Baby boom
A baby boom is a period marked by a significant increase of birth rate. This demographic phenomenon is usually ascribed within certain geographical bounds of defined national and cultural populations. People born during these periods are often called baby boomers; however, some experts distinguish between those born during such demographic baby booms and those who identify with the overlapping cultural generations. The cause of baby booms involves various fertility factors. The most well-known baby boom occurred in the mid-twentieth century, beginning in the late 1930s or early 1940s and ending in the 1960s.[1] It was a change of trend that was largely unexpected, because in most countries it occurred in the midst of a period of improving economies and rising living standards.[2]
The baby boom occurred in countries that experienced tremendous damage from the war and were going through dramatic economic hardships. These countries include Germany and Poland. In the United States the baby boom was attributed to the number of veterans returning home after the war ended in 1945. It also was due to the strong post-war American economy. The U.S. Congress passed the G.I. Bill of Rights to encourage home ownership and higher levels of education by charging very low or no interest at all on loans for veterans. Getting settled in with a more comfortable economic position allowed families to have a place to live, be educated, and start having babies. "Now thriving on the American Dream, life was simple, jobs were plentiful, and a record number of babies were born."
The U.S. birthrate exploded after World War II. From 1941 to 1961, more than 65 million children were born in the United States.[3] At the height of this baby boom, a child was born every seven seconds on average. Factors that contributed to the baby boom consisted of young couples who started families after putting off marriage during the War, government encouragement of growth of families through the aid of GI benefits, and popular culture that celebrated pregnancy, parenthood, and large families.
The baby boom was the result of couples holding off on having children due to the Great Depression and World War II. Once the baby boom began, the average woman started getting married around the age of 20 instead of 22. Couples were eager to have babies after the war ended because they knew that the world would be a safer place to start a family.[4]
Another leading cause that led to the baby boom was that people were able to afford moving out to the suburbs to raise a family instead of living in the city. Additionally, the cost of living in the suburbs was very low, especially for those returning from the military. This was also the time period where women were encouraged to take on their "roles", meaning that they were encouraged to stay home as a housewife along with being a mother while the husband worked.
The market became a seller's market. Many families were adapting to popular culture changes that included purchasing TVs, opening credit card accounts, and buying mouse ears to wear while watching The Mickey Mouse Club. Once economists realized how many children were being born, concern arose about enough resources being available, especially when those born in the baby boom time period started having kids of their own.[5]
The issues of the baby boom time period are that it could hugely impact the population change and cause social and economic impacts. One economic impact of the baby boom is the concern that when baby boomers get older and retire, the dependency ratio will increase. The Census Bureau estimates that the dependency ratio in the United States will be 65 by 2020 and reach a record-breaking high of 75, the highest it has been since the 1960s and 1970s when those baby boomers were children.[6] The economics of an area or country could benefit from the baby boom: It could increase the demand of housing, transportation, facilities and more for the increasing population. With an increase in population, the demand for food also increased. If a country cannot keep up with a rapidly increasing population, it could cause a food shortage and insufficient health care facilities. Without the sufficient supplies needed for the population, it could cause poor health that could lead to deaths in the population.[7]
Africa
"According to the new UNICEF report, almost 2 billion babies will be born in Africa between 2015 and 2050 and the 2 main driving forces behind this surge in births and children are continued high fertility rates and rising numbers of women able to have children of their own."[8]
The HIV/AIDS crisis in Africa has contributed locally to a population boom. Aid money used for contraceptives has been diverted over the past two decades into fighting HIV, which lead the number of babies born far outstripping the deaths from AIDS.[9]
France
After being in a lull of low birth rates, France experienced a baby boom after 1945.[10] The sense that the population was too small, especially in regard to the more powerful Germany, was a common theme in the early 20th century. Pronatalist policies were proposed in the 1930s and implemented in the 1940s.[11][12]
In addition, there was steady immigration, especially from former French colonies in North Africa. The population of France grew from 40.5 million in 1946 to nearly 50 million in 1968 and just under 60 million by 1999. The farm population declined sharply, from 35% of the workforce in 1945 to under 5% by 2000. By 2004, France had the second highest birthrate in Europe, behind only Ireland.[13][14]
Japan

- The First Baby Boom
In Japan, the first baby boom occurred between 1947 and 1949.[15][note 1][note 2] The number of births in the past three years exceeds 2.5 million every year, bringing the total number of births to about 8 million. The 2.69 million births in 1949 are the largest ever in postwar statistics.[note 3] The people born in this period is called the "baby boom generation" (団塊の世代, dankai no sedai, means "the generation of nodule").
- The Second Baby Boom
It often refers to a period of more than 2 million births from 1971 to 1974, with the number of births in 1973 peaking at 2.09 million.[16] However, unlike the first baby boom, this increase in the number of births is an increase in the number of births not accompanied by an increase in the total fertility rate. The people born during this period is often called "baby boom junior" (団塊ジュニア, dankai junia, means "the juniors of the generation of nodule").
The rate of births has been declining since the second baby boom.[17]
Romania
- Decreţei: (1967–1989), A baby boom in Romania was caused by a ban on abortion and contraception, consequently, hospitals became overcrowded. From the Chicago Tribune on December 26, 1967, the article stated that a doctor had to beg a woman to have a home birth due to overcrowding at the hospital, "Please stay at home, we have no rooms". The column also stated how "pregnant women were having to share hospitals beds and sickly babies were being put into oxygen tents in groups". The baby boom in Romania caused problems that began affecting the health of its residents. Abortion before being banned in 1966 was the only form of birth control, leaving people without access to that form of family planning. Another set of policies from Romania's Leader at the time, Nicolae Ceausescu, contributed to the baby boom based upon ethno-nationalism. To encourage people to have more children from dominant ethnic groups, the Romanian Government created financial incentives to have children, specifically a tax for anyone over 25 without a child. This motivated a lot of people to have children at a younger age, and with ethnic Romanian partners. Which lead to an initial surge of babies being born but then began to decrease in the birth rate to 14.3 births per 1000 individuals by the 80's. In an effort to ramp up birth rates Ceausescu made new policies. Changing the legal age to marry to 15, social media campaigns and mandating monthly gynecological exams to all women of children bearing age. This caused a near 5x increase in spending for incentives, yet managed to decrease the birth rate by 40%.[18]
United States
The term "baby boom" most often refers to the post–World War II baby boom (1941–1964) when the number of annual births exceeded 2 per 100 women (or approximately 1% of the total population size).[19] There are an estimated 78.3 million Americans who were born during this period.[20] The term is a general demographic and is also applicable to other similar population expansions.
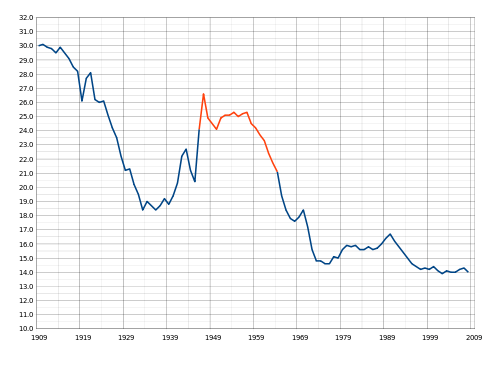
Recent baby boom periods include the following:
- Post–World War I baby boom: (1918–1929)
- Mid-twentieth century baby boom, commonly called post-World War II baby boom: Years of duration vary, depending on the source.
- Echo Boomers (Millennials): (researchers and commentators use birth years typically ranging from the early 1980s to the mid 1990s) are mostly the children of baby boomers and a few members of the Silent Generation and Gen X.[23][24]
Effects on dependency caused by the Baby boom (1941–1964)
During the baby boom the U.S. experienced after World War II, the dramatic rise in births led to a higher dependency ratio, which means that there is a large portion of the population under the age of 15 and over the age of 65 that relies on those in the work force (ages 15–64). The Cohort of this baby boom is expected to once again increase the dependency ratio once the majority is over the age of 65, as these people will no longer be part of the work force.[25] Some of the 75 million baby boomers began to reach retirement age in 2011. In the year 2000, only 12.4% of the population was 65 or over and is predicted to rise to 18% by 2020, largely due to the baby boom. Currently the Government supports social security to the population over 65, which may lead the states increasing their budget to fund programs like Medicaid.[26]
See also
Notes
- Although there are no official "vital statistics" in 1945 and 1946, the number of births in 1946 is estimated to be around 1.6 million. Therefore, it is not appropriate to set the beginning of the baby boom to 1946.
- Changes in the number of births in Japan Teikoku-shoin Co., Ltd. The trend is the same, although there are annual numbers that are slightly different from official vital statistics. Note that the number of births in 1946 is 15.7 million.
- The number of births in 1949 does not include the number of births in Okinawa prefecture before return to the mainland.
References
- Van Bavel, Jan; Reher, David S. (2013). "The Baby Boom and Its Causes: What We Know and What We Need to Know". Population and Development Review. 39 (2): 257–288. doi:10.1111/j.1728-4457.2013.00591.x.
- Reher DS (2015). "Baby booms, busts, and population ageing in the developed world". Popul Stud (Camb). 69 Suppl 1: S57–68. doi:10.1080/00324728.2014.963421. PMID 25912917.
- "Baby Boom – Birthrates Since World War II – Growth through Natural Increase: Births – Growth of U.S. Population – People – USA – North America: tubal ligation, adult baby, birth control, security system, million baby". www.countriesquest.com. Retrieved 2017-06-14.
- "The baby boom". Khan Academy. Retrieved 2017-06-14.
- "Baby Boomers - Facts & Summary". HISTORY.com. Retrieved 2017-03-21.
- Casselman, Ben (7 May 2014). "What Baby Boomers' Retirement Means For the U.S. Economy". FiveThirtyEight.
- Cromartie, John (2009). Baby Boom Migration and Its Impact on Rural America (PDF). United States Department of Agriculture.
- "Africa's Baby boom".
- Rosenthal, Elisabeth (14 April 2012). "In Nigeria, a Preview of an Overcrowded Planet". The New York Times.
- King, Leslie (1998). "France needs children". Sociological Quarterly. 39 (1): 33–52.
- Huss, Marie-Monique (1990). "Pronatalism in the inter-war period in France". Journal of Contemporary History. 25 (1): 39–68. JSTOR 260720.
- Dyer, Colin L. (1978). Population and Society in 20th-Century France. ISBN 9780841903081.
- Jones, Colin (2004). Paris: Biography of a City. p. 438.
- Pison, Gilles (March 2006). "La population de la France en 2005" (PDF). Population et Sociétés (in French) (421).
- "An overview of vital statistics (the official number)" (PDF). Retrieved 2013-06-22.
- Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications "The 2006 Youth White Paper"
- Population decline and Sub-replacement fertility by Wikipedia
- King, Leslie (2002). "Demographic trends, pronatalism, and nationalist ideologies in the late twentieth century". Ethnic and Racial Studies. 25:3 (3): 367–389. doi:10.1080/01419870020036701d.
- Bouvier, L. F. (1980-04-01). "America's baby boom generation: the fateful bulge". Population Bulletin. 35 (1): 1–36. ISSN 0032-468X. PMID 12309851.
- "Baby Boom Population: U.S. Census Bureau, USA and by State". Boomers Life. 2008-07-01. Archived from the original on 5 June 2009. Retrieved 2009-05-18.
- CDC Cdc.gov "Vital Statistics of the United States, 2003, Volume I, Natality", Table 1-1 "Live births, birth rates, and fertility rates, by race: United States, 1909-2003."
- "U.S. Census Bureau — Oldest Boomers Turn 60 (2006)".
- Leung, Rebecca (2005-09-04). "The Echo Boomers". 60 Minutes. CBS News. Archived from the original on 30 August 2010. Retrieved 2010-08-24.
- Marino, Vivian (August 20, 2006). "College-Town Real Estate: The Next Big Niche?". The New York Times. p. 1. Retrieved September 25, 2010.
College enrollments have been on the rise as the baby boomers' children — sometimes known as the "echo boom" generation — come of age. This group, born from 1982 to 1995, is about 80 million strong.
- Colby, Sandra L.; Ortman, Jennifer M. The baby boom cohort in the United States: 2012 to 2060: Population estimates and projections (2014) (PDF) (Report). CDC. pp. 1–16.
- Brucker, Eric (16 August 2006). "Demographic, Employment, Expenditure, and Income‐Related Dependency Ratios: Population Aging in the Fifty States". Public Budgeting & Finance. 26 (3): 65–80. doi:10.1111/j.1540-5850.2006.00855.x.