Australian rules football playing field
An Australian rules football playing field is a venue where Australian rules football is played.
The playing field is typically a large oval-shaped grass surface (often modified cricket fields). These fields may vary especially for variations of the game. However, for official Australian Football League matches, strict requirement specifications must be met for stadiums.
Standard specifications
Ground dimensions
Australian rules football grounds, even at the highest level of the game, have no fixed dimensions. For senior football, the playing field is an oval, typically between 135–185 metres (148–202 yd) long goal-to-goal and 110–155 metres (120–170 yd) wide wing-to-wing. Grounds can vary from long and narrow to almost circular, and are not necessarily symmetrical, depending upon how and where the field was constructed. At least 5 metres (5.5 yd) of space between the boundary line and any fence is required for safety.
Smaller fields are generally used for junior football; some are purpose-built, and some are temporarily marked out within the confines of full-sized oval; as for a senior match, there are no fixed dimensions for a junior-sized field. The Western Australian Football Commission advises that a good rule of thumb is to set the length of the field equivalent to 3 1⁄2 times the length of an average kick of the age group playing.[1]
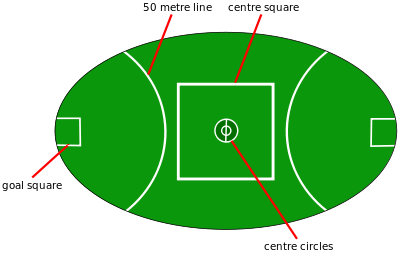
Ground markings
A top-level Australian rules football ground has the following markings:[1]
- Two goal-lines, one at each end of the field, which are straight and 19.2 m (21 yd) long.
- Two boundary lines, which are curved around the edge of the field and connect the two goal-lines. Together, the boundary-lines and the goal-lines mark out the playing area, in a slightly truncated oval.
- Two goal squares, one at each end of the field, which are 6.4 m × 9 m (7 yd × 10 yd) in front of each goal-face. The line parallel to the goal line is called the kick-off line. The goal square is the area from which a kick-in can occur.
- The centre square, which is 50 m × 50 m (55 yd × 55 yd) in the centre of the ground.[2] This square dictates how many midfielders can be present at a centre bounce.
- The centre circles: two concentric circles of 3 m (3.3 yd) and 10 m (11 yd) diameter, with a line bisecting them running wing-to-wing. These markings dictate where the ruckmen can stand during a centre bounce.
- Two fifty-metre arcs: a circular arc at each end of the field drawn between the boundary lines at a distance of 50 m (55 yd) from the centre of the goal-line. Except in competitions which allow for super goals, these arcs serve only as an informative visual indicator of distance.
- Interchange gates: two short markings on the boundary line near the interchange benches, which dictate where players may enter and exit the ground for interchanges.
Grounds at lower or junior levels, particularly small grounds, may lack some of these markings.
Goal posts
At each end of the ground there are two goal posts, spaced 6.4 m (7 yd) apart; these are conventionally painted white. A further 6.4 m (7 yd) on either side of these are behind posts; the behind posts are shorter than the goal posts; additionally, in South Australia it is customary for behind posts to be painted red, 5 metres (16 ft) in height.[3] All posts are typically padded with wall padding to minimise injury due to players colliding with them.[1]
Surface
Playing surface is a controversial issue in Australian rules football due to possible injuries caused to players moving at high speed including marking, jumping, turning and being tackled without protective padding. For these reasons the playing field standards imply use of lawn as a surface.
Purpose-built stadiums
Almost all Australian rules football fields are of a suitable size and shape for cricket; and in the majority of cases, the fields are used for cricket in the summer and Australian rules football in the winter, a seasonal strategy which is part of the history of Australian sport. As a consequence of this, there are very few fields which were purpose-built for and used by Australian rules football to the exclusion of cricket and all other sports.
However, there are many grounds – particularly those built more recently – which were built with Australian rules football as the primary intended purpose, but upon which other sports, including cricket, have been played.
| Stadium | Location | Opened | Built for | Capacity at Construction | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Casey Fields VFL Oval | Cranbourne, Victoria | 2006 | City of Casey | 15,000 | Other ovals in the complex are used for cricket |
| Docklands Stadium | Melbourne Docklands, Victoria | 2000 | Australian Football League | 53,000 | Primarily for Australian rules football, but regularly hosts other football codes, concerts and cricket |
| Football Park | West Lakes, South Australia | 1971 | South Australian National Football League | 60,000 | Hosted World Series Cricket matches |
| Waverley Park | Mulgrave, Victoria | 1970 | Victorian Football League | 78,000 | Hosted World Series Cricket matches |
| Skinner Reserve | Braybrook, Victoria | 1966 | Victorian Football Association | Has been opened to other sports since 1989[4] | |
| Richmond Oval | Adelaide, South Australia | 1958 | West Adelaide Football Club | 16,500 | Has also hosted American football |
Variations
Variations of the standard field dimensions and layout exist. For junior levels, smaller fields are often used. Rectangular fields have also been used in the past in Australia and also overseas, as well as adapted fields from other sports such as Association Football and American Football.
References
- Western Australian Football Commission Inc. "Dimensions for football – Australian rules". Government of Western Australia, Department of Sport and Recreation. Retrieved 12 April 2014.
- Laws of Football 2017, p12
- Michelangelo Rucci (28 March 2014). "Footy fans march back to the Adelaide Oval of the future". The Advertiser. Adelaide, SA. Retrieved 12 April 2014.
- Santo Caruso; Marc Fiddian; Jim Main (2002), Football Grounds of Melbourne, Essendon North, VIC: Pennon Publishing, p. 146