(316179) 2010 EN65
(316179) 2010 EN65 is a trans-Neptunian object (TNO) orbiting the Sun. However, with a semi-major axis of 30.8 AU, the object is actually a jumping Neptune trojan, co-orbital with Neptune, as the giant planet has a similar semi-major axis of 30.1 AU. The body is jumping from the Lagrangian point L4 into L5 via L3.[2] As of 2016, it is 54 AU from Neptune. By 2070, it will be 69 AU from Neptune.[4]
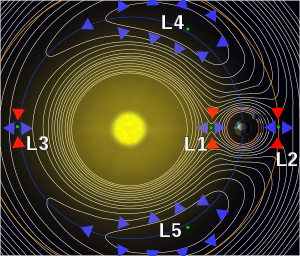 2010 EN65 is jumping from L4 to L5 via L3. | |
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | D. L. Rabinowitz S. W. Tourtellotte |
| Discovery site | La Silla Obs. |
| Discovery date | 7 March 2010 |
| Designations | |
| (316179) 2010 EN65 | |
| TNO [1] · Neptune trojan [2] · distant [3] | |
| Orbital characteristics [1] | |
| Epoch 23 March 2018 (JD 2458200.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 2 | |
| Observation arc | 25.45 yr (9,296 days) |
| Aphelion | 40.367 AU |
| Perihelion | 21.148 AU |
| 30.758 AU | |
| Eccentricity | 0.3124 |
| 170.58 yr (62,306 days) | |
| 48.107° | |
| 0° 0m 20.88s / day | |
| Inclination | 19.209° |
| 234.47° | |
| 225.77° | |
| Physical characteristics | |
Mean diameter | 200 km |
| 7.1[1] | |
Discovery
(316179) 2010 EN65 was discovered on March 7, 2010 by David L. Rabinowitz and Suzanne W. Tourtellotte using the 1.3-m reflector from Cerro Tololo.[5]
Orbit
(316179) 2010 EN65 follows a rather eccentric orbit (0.31) with a semi-major axis of 30.72 AU and an inclination of 19.3º.[1] Its orbit is well determined with images dating back to 1989.
Physical properties
(316179) 2010 EN65 is a quite large minor body with an absolute magnitude of 6.9 and a diameter likely close to 200 km (120 mi).[1]
Jumping trojan
(316179) 2010 EN65 is another co-orbital of Neptune, the second brightest after the quasi-satellite (309239) 2007 RW10. (316179) 2010 EN65 is currently transitioning from librating around Lagrangian point L4 to librating around L5.[2] This unusual trojan-like behavior is termed "jumping trojan".[6]
Numbering and naming
This minor planet was numbered by the Minor Planet Center on 7 February 2012.[7] As of 2018, it has not been named.[3] If named, it will follow the naming scheme already established with 385571 Otrera and 385695 Clete, which is to name these objects after figures related to the Amazons, an all-female warrior tribe that fought in the Trojan War on the side of the Trojans against the Greek.[8]
References
- "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: 316179 (2010 EN65)" (2015-04-18 last obs.). Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Retrieved 25 February 2018.
- de la Fuente Marcos, C.; de la Fuente Marcos, R. (November 2012). "Four temporary Neptune co-orbitals: (148975) 2001 XA255, (310071) 2010 KR59, (316179) 2010 EN65, and 2012 GX17". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 547: 7. arXiv:1210.3466. Bibcode:2012A&A...547L...2D. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201220377. Retrieved 7 September 2016. (rotating frame)
- "316179 (2010 EN65)". Minor Planet Center. Retrieved 25 February 2018.
- 2010 EN65 at JPL Horizons Change "Observer Location" to @Neptune
- Lowe, A.; Helin, E. F.; Pravdo, S.; Lawrence, K.; Hicks, M.; Thicksten, R.; Rabinowitz, D.; Tourtellotte, S.; Marsden, B. G. (7 May 2010). "2010 EN65". Minor Planet Electronic Circular. 2010-J33.
- Tsiganis, K.; Dvorak, R.; Pilat-Lohinger, E. (February 2000). "Thersites: a `jumping' Trojan?". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 354: 1091–1100. Bibcode:2000A&A...354.1091T.
- "MPC/MPO/MPS Archive". Minor Planet Center. Retrieved 25 February 2018.
- Ticha, J.; et al. (10 April 2018). "DIVISION F / Working Group for Small Body Nomenclature Working Group for Small Body Nomenclature. THE TRIENNIAL REPORT (2015 Sept 1 - 2018 Feb 15)" (PDF). IAU. Retrieved 25 August 2018.
External links
- List of Centaurs and Scattered Disk Objects, Minor Planet Center
- List of Trans Neptunian Objects, Minor Planet Center
- Another list of TNOs
- (316179) 2010 EN65 at the JPL Small-Body Database