48 Doris
Doris (minor planet designation: 48 Doris) is one of the largest main belt asteroids. It was discovered on 19 September 1857 by Hermann Goldschmidt from his balcony in Paris.
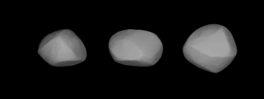 Three-dimensional model of 48 Doris created based on light-curve | |
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Hermann Mayer Salomon Goldschmidt |
| Discovery date | September 19, 1857 |
| Designations | |
| (48) Doris | |
| Pronunciation | /ˈdɔːrɪs/[1] |
Named after | Doris |
| Main belt | |
| Adjectives | Dorian /ˈdɔːriən/[2] |
| Orbital characteristics[3] | |
| Epoch December 31, 2006 (JD 2454100.5) | |
| Aphelion | 500.093 Gm (3.343 AU) |
| Perihelion | 430.463 Gm (2.877 AU) |
| 465.278 Gm (3.110 AU) | |
| Eccentricity | 0.075 |
| 2003.453 d (5.49 a) | |
| 336.191° | |
| Inclination | 6.554° |
| 183.754° | |
| 257.583° | |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions | 278×142km[4] 221.8 ± 7.5 km (IRAS)[3] |
| Mass | (1.23±0.60)×1019 kg[lower-alpha 1][5] |
Mean density | 2.12±1.07 g/cm3[6] |
| 11.89 h[3] | |
| 0.062[3][7] | |
| C[3] | |
| 6.90[3] | |
Name
To find a name for the object, Jacques Babinet of the Academy of Sciences created a shortlist and asked the geologist Élie de Beaumont to make the selection. De Beaumont chose Doris, after an Oceanid in Greek mythology. Since Doris was discovered on the same night as 49 Pales, de Deaumont suggested naming the two "The Twins".[8]
Physical characteristics
An occultation on March 19, 1981, suggested a diameter of 219±25 km.[9] Observations of an occultation on October 14, 1999, using four well-placed chords, indicate an ellipsoid of 278×142 km and that 48 Doris is an extremely irregularly shaped object.[4]
In popular culture
48 Doris is a location in the text-based science fiction game Federation 2.
Notes
- 6.1 ± 3.0) × 10−12 M☉
References
- "Doris". Merriam-Webster Dictionary.
- "Dorian". Oxford English Dictionary (3rd ed.). Oxford University Press. September 2005. (Subscription or UK public library membership required.)
- "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: 48 Doris" (2008-06-13 last obs). Retrieved 10 November 2008.
- "Occultation of HIP 29126 by (48) Doris - 2001 November 28". Royal Astronomical Society of New Zealand. Retrieved 30 November 2008.
- Kochetova (2004)
- Masses and densities of minor planets Archived 2011-06-04 at the Wayback Machine - Yu. Chernetenko, O. Kochetova, and V. Shor
Kochetova (2004) - Asteroid Data Sets Archived 2009-12-17 at the Wayback Machine
- Schmadel, Lutz D. (2003). Dictionary of Minor Planet Names. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 20. ISBN 978-3-540-00238-3.
- Ludek Vasta; Jan Manek (26 July 2005). "Observed Minor Planet Occultation Events". Asteroidal Occultations (Czech Astronomical Society). Retrieved 7 December 2008.
- "JPL Close-Approach Data: 48 Doris" (2009-08-11 last obs). Retrieved 23 February 2010.
External links
- 48 Doris at AstDyS-2, Asteroids—Dynamic Site
- 48 Doris at the JPL Small-Body Database
