Awan (ancient city)
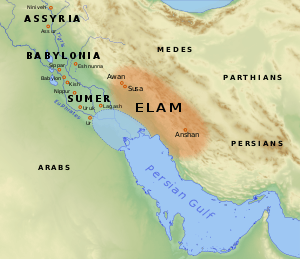
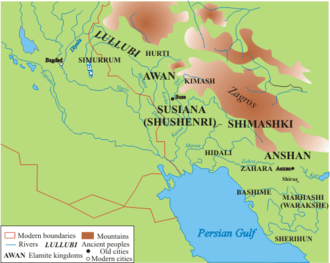
Awan (Sumerian cuneiform: 𒀀𒉿𒀭𒆠 a-wa-anki, "Country of Awan") was an ancient city-state or region of Elam in the western area of modern Iran. It often appears together with the cities of Susa and Anshan in the early history of Mesopotamia, having many conflictual interactions with Sumer.[2] The city of Awan still has not been located archaeologically.[3]

A dynasty of Elamite rulers was named after the city, the Awan Dynasty. It was founded by a ruler named Peli, and is therefore sometimes called "the dynasty of Peli".[2] According to the Sumerian King List, Awan put an end to the First Dynasty of Ur circa 2450 BCE, and three kings of Awan then ruled over the southern regions of Sumer.
Circa 2300-2200 BCE, the Akkadian Empire claimed numerous victories over Awan, under its rulers Sargon of Akkad and Rimush.[2] Naram-Sin however signed an alliance with Khita, the 9th king of Awan.[2][4]
Awan wrestled independence from the Akkadians during the reign of Shar-Kali-Sharri.[4] But some time later, the Awan Dynasty ended with the demise of its last king, Kutik-Inshushinak, followed by the control of the Third Dynasty of Ur over the region, circa 2100-2000 BCE.[2][4]
After these events, the name "Awan" disappears from history.[2]
References
- "Awan King List".
- Gershevitch, I. (1985). The Cambridge History of Iran. Cambridge University Press. p. 26. ISBN 978-0-521-20091-2.
- Liverani, Mario (2013). The Ancient Near East: History, Society and Economy. Routledge. p. 142. ISBN 978-1-134-75084-9.
- Hansen, Donald P. (2002). Leaving No Stones Unturned: Essays on the Ancient Near East and Egypt in Honor of Donald P. Hansen. Eisenbrauns. p. 233. ISBN 978-1-57506-055-2.