Tuition fees in the United Kingdom
Tuition fees were first introduced across the entire United Kingdom in September 1998 under the Labour government as a means of funding tuition to undergraduate and postgraduate certificate students at universities, with students being required to pay up to £1,000 a year for tuition.[1][2] However, as a result of the establishment of devolved national administrations for Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland, different arrangements now exist with regard to the charging of tuition fees in each of the countries of the United Kingdom.
History
In May 1996, Gillian Shephard, Secretary of State for Education and Employment, commissioned an inquiry, led by the then Chancellor of the University of Nottingham, Sir Ron Dearing, into the funding of British higher education over the next 20 years.[3] This National Committee of Inquiry into Higher Education reported to the new Labour Government, in the summer of 1997, stating additional billions of funding would be needed over the period, including £350 million in 1998–99 and £565 million in 1999–2000, in order to expand student enrolment, provide more support for part-time students and ensure an adequate infrastructure.[4][5] The committee, as part of its brief, had controversially investigated the possibility of students contributing to the cost of this expansion, either through loans, a graduate tax, deferred contributions or means testing state assistance, as their report notes[6]:
20.40 We do not underestimate the strength of feeling on the issue of seeking a contribution towards tuition costs: nor do we dispute the logic of the arguments put forward. A detailed assessment of the issues has, however, convinced us that the arguments in favour of a contribution to tuition costs from graduates in work are strong, if not widely appreciated. They relate to equity between social groups, broadening participation, equity with part-time students in higher education and in further education, strengthening the student role in higher education, and identifying a new source of income that can be ring-fenced for higher education.
20.41 We have, therefore, analysed the implications of a range of options against the criteria set out in paragraph 20.2. There is a wide array of options from which to choose, ranging from asking graduates to contribute only to their living costs through to asking all graduates to contribute to their tuition costs. We have chosen to examine four options in depth
In response to the findings, the Teaching and Higher Education Act 1998 was published on 26 November 1997, and enacted on 16 July 1998, part of which introduced tuition fees in all the countries of the United Kingdom.[7]
The act introduced a means-tested method of payment for students based on the amount of money their families earned.[8] Starting with 1999–2000, maintenance grants for living expenses would also be replaced with loans and paid back at a rate of 9% of a graduate's income above £10,000.[7]
Following devolution in 1999, the newly devolved governments in Scotland and Wales brought in their own acts on tuition fees. The Scottish Parliament established, and later abolished a graduate endowment to replace the fees.[9] Wales introduced maintenance grants of up to £1,500 in 2002, a value which has since risen to over £5000.[10]
In England, tuition fee caps rose with the Higher Education Act 2004. Under the Act, universities in England could begin to charge variable fees of up to £3,000 a year for students enrolling on courses as from the academic year of 2006–07 or later. This was also introduced in Northern Ireland in 2006–07 and introduced in Wales in 2007–08. In 2009–10 the cap rose to £3,225 a year to take account of inflation.[11] Following the Browne Review in 2010, the cap was controversially raised to £9,000 a year, sparking large student protests in London.
A judicial review against the raised fees failed in 2012, and so the new fee system came into use that September.[12]
Students pay interest on loans. In 2012 this rate was set at the retail price index (RPI) plus 3%. Students who started university between 1998 and 2011 pay Bank of England base rate plus 1%. Students who started university before 1998 pay interest set at the RPI rate. As a consequence of the 2012 change, students who graduate in 2017 will pay 6.1% interest, despite the Bank of England base rate being 0.25%.[13]
Further adjustments were put forth in the 2015 budget, with a proposed fee increase in line with inflation from the 2017–18 academic year onwards, and the planned scrapping of maintenance grants from September 2016.[14] The changes were debated by the Third Delegated Legislation Committee in January 2016, rather than in the Commons. The lack of a vote on the matter has drawn criticism, as by circumventing the Commons the measures "automatically become law".[15] Tuition fees and perceptions about them are directly linked to satisfaction.[16]
Current systems
England
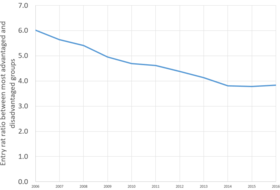
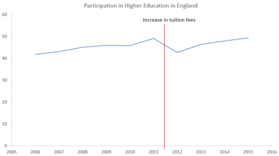
In England, tuition fees are capped at £9,250 a year for UK and EU students, with around 76% of all institutions charging the full amount in 2015–16.[19] A loan of the same size is available for most universities, although students of private institutions are only eligible for £6,000 a year loans.
From 2017–18 onwards, the £9,000 fee cap will rise with inflation. Maintenance grants are also available to current students in England, although these are scheduled to cease with the 2016–17 academic year.[15] Maintenance loans are available for living costs, and these are means tested. These loans are scheduled to increase in size for 2016–17, when the maintenance grant system is phased out.[20] There will be a vote in the autumn to consider a further increase effective with the 2017–18 year. Several universities have already advertised fees of £9,250 for the year in anticipation of such a vote passing.[21]In October 2017, the Prime Minister Theresa May announced that tuition fees would be temporarily frozen at £9,250[22]. In 2018, this temporary freeze remains in place and it is likely to be extended as a university funding review is carried out[23]. The latter, which was launched by Theresa May, is being chaired by Philip Augar[24].
In the 2015 spending review, the government also proposed a freeze in the repayment threshold for tuition fee loans at £21,000; a figure which was previously set to rise with average earnings. The changes, if passed, will affect all Plan 2 tuition fee loans, backdated to cover loans taken out from 2012.[25][26]
Effect
Many commentators suggested that the 2012 rise in tuition fees in England would put poorer students off applying to university.[27] However, the gap between rich and poor students has slightly narrowed (from 30.5% in 2010 to 29.8% in 2013) since the introduction of the higher fees.[28] This may be because universities have used tuition fees to invest in bursaries and outreach schemes.[29] In 2016, The Guardian noted that the number of disadvantaged students applying to university had increased by 72% from 2006 to 2015, a bigger rise than in Scotland, Wales or Northern Ireland.[30] It wrote that most of the gap between richer and poorer students tends to open up between Key Stage 1 and Key Stage 4 (i.e. at secondary school), rather than when applying for university, and so the money raised from tuition fees should be spent there instead.[30]
A study by Murphy, Scott-Clayton, and Wyness found that the introduction of tuition fees had "increased funding per head, rising enrolments, and a narrowing of the participation gap between advantaged and disadvantaged students".[31]
Northern Ireland
Tuition fees are currently capped at £4,030 in Northern Ireland, with loans of the same size available from Student Finance NI.[32] Loan repayments are made when income rises above £17,335 a year, with graduates paying back a percentage of their earnings above this threshold.[33]
Scotland
Tuition is handled by the Student Awards Agency Scotland (SAAS), which does not charge fees to what it defines as "Young Students". Young Students are defined as those under 25, without children, marriage, civil partnership or cohabiting partner, who have not been outside of full-time education for more than three years. Fees exist for those outside the young student definition, typically from £1,200 to £1,800 for undergraduate courses, dependent on year of application and type of qualification. Postgraduate fees can be up to £3,400.[34]
The system has been in place since 2007 when graduate endowments were abolished.[35] Labour's education spokesperson Rhona Brankin criticised the Scottish system for failing to address student poverty.[36] Scotland has fewer disadvantaged students than England, Wales or Northern Ireland and disadvantaged students receive around £560 a year less in financial support than their counterparts in England do.[29]
Wales
Like their English counterparts, Welsh universities are able to charge up to £9,000 a year in tuition fees. However, Welsh students can apply for fee grants of up to £5,190, in addition to a £3,810 loan to cover these costs.[37] This system also applies to Welsh students who study elsewhere in the United Kingdom.
Possible alternatives
There have been two main proposed alternative ways of funding university studies: from general taxation or by a graduate tax.
Funding from general taxation
Tuition is paid for by general taxation in Germany, although only 27% of young people gain higher education qualification there, whereas in the UK the comparable figure is 48%.[38] Fully or partly funding universities from general taxation has been criticised by the Liberal Democrat party as a 'tax cut for the rich and a tax rise for the poor' because people would be taxed to pay for something that many would not derive a benefit from, while graduates generally earn more due to their qualifications and only have to pay them back.[39]
Jeremy Corbyn, current Labour leader, has stated that he would remove tuition fees and instead fund higher education by increasing National Insurance and Corporation Tax.[40] In the long term this has been expected to cost the government about £8 billion a year.[41]
In July 2017 Lord Adonis, former Number 10 Policy Unit staffer and education minister largely responsible for introducing tuition fees, said that the system had become a "Frankenstein's monster" putting many students over £50,000 in debt. He argued the system should either be scrapped or fees reverted to between £1,000 and £3,000 per the initial scheme.[42][43]
Graduate tax
During the 2015 Labour leadership election, Andy Burnham said that he would introduce a graduate tax to replace fees. He was ultimately unsuccessful in his bid for leadership. A graduate tax has been criticised because there would be no way to recover the money from students who move to a different country, or foreign students who return home.[44]
References
- ↑ "BBC Q&A: Student Fees". BBC News. 2009-07-09. Retrieved 2010-10-11.
- ↑ Stuart Alley and Mat Smith (2004-01-27). "Timeline: Tuition fees". London: The Guardian. Retrieved 2011-02-12.
- ↑ Anderson, Robert (8 February 2016). "University fees in historical perspective". History & Policy. History & Policy. Retrieved 19 July 2016.
- ↑ "The Dearing Report". BBC Politics 1997. BBC. 1997. Retrieved 2011-02-12.
- ↑ "The Dearing Report - List of recommendations". Leeds.ac.uk. Retrieved 2011-02-12.
- ↑ Dearing, Ronald. "Higher Education in the learning society (1997) - Main Report". Education In England. Her Majesty's Stationery Office. Retrieved 28 May 2017.
- 1 2 "Teaching and Higher Education Act". BBC News. 1999-05-06. Retrieved 2011-02-12.
- ↑ Bolton, Paul. "Tuition Fee Statistics", Library of the House of Commons, 23 November 2010, page 2, section 1.1
- ↑ Bolton, Paul. "Tuition Fee Statistics" , Library of the House of Commons, 23 November 2010, page 3, section 1.4
- ↑ "Grants return sets Wales apart". BBC News. 2002-02-12. Retrieved 2011-02-12.
- ↑ Bolton, Paul. "Tuition Fee Statistics" , Library of the House of Commons, 23 November 2010, page 2, section 1.2
- ↑ "Tuition fees case: Callum Hurley and Katy Moore lose". BBC News. 2012-02-17.
- ↑ Jones, Rupert (11 April 2017). "Student loan interest rate set to rise by a third after UK inflation surge". The Guardian. Retrieved 8 July 2017.
- ↑ https://www.bbc.com/news/education-33444557
- 1 2 https://www.mirror.co.uk/news/uk-news/tories-bypass-mps-sneak-through-7178418
- ↑ Maxwell-Stuart, Rebecca; Taheri, Babak; Paterson, Audrey S.; O’Gorman, Kevin; Jackson, William (2016-11-24). "Working together to increase student satisfaction: exploring the effects of mode of study and fee status". Studies in Higher Education. Forthcoming. doi:10.1080/03075079.2016.1257601.
- ↑ https://www.ucas.com/file/86461/download?token=iMCCLWdB
- ↑ "Participation rates in higher education in England".
- ↑ "Undergraduate tuition fees and student loans".
- ↑ http://university.which.co.uk/advice/student-finance/quick-guide-to-fees-and-finance-if-youre-studying-in-england
- ↑ https://www.bbc.com/news/education-36845106
- ↑ Hubble, Sue; Bolton, Paul (2018). Prime Minister’s announcement on changes to student funding (PDF). London: House of Commons Library.
- ↑ Coughlan, Sean (2018-02-19). "May rules out scrapping tuition fees". BBC News. Retrieved 2018-10-12.
- ↑ Coughlan, Sean (2018-02-19). "May rules out scrapping tuition fees". BBC News. Retrieved 2018-10-12.
- ↑ https://www.independent.co.uk/student/news/spending-review-2015-government-betrays-a-generation-of-students-by-secretly-backtracking-on-a-2012-a6748801.html
- ↑ https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/447565/BIS-15-445-student-loan-repayment-threshold-consultation.pdf
- ↑ "University tuition fees hike 'will deter most poorer students' – poll".
- ↑ "University tuition fee rise has not deterred poorer students from applying".
- 1 2 "The worst place for poor students in the UK? Scotland".
- 1 2 "The evidence suggests I was completely wrong about tuition fees".
- ↑ Murphy, Richard; Scott-Clayton, Judith; Wyness, Gillian (February 2018). "The End of Free College in England: Implications for Quality, Enrolments, and Equity". NBER Working Paper No. 23888. doi:10.3386/w23888.
- ↑ http://www.nidirect.gov.uk/tuition-fees-for-academic-year
- ↑ "How and when you repay your student loan (courses starting from 1998)".
- ↑ http://www.saas.gov.uk/_forms/fees_student.pdf
- ↑ "Scottish Government - Graduate endowment scrapped". Retrieved 29 October 2014.
- ↑ "MSPs vote to scrap endowment fee". BBC News. 2008-02-28. Retrieved 2011-02-12.
- ↑ http://university.which.co.uk/advice/student-finance/quick-guide-to-fees-and-finance-if-youre-studying-in-wales
- ↑ "How Germany abolished tuition fees".
- ↑ http://www.libdemvoice.org/opinion-labours-tuition-fees-policy-is-a-tax-cut-for-the-rich-paid-for-by-the-poor-44497.html
- ↑ "Jeremy Corbyn: Scrap tuition fees and give students grants again, says Labour leadership contender". The Independent. Retrieved 13 September 2015.
- ↑ https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/election-2017-40000409
- ↑ Adams, Richard (7 July 2017). "Tuition fees should be scrapped, says 'architect' of fees Andrew Adonis". The Guardian. Retrieved 8 July 2017.
- ↑ Adonis, Andrew (7 July 2017). "I put up tuition fees. It's now clear they have to be scrapped". The Guardian. Retrieved 8 July 2017.
- ↑ http://www.ifs.org.uk/budgets/gb2002/chap8.pdf
External links
| Wikinews has related news: UK Parliament to vote on tuition fee rise on Thursday |
- Text of Higher Education Act 2004, which introduced top-up fees
- BBC News Q&A: Student Fees
- The Guardian: All Change (guide to fees)
- Student Loans Company (the body responsible for providing and administering student loans in the UK)
- Dearing Report