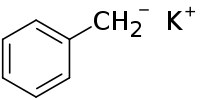
Benzyl potassium
Benzyl potassium is an organopotassium compound with the formula C6H5CH2K that takes the form of an air sensitive orange powder. Like organo-alkali metal reagents in general, benzyl potassium is highly reactive, so much so that its use in coordinating solvents such as ethers and amines is less common than in hydrocarbons, as gradual decomposition occurs.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Potassium benzyl | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H7K | |
| Molar mass | 130.231 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Orange solid |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Ignites in air |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Synthesis
One early synthesis proceeds by two-step transmetallation reaction via p-tolylpotassium:[1]
- (CH3C6H4)2Hg + 2 K → 2 CH3C6H4K + Hg
- CH3C6H4K → KCH2C6H5
A modern synthesis involves the reaction of butyllithium, potassium tert-butoxide, and toluene.[2] Although potassium hydride can also be used as a strong base for preparing potassium salts, benzyl potassium has the advantage of being molecular and hence more fast-acting.
References
- Gilman, Henry; Pacevitz, Henry A; Baine, Ogden (1940). "Benzylalkali Compounds1". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 62 (6): 1514. doi:10.1021/ja01863a054.
- Lochmann, L; Trekoval, J (1987). "Lithium-potassium exchange in alkyllithium/potassium t-pentoxide systems". Journal of Organometallic Chemistry. 326: 1. doi:10.1016/0022-328X(87)80117-1.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.