beta-Naphthoflavone
beta-Naphthoflavone, also known as 5,6-benzoflavone, is a potent agonist of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor and as such is an inducer of such detoxification enzymes as cytochromes P450 (CYPs) and uridine 5'-diphospho-glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs).[1] β-Naphthoflavone is a putative chemopreventive agent.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
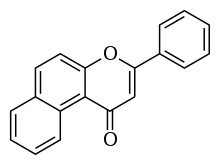
| IUPAC name
3-phenyl-1H-benzo[f]chromen-1-one | |
| Other names
5,6-Benzoflavone, BNF | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.025.417 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C19H12O2 | |
| Molar mass | 272.303 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Chlouchi A, Girard C, Bonet A, Viollon-Abadie C, Heyd B, Mantion G, Martin H, Richert L (2007). "Effect of chrysin and natural coumarins on UGT1A1 and 1A6 activities in rat and human hepatocytes in primary culture". Planta Med. 73 (8): 742–7. doi:10.1055/s-2007-981548. PMID 17599282.
- Izzotti A, Bagnasco M, Cartiglia C, Longobardi M, Camoirano A, Tampa E, Lubet RA, De Flora S (2005). "Modulation of multigene expression and proteome profiles by chemopreventive agents". Mutat Res. 591 (1–2): 212–23. doi:10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2005.03.032. PMID 16083920.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.