Banda Api
The small island of Banda Api (Indonesian api, fire) is an active volcano in the Banda Sea, at the center of the Banda Islands group. It has been known to Europeans since the Age of Exploration, when the Portuguese Empire and the Kingdom of the Netherlands competed in the area for spice trade. A 7 km wide and mostly submerged caldera is located at the northwest corner of the volcano.[1]
| Banda Api | |
|---|---|
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 640 m (2,100 ft) [1] |
| Listing | Spesial Ribu |
| Coordinates | 4°31′30″S 129°52′16″E |
| Geography | |
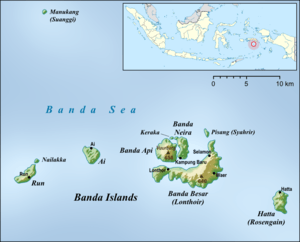 | |
| Location | Banda Api in the center of the Banda Islands |
| Geology | |
| Mountain type | Caldera |
| Last eruption | May 1988 |
Banda Api erupted on May 10, 1988, from a N-SSW-trending fissure that cut across the island, with both explosive activity and lava effusion occurring.[2]
See also
References
- "Banda Api". Global Volcanism Program. Smithsonian Institution. Retrieved 2006-12-29.
- "Types and Processes Gallery - Fissure Vents". Smithsonian Institution National Museum of Natural History: Global Volcanism Program. Retrieved 2019-03-22.
Further reading
- Alexander E. Gates and David Ritchie (2006). "Banda Api". Encyclopedia of Earthquakes and Volcanoes. Infobase Publishing. p. 25. ISBN 978-0-8160-6302-4. ISBN 0816063028.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.