BH11960
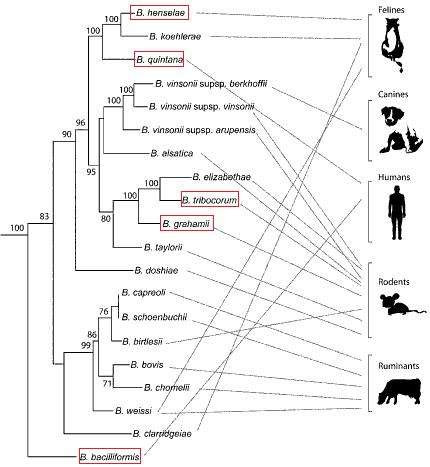
Bartonella henselae hypothetical protein 11960 (BH11960) is encoded by the BH11960 gene. This hypothetical protein is conserved in all Bartonella species whose genomes have been sequenced to date and are highlighted in the picture below.

Properties
| Nucleotides | 2085 |
| Amino acids | 934 |
| Position on genome | 1328993-1331797 |
| Molecular weight | 104093.4 |
| Motifs | Aerotolerance regulator N-terminal (E-value 5.3e-17) |
| Isoelectric Point | 9.23 |
| AA composition | 14.2% leucine |
| Estimated half-life | >10 hours in E. coli, in vivo, 30 hours in mammalian reticulocytes |
| Instability index | 41.68 unstable |
“Hypothetical protein BH11960 (Bartonella henselaei str. Houston-1”. .
Function
The function of the BH11960 protein is not known. However, it is hypothesized that its function is involved in signal transduction that regulates aerotolerance in conjunction with the other genes within its cluster. Evidence for such function is as follows:
- Presence of a PRKEL signal peptide domain at the N-terminus of the protein on all orthologs.
- Presence of MoxR-AAA family protein in the four gene cluster which is predicted to serve as a chaperone.
- Hypothesis: The signal peptide PRKEL allows for the cleavage of the N-terminal aerotolerance regulator, which is released into the cytoplasm and folded by the interacting chaperone. This cleaved and modified protein serves as a sensor for oxygen concentration changes and may go on to interact with other parts of the cell to induce a response mechanism.
Protein Sequence
The importance of this protein lies in the beginning of the sequence and is represented in the conceptual translation below. This region contains the aerotolerance motif, the transmembrane hydrophobic segment highlighted in yellow, and a high conservation region represented in all studied orthologs. Furthermore, a signal peptide protein is present in this region which allows transport of a protein.

Based on sequence analysis performed by PSortB program, this protein is located in the cytoplasmic membrane of this gram-negative bacteria and contains a double transmembrane domain.
Gene neighborhood
The four gene cluster of BH11940, BH11950, BH11960, and BH11970 are all proteins of unknown function transcribed on the sense strand and encoded by the same promoter. The promoter is ubiquitously conserved in the other Bartonella species and contains a TATA box. BH11960 is the largest of the four proteins.

Homologs
| Genus/Species | Gene Name | Accession number | Sequence Length | Sequence similarity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bartonella henselae | Hypothetical protein | BX897699.1 | 2805nt/934aa | 100 |
| Bartonella quintana | Hypothetical protein | BX897700.1 | 2805nt/934aa | 91 |
| Bartonella grahamii | Transcription regulator | CP001562.1 | 2799nt/932aa | 87 |
| Bartonella tribocorum | Alanyl-tRNA synthetase | AM260525.1 | 2799nt/932aa | 87 |
| Methylobacterium nodulans | Hypothetical protein | YP_002500318.1 | 2820nt/939aa | 53 |
| Nitrobacter hamburgensis | Double transmembrane region like | YP_578448.1 | 2817nt/938aa | 53 |
| Hyphomicrobium denitrificans | Conserved hypothetical protein | ZP_05374729.1 | 2973nt/990aa | 53 |
| Rhodopseudomonas palustris | Double transmembrane region like | YP_568432.1 | 2826nt/941aa | 54 |
| Hoeflea phototrophica | Double transmembrane region like | YP_002289983.1 | 1832nt/943aa | 55 |
| Oceanicola batsensis | hypothetical protein OB2597_11306 | ZP_00998791.1 | 2771nt/923aa | 48 |
Further reading
- Aslmark, C.M., et al. 2004. The louse-borne human pathogen Bartonella Quintana is a genomic derivative of the zoonotic agent Bartonella henselae. Proclamations of the National Academy of Science. 26: 9716-9721.