Airplane game
An airplane game, also known as the Plane Game, was a style of pyramid scheme active in the 1980s in North America.
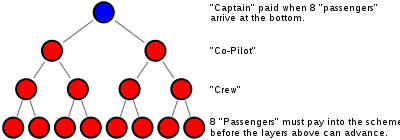
The common version of the system involved joining an "airplane" by paying a "pilot" to become one of eight "passengers".[1][2] Passengers started at the fourth step from being paid. Already on the airplane were four "flight attendants" who were a step ahead, and two "co-pilots" next in line behind the pilot. Once a pilot collected $12,000 from passengers to retire, the group split into two "airplanes", with each co-pilot becoming the pilot of the new airplane, taking half the participants and promoting everyone a level. Bringing in new passengers sped up everyone's progression towards retiring as a pilot.[1] However, the structure of the scheme results in a participant losing the entire payment unless 14 new participants join.[2]
The scheme had spread from New York to Texas to California then South Florida by early 1987,[2] with police raiding meetings in all four states,[3][1][2][4] and reports of more airplane schemes operating in Dallas.[4] In Dade County, Florida, at least one recruiting session was reported with 1,000 attendees.[2] Though common versions at the time required passengers to pay $1,500 to receive $12,000 as a pilot,[1][2][4] some airplanes were being run with $5,000 passengers and a $40,000 pilot payout.[2]
The scheme has also gone by the names Concorde and Golden Galaxy with similar names for the steps. Cash Club, Victoria operated in the same way but with different amounts and the steps renamed to "club member", "committee member", "vice-president", and "president". "Krona Klub" was a similar scheme with more complex payout rules, as was a so-called game variously called "Cosmic Adventure", "Flying Saucer", or "Flying Starship".[5]
The scheme resurfaced in 2020, conducted over Instagram and other social media platforms, going by a variety of names including Loom Game[6] and Wheel [7]
References
- Neuffer, Elizabeth (April 7, 1987). "'Airplane': High-Stakes Chain Letter". The New York Times (National ed.). p. B7. Retrieved 2018-04-10.
- Enscoe, David (March 26, 1987). "Pyramid Scheme Takes Off Thousands Invest In 'Plane Game'". Sun-Sentinel. Retrieved 2018-04-10. Published in print edition as "'Plane Game' taking many for a big ride".
- "Pyramid Scheme Grounded". Houston Chronicle. October 31, 1986.
- "Police Clip Wings of 'Airplane Game' : Arrest Four Alleged Promoters of Version of Pyramid Scheme". Los Angeles Times (online ed.). March 19, 1987. Retrieved 2018-04-10.
- Branscum, Bill E. (2002). "Pyramid Scheme: Real Scams for Your Study and Review". FraudsAndScams.com. Naples, Florida. Retrieved 2018-04-10.
- "Loom Game: Reddit r/scams". Reddit r/scams. Retrieved 21 April 2020.
- "Reddit.com /r/antiMLM " Just because you call it a wheel doesn't mean it's not a pyramid scheme."". Reddit.com /r/antiMLM. Retrieved 21 April 2020.
External links
- Linda Rosewood Hooper. "The Pyramid Game: It's a Lie, It's a Scam, and It Won't Work". Linda Rosewood Hooper: Writings (personal website). Santa Cruz, California: University of California, Santa Cruz. Retrieved 2017-04-10. Originally written in Spring 1993.