Arduino IDE
The Arduino Integrated Development Environment (IDE) is a cross-platform application (for Windows, macOS, Linux) that is written in functions from C and C++[2]. It is used to write and upload programs to Arduino compatible boards, but also, with the help of 3rd party cores, other vendor development boards.[3]
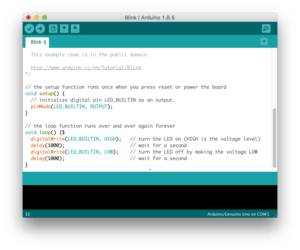 Screenshot of Arduino IDE showing Blink program | |
| Developer(s) | Arduino Software |
|---|---|
| Stable release | 1.8.13
/ 16 June 2020[1] |
| Repository | |
| Written in | C, C++, Java |
| Operating system | Windows, macOS, Linux |
| Platform | IA-32, x86-64, ARM |
| Type | Integrated development environment |
| License | LGPL or GPL license |
| Website | www |
The source code for the IDE is released under the GNU General Public License, version 2.[4] The Arduino IDE supports the languages C and C++ using special rules of code structuring.[5] The Arduino IDE supplies a software library from the Wiring project, which provides many common input and output procedures. User-written code only requires two basic functions, for starting the sketch and the main program loop, that are compiled and linked with a program stub main() into an executable cyclic executive program with the GNU toolchain, also included with the IDE distribution.[6] The Arduino IDE employs the program avrdude to convert the executable code into a text file in hexadecimal encoding that is loaded into the Arduino board by a loader program in the board's firmware.[7] By default, avrdude is used as the uploading tool to flash the user code onto official Arduino boards[8].
| Developer(s) | Arduino Software |
|---|---|
| Preview release | v0.0.2
/ 28 October 2019[9] |
| Repository | |
| Written in | C, C++ |
| Operating system | Windows, macOS, Linux |
| Platform | IA-32, x86-64, ARM |
| Type | Integrated development environment |
| License | LGPL or GPL license |
| Website | blog |
With the rising popularity of Arduino as a software platform, other vendors started to implement custom open source compilers & tools (cores) that can build and upload sketches to other MCUs that are not supported by Arduino's official line of MCUs.
In October 2019 the Arduino organization began providing early access to a new Arduino Pro IDE with debugging[10] and other advanced features.[11]
References
- "Arduino Software Release Notes". Arduino Project. Retrieved September 25, 2019.
- https://www.arduino.cc/en/main/FAQ#toc13
- "Updated: Arduino announces FPGA board, ATmega4809 in Uno Wi-Fi mk2, cloud-based IDE and IoT hardware". Electronics Weekly. 2018-05-18. Retrieved 2018-06-14.
- "The arduino source code". The Arduino source code.
- Purdum, Jack J. Beginning C for Arduino : learn C programming for the Arduino (Second ed.). [New York]. ISBN 9781484209400. OCLC 912875060.
- Castro, Jorge R. Building a home security system with Arduino : design, build, and maintain a home security system with Arduino Uno. Birmingham, UK. p. 15. ISBN 9781785283802. OCLC 922588951.
- Banzi, Massimo; Shiloh, Michael. Getting started with Arduino (Third ed.). Sebastopol, CA. ISBN 9781449363314. OCLC 898290173.
- "Sketch build process - Arduino CLI". arduino.github.io. Retrieved 2020-03-24.
- "Arduino Pro Release Notes". Arduino Project. Retrieved November 4, 2019.
- "The Arduino IDE Finally Grows Up". Hack A Day. 2019-10-21. Retrieved 2019-11-04.
- "Introducing New Arduino Pro IDE with Advanced Features". SEEED Studio. 2019-10-21. Retrieved 2019-11-04.