Union Station (Chattanooga)
Union Station | |
|---|---|
| Inter-city rail | |
| Line(s) | W&A, TA&G, NC&StL, M&C, ET&G, L&N |
| History | |
| Opened | 1859 |
| Closed | 1970 (demolished 1972) |
| Rebuilt | 1882, 1900, 1926 |
Chattanooga Union Station, more commonly known as the Union Depot in Chattanooga, constructed between 1857-1859, served as a train car shed in Chattanooga, TN, and was one of two major railroad terminals in the city, the other being Terminal Station.
It stood at Broad Street and Ninth Street, which is now Martin Luther King Blvd.
Modifications were added in 1868 and 1881 to include offices and waiting rooms. The train car shed was in use during and after the Civil War. After failed efforts to preserve the structure, the Union Depot was torn down in 1972.[1]
History
The Union Depot was constructed of limestone and brick; the bricks used were made by slaves. The center line of the train car shed was the boundary line between the Western & Atlantic Railway and the Nashville & Chattanooga Railway.[2] During the Civil War, the train car shed was used as an army hospital. A head house was added in 1882, and the south end was demolished and replaced with butterfly sheds in 1926.[3] In 1900, Georgian marble floors were added to the building, which was appropriate because Georgia owned the land that the Union Depot stood on.[4]
There was disagreement over the facility' ownership. The courts ultimately ruled in favor of Georgia, and determined that the Western & Atlantic Railway and the Nashville & Chattanooga Railway were the rightful owners. The debate over ownership resulted in the organization of the Chattanooga Station Company in 1905. The company was formed by the three lines of the Southern Railway System and the Central of Georgia Railway.[2]
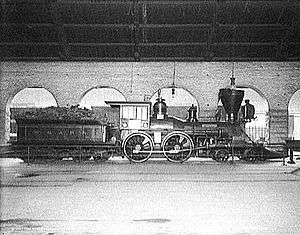
In 1901, the Western and Atlantic's General locomotive was placed on display in the station. It remained displayed until 1961, when Western & Atlantic's successor, the Louisville and Nashville removed the engine to be restored to operating condition. The engine then toured various parts of the eastern United States until 1967, when despite efforts by Chattanooga's then mayor Ralph Kelley to keep the engine in the city, the engine was ultimately given to the state of Georgia, who placed it on display in the Southern Museum of Civil War and Locomotive History, where it currently remains.[5]
Restoration efforts and destruction
In 1971, an English class from UTC taught by Dr. Tom Preston proposed a visionary plan to save the Union Depot from demolition. The plan proposed restoration and utilization as the center of a midtown mall. The class presented a paper and a video to the Chattanooga City Commission on July 19, 1971. Mayor Robert Kirk Walker recommended that the students take their presentation to the Downtown Development Committee. The Chattanooga Area Historical Association joined the fight to save the Union Depot in November 1971. However, on September 26, 1971, Georgia decided to sell some of the land it owned, including the depot site.[4] The structure was torn down the following year, and the site currently houses office buildings. A historical marker was placed at the location of the Union Depot.[6]
While the group was unsuccessful in saving the station, their efforts did manage to save Terminal Station from a similar fate.
References
- ↑ Prince, Richard E. (1967). The Nashville, Chattanooga, and St. Louis Railway: History and Steam Locomotives. Indiana University Press.
- 1 2 Prince, Richard E. (1967). The Nashville, Chattanooga, and St. Louis Railway: History and Steam Locomotives. Indiana University Press. ISBN 0-253-33927-8.
- ↑ Storey, Steve. "Chattanooga, TN, Stations".
- 1 2 Jolley, Harmon. "Visionary Plan in 1971 to Save Union Station".
- ↑ http://www.timesfreepress.com/news/opinion/columns/story/2016/dec/11/elliott-sam-d-elliott/402072/
- ↑ The Union Depot, 2B 25, Tennessee Historical Commissio]ttanooga, TN.
Sources
The station closed in 1971, the day Amtrak took over. The last passenger train, the St. Louis-Atlanta Georgian, was not continued by Amtrak.