Acidic leucine-rich nuclear phosphoprotein 32 family member A
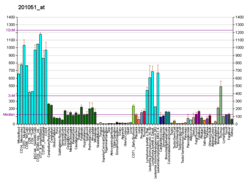
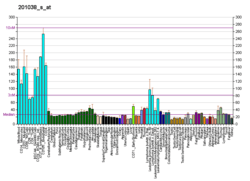
Acidic leucine-rich nuclear phosphoprotein 32 family member A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ANP32A gene.[3][4][5] It is one of the targets of an oncomiR, MIRN21.
Interactions
Acidic leucine-rich nuclear phosphoprotein 32 family member A has been shown to interact with MAP1B,[6] TAF1A[7] and Protein SET.[7][8]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000140350 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Chen TH, Brody JR, Romantsev FE, Yu JG, Kayler AE, Voneiff E, Kuhajda FP, Pasternack GR (March 1997). "Structure of pp32, an acidic nuclear protein which inhibits oncogene-induced formation of transformed foci". Mol Biol Cell. 7 (12): 2045–56. doi:10.1091/mbc.7.12.2045. PMC 276049. PMID 8970164.
- Ulitzur N, Humbert M, Pfeffer SR (June 1997). "Mapmodulin: a possible modulator of the interaction of microtubule-associated proteins with microtubules". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 94 (10): 5084–9. Bibcode:1997PNAS...94.5084U. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.10.5084. PMC 24635. PMID 9144194.
- "Entrez Gene: ANP32A Acidic (leucine-rich) nuclear phosphoprotein 32 family, member A".
- Opal, Puneet; Garcia Jesus J; Propst Friedrich; Matilla Antoni; Orr Harry T; Zoghbi Huda Y (September 2003). "Mapmodulin/leucine-rich acidic nuclear protein binds the light chain of microtubule-associated protein 1B and modulates neuritogenesis". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (36): 34691–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M302785200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 12807913.
- Seo, S B; McNamara P; Heo S; Turner A; Lane W S; Chakravarti D (January 2001). "Regulation of histone acetylation and transcription by INHAT, a human cellular complex containing the set oncoprotein". Cell. 104 (1): 119–30. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00196-9. ISSN 0092-8674. PMID 11163245.
- Fan, Zusen; Beresford Paul J; Zhang Dong; Lieberman Judy (April 2002). "HMG2 interacts with the nucleosome assembly protein SET and is a target of the cytotoxic T-lymphocyte protease granzyme A". Mol. Cell. Biol. 22 (8): 2810–20. doi:10.1128/MCB.22.8.2810-2820.2002. ISSN 0270-7306. PMC 133744. PMID 11909973.
Further reading
- Matilla A, Radrizzani M (2005). "The Anp32 family of proteins containing leucine-rich repeats". Cerebellum. 4 (1): 7–18. doi:10.1080/14734220410019020. PMID 15895553.
- Schraven B, Kirchgessner H, Gaber B, et al. (1991). "A functional complex is formed in human T lymphocytes between the protein tyrosine phosphatase CD45, the protein tyrosine kinase p56lck and pp32, a possible common substrate". Eur. J. Immunol. 21 (10): 2469–77. doi:10.1002/eji.1830211025. PMID 1655467.
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (1994). "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene. 138 (1–2): 171–4. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
- Vaesen M, Barnikol-Watanabe S, Götz H, et al. (1994). "Purification and characterization of two putative HLA class II associated proteins: PHAPI and PHAPII". Biol. Chem. Hoppe-Seyler. 375 (2): 113–26. doi:10.1515/bchm3.1994.375.2.113. PMID 8192856.
- Fink TM, Vaesen M, Kratzin HD, et al. (1996). "Localization of the gene encoding the putative human HLA class II associated protein (PHAPI) to chromosome 15q22.3-q23 by fluorescence in situ hybridization". Genomics. 29 (1): 309–10. doi:10.1006/geno.1995.1257. PMID 8530098.
- Andersson B, Wentland MA, Ricafrente JY, et al. (1996). "A "double adaptor" method for improved shotgun library construction". Anal. Biochem. 236 (1): 107–13. doi:10.1006/abio.1996.0138. PMID 8619474.
- Li M, Makkinje A, Damuni Z (1996). "Molecular identification of I1PP2A, a novel potent heat-stable inhibitor protein of protein phosphatase 2A". Biochemistry. 35 (22): 6998–7002. doi:10.1021/bi960581y. PMID 8679524.
- Yu W, Andersson B, Worley KC, et al. (1997). "Large-scale concatenation cDNA sequencing". Genome Res. 7 (4): 353–8. doi:10.1101/gr.7.4.353. PMC 139146. PMID 9110174.
- Matilla A, Koshy BT, Cummings CJ, et al. (1997). "The cerebellar leucine-rich acidic nuclear protein interacts with ataxin-1". Nature. 389 (6654): 974–8. Bibcode:1997Natur.389..974M. doi:10.1038/40159. PMID 9353121.
- Suzuki Y, Yoshitomo-Nakagawa K, Maruyama K, et al. (1997). "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene. 200 (1–2): 149–56. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3. PMID 9373149.
- Kadkol SS, Brody JR, Pevsner J, et al. (1999). "Modulation of oncogenic potential by alternative gene use in human prostate cancer". Nat. Med. 5 (3): 275–9. doi:10.1038/6488. PMID 10086381.
- Brody JR, Kadkol SS, Mahmoud MA, et al. (1999). "Identification of sequences required for inhibition of oncogene-mediated transformation by pp32". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (29): 20053–5. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.29.20053. PMID 10400610.
- Brennan CM, Gallouzi IE, Steitz JA (2000). "Protein ligands to HuR modulate its interaction with target mRNAs in vivo". J. Cell Biol. 151 (1): 1–14. doi:10.1083/jcb.151.1.1. PMC 2189805. PMID 11018049.
- Seo SB, McNamara P, Heo S, et al. (2001). "Regulation of histone acetylation and transcription by INHAT, a human cellular complex containing the set oncoprotein". Cell. 104 (1): 119–30. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00196-9. PMID 11163245.
- Bai J, Brody JR, Kadkol SS, Pasternack GR (2001). "Tumor suppression and potentiation by manipulation of pp32 expression". Oncogene. 20 (17): 2153–60. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1204294. PMID 11360199.
- Beresford PJ, Zhang D, Oh DY, et al. (2001). "Granzyme A activates an endoplasmic reticulum-associated caspase-independent nuclease to induce single-stranded DNA nicks". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (46): 43285–93. doi:10.1074/jbc.M108137200. PMID 11555662.
- Gallouzi IE, Steitz JA (2001). "Delineation of mRNA export pathways by the use of cell-permeable peptides". Science. 294 (5548): 1895–901. Bibcode:2001Sci...294.1895G. doi:10.1126/science.1064693. PMID 11729309.
External links
- Human ANP32A genome location and ANP32A gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.