rotary wing
- Fighter Aviation Group: Grupo de Aviação de Caça (GAvCa); Fighter, attack planes
- Troop Transport Group: Grupo de Transporte de Tropas (GTT): Transports, troop carrying, parachutist drop
- Special Flight Inspection Group: Grupo Especial de Inspeção em Vôo (GEIV): Calibration
- Special Test Flights Group: Grupo Especial de Ensaios de Vôo (GEEV): Test flights
- Special Transport Group: Grupo de Transporte Especial (GTE): VIP transport
Common used designations for squadrons are:
- Air Transport Squadron: Esquadrão de Transporte Aéreo (ETA)
- Air Training Squadron: Esquadrão de Instrução Aérea (EIA)
- Demonstration flying team: Esquadrão de Demonstração Aérea (EDA) (also called "Esquadrilha da Fumaça")
The Air Bases of the Brazilian Air Force are:
Photo gallery with current main aircraft
_Opera%C3%A7%C3%A3o_%C3%81gata_11_(27543292150).jpg) Northrop F-5EM (FAB).
Northrop F-5EM (FAB). AMX International A-1A (FAB).
AMX International A-1A (FAB). A-29 Super Tucano (FAB).
A-29 Super Tucano (FAB)..jpg) UH-60L (FAB).
UH-60L (FAB)..jpg) EC-725 Caracal (FAB).
EC-725 Caracal (FAB)..jpg) Mi-35M (FAB).
Mi-35M (FAB)..jpg) P-3AM (FAB).
P-3AM (FAB)..jpg) EMB145 E-99 (FAB).
EMB145 E-99 (FAB).- EMB145 R-99 (FAB).
_Rafael_Luiz_(28938052151).jpg) Boeing 767 (FAB).
Boeing 767 (FAB)..jpg) Airbus A-319CJ (FAB).
Airbus A-319CJ (FAB). EMB-195 (FAB).
EMB-195 (FAB)..jpg) C-390 (FAB).
C-390 (FAB).%2C_Brazil_-_Air_Force_AN1976288.jpg) Casa C-295 (FAB).
Casa C-295 (FAB)..jpg) Lockheed C-130M (FAB).
Lockheed C-130M (FAB)._Rafael_Luiz_(28981352976).jpg) Cessna 208 Caravan (FAB).
Cessna 208 Caravan (FAB)._(9028199498).jpg) EMB 110 (FAB).
EMB 110 (FAB)..jpg) EMB 111A (FAB).
EMB 111A (FAB)._(8101398607).jpg) UAV IAI Hermes 450 (FAB).
UAV IAI Hermes 450 (FAB).
Brazilian Air Force Infantry
The Infantry Battalions are composed of Air Force Police Companies, Air Force Infantry Companies, Firefighting Companies and Quick Reaction Companies, in addition, they are organized into:
- Battalion Staff
- Battalion Band
- Ceremonial Units
- Supply and Logistics
- Enlisted Training Section
- Mobilization and National Service
- Infantry Training and Formation
It is also considered as a linked unit to the activities of Air Force Infantry, Esquadrão Aeroterrestre de Salvamento,known as PARAR-SAR. Although it is operationally subordinated to II FAE.
Destined to the protection of the air force bases and other terrestrial installation, the air defense forces also manned by the Air Force Infantry. At FAB, there are three groups, each stationed in the air bases in Canoas, Manaus and Anápolis.
The Fire Fighting Service, whether be in the Air Force Command or in air bases, is responsible for maintaining the safety of the various military airfields, shared or not, as well as the buildings of interest of this command. Follows international standards of protection to the flight, having like the Central Organ of its management, the Direction of Aeronautical Engineering. The military and civilians belonging to this sector are properly qualified professionals and have the need to be continuously alert for the prompt attendance of aeronautical emergencies, which according to ICAO rules have only 3 minutes to attend an aeronautical emergency that occurs in the area Of the aerodrome.[40]
Formed in 1941 with the formation of the Air Force the Air Force Infantry is organized on a regional basis with units stationed in air bases all over Brazil.
Airborne Rescue Squadron (PARA-SAR)
.jpg)
The Esquadrão Aeroterrestre de Salvamento (EAS) (English: Airborne Rescue Squadron), known by its nickname Para-SAR, is a Brazilian Air Force airborne search and rescue squadron, based in the city of Rio de Janeiro.
The unit has no aircraft of its own and its airborne personnel conduct operations by being dropped from other units' aircraft. The unit has seven SAR teams located in seven states.
Each Para-SAR detachment is made up of SAR qualified military parachutists. Members of this unit can be distinguished by their maroon berets and orange baseball caps.
The Brazilian Air Force has a long history of parachute training. In 1943, at the former Alfonsos Field School of Aeronautics and with the support of the Air Force, cadet gymnastics instructor Achile Garcia Charles Astor first introduced civil parachute training in Brazil.
.jpg)
Seeing the usefulness of having a parachuting unit, the Electronics and Flight Protection Administration conducted studies to see how such a unit could be created under the auspices of the air force. The results of that study gave rise to the Para-SAR.
In 1946, the Brazilian Army formed its parachute school, the now-named General Penha Brazil Parachutist's Instruction Center. It graduated its first class of Brazilian Air Force students in 1959.
The group initially consisted of a division of three officers and five sergeants whose mandate was to provide instruction to the cadets of the School of Aeronautics and to provide search and rescue, by means of the DEPV. The unit also consisted of a group of volunteers who trained at the old military aviation school and went on to provide help in accidents and under special circumstances.
Eventually, on 2 September 1963, the Airborne Rescue unit was formed. Para-SAR is the traditional name given to the search and rescue arm of the air force and is housed in the old School of Aeronautics.
By November 20, 1973, the flotilla no longer existed, becoming the Airborne Rescue Squadron, or EAS. Its mandate was to continue training of the BAF parachutists, the instruction and the administration of the rescue teams and helicopter squadrons among other tasks.[40]
See also
References
- Personalidades [Personalities] (in Portuguese), Força aérea brasileira, archived from the original on 2008-05-21.
- "World Air Forces 2019". Flightglobal Insight. 2019. Retrieved 4 May 2019.
- "The Best Little Air Force You're Barely Aware Of". War Is Boring. 24 January 2014. Archived from the original on 17 August 2016. Retrieved 11 August 2016.
- "1", História Geral da Aeronáutica [General History of Aeronautics] (in Portuguese), 3, Incaer, 1991.
- Ad luna [To the Moon], BR: Universo online, archived from the original on 2011-09-09, retrieved 2009-11-07.
- FAB, Guerra Mundial [Brazilian Air Force, World War] (PDF) (opuscule) (in Portuguese), Força aérea brasileira, archived (PDF) from the original on 2011-07-06, retrieved 2009-11-07.
- II guerra [World War] (in Portuguese), BR, archived from the original on 2011-07-06.
- P Brasil [P Brazil] (in Portuguese), Word press, 2009-08-23, archived from the original on 2009-12-07, retrieved 2009-11-07.
- "The Type IXD2 boat U-199". German U-boats of WWII. UBoat. Archived from the original on 3 March 2010. Retrieved 9 March 2010.
- Morison, Samuel Eliot (March 2001). History of United States Naval Operations in World War II. 10: The Atlantic Battle Won. Castle Books. p. 219. ISBN 0-7858-1311-X.
- Buyers, John W, História dos 350th Fighter Group da Força Aérea Americana [History of the USAF 350th Fighter Group] (in Portuguese).
- "F‐X BR 2001–4", Global security, archived from the original on 2014-01-16, retrieved 2014-01-16.
- Carinhana Junior, Dermeval; Dacal, Luis Carlos Ogando; de Carvalho, Thiago Mendes (2015). "Atividades de Pesquisa e Desenvolvimento" (PDF). Workshop Anual de Pesquisa e Desenvolvimento do IEAv. Instituto de Estudos Avançados (Brazilian Air Force's Institute for Advanced Studies). 8: 73. ISSN 1983-1544. Archived (PDF) from the original on 6 February 2017. Retrieved 17 August 2016.
- "F‐X BR", Global security, archived from the original on 2013-12-16, retrieved 2014-01-16.
- "Brazil Offered F-16s, Not F-35s", Aviation Week, archived from the original on 2012-03-07, retrieved 2019-03-16.
- "Brazilian fighter programme ready to fly", Flight International, Flight global, 3 April 2009, archived from the original on 8 April 2009, retrieved 6 April 2009.
- "Negociações para compra de caça francês estão 'muito avançadas', diz Lula" [Negotiations for fighter acquisition are ‘very developed’, says ‘Lula’], G1 (in Portuguese), Globo, 2009-09-06, archived from the original on 2014-01-16, retrieved 2014-01-16.
- Guerreiro, Gabriela (2009-09-07), "Brasil confirma accordo para compra aviões militares da França" [Brazil confirms agreement to acquire military airplanes from France], Folha de S.Paulo (in Portuguese), Brasília, DF, BR: Universo online, archived from the original on 2009-09-10, retrieved 2009-09-07.
- Gripen favorit i Brasilien [Gripen favourite with Brazilians] (in Swedish), DNS, archived from the original on 2010-01-07, retrieved 2010-02-07.
- "Brazilian president confirms new slip to F-X2 fighter decision". Flight global. 2011-02-23. Archived from the original on 2011-02-27. Retrieved 2011-03-08.
- "Brazil jet bid extended 6 months", Space daily, AFP, 7 July 2012, archived from the original on 12 April 2013, retrieved 8 July 2012.
- "Brazil likely won't have new jets for World Cup", Reuters, 2013-03-08, archived from the original on 2015-09-24, retrieved 2017-06-30.
- Winter, Brian (4 June 2013). "Brazil closer to Boeing on jets deal after Biden visit". Thomson Reuters. Archived from the original on 19 December 2013. Retrieved 18 December 2013.
- "Brazil aims to build advanced fighter jets with Russia". Defence talk. October 16, 2013. Archived from the original on October 20, 2013. Retrieved October 20, 2013.
- "Brazil may reject US fighter jet deal over NSA spying scandal", RT, 2013-08-13, archived from the original on 2013-12-13, retrieved 2013-12-08.
- Mallén, Patricia Rey (September 12, 2013), "Boeing Might Lose $4B Brazil Deal For F-18 Jets After NSA Surveillance Scandal; Analysts Say Politics Won't Trump Business", International Business Times, archived from the original on December 18, 2013, retrieved December 8, 2013.
- "Russia to offer Brazil a stake in future advanced fighter project", RIA Novosti, 2013-10-14, archived from the original on 2013-12-19, retrieved 2013-12-08.
- "Russia offers PAK‐FA T‐50 to Brazil", Defence aviation, Oct 2013, archived from the original on 2013-12-11, retrieved 2013-12-08.
- "Brazil to award fighter jet deal to Saab", Reuters, 2013-12-18, archived from the original on 2015-09-24, retrieved 2017-06-30.
- "Saab Gripen NG wins Brazil jet fighter F-X2 competition and outbid Dassault Rafale and Boeing F-18". Air recognition. December 18, 2013. Archived from the original on December 19, 2013. Retrieved December 19, 2013.
- Winter, Brian (20 December 2013). "Insight: How US spying cost Boeing multibillion-dollar jet contract". Reuters. Thomson Reuters. Archived from the original on 20 December 2013. Retrieved 20 December 2013.
- Aboulafia, Richard (2013-12-19), Brazil's Fighter Buy: That NSA Narrative Is Probably Wrong, Forbes, archived from the original on 2018-01-26, retrieved 2017-08-25,
There’s a chance the NSA scandal played a role in Brazil’s decision. But it’s just as likely that this decision was an honest reflection of Brazilian Air Force (BAF) requirements, and a realistic appraisal of the options on offer. […] In short, the NSA scandal was probably a completely marginal factor in Brazil’s fighter decision. But for Brazil’s politicians and some of its media, the FX-2 decision provides a convenient rationale for criticizing the US.
- Haynes, Brad; Oatis, Jonathan (21 December 2013). "Brazil may wait over four years for new fighters, says Saab". Reuters. Thomson Reuters. Archived from the original on 24 December 2013. Retrieved 21 December 2013.
- "Suécia rejeita rever juros de contrato de compra dos caças Gripen NG do Brasil". Poder Aéreo. Alexandre Galante. 28 July 2015. Archived from the original on 29 July 2015. Retrieved 29 July 2015.
- "Brasil fecha acordo com Suécia para financiamento de caças da Saab". Reuters. Anthony Boadle. 29 July 2015. Archived from the original on 19 August 2015. Retrieved 29 July 2015.
- Brazil finalises $4.68bn Gripen NG deal, Flight Global, 10 September 2015. Archived 13 November 2017 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved 2017-02-14
- Saab's Next-Gen Gripen Fighter Jets Ready in May, Defense News, February 18, 2016. Retrieved 2017-02-14
- Lei complementar [Complementar law] (in Portuguese), BR: Presidency, 9 June 1999, archived from the original on 2007-02-23, retrieved 2007-01-07.
- "Força Aérea Brasileira". fab.mil.br. Archived from the original on 14 July 2016. Retrieved 11 August 2016.
- EAS (n.d.). "EAS (in Portuguese)". Archived from the original on 2009-02-03. Retrieved 2008-12-27.
Bibliography
- Hackett, James, ed. (2010-02-03), The Military Balance, London: International Institute for Strategic Studies, Routledge, ISBN 1-85743-557-5
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Air force of Brazil. |
- Brazilian Air Force website (in Portuguese)
- Brazilian Air Force page at Scramble
- History of Brazilian Air Force in World War II (in Portuguese)
- History of the Brazilian Air Force
- Milavia – Brazilian Air Force
- Military orders and medals from Brazil (in Portuguese)