Timeline of Chinese history
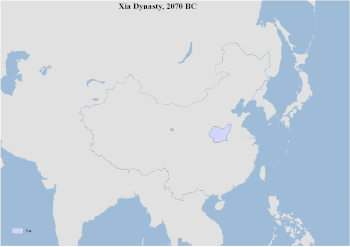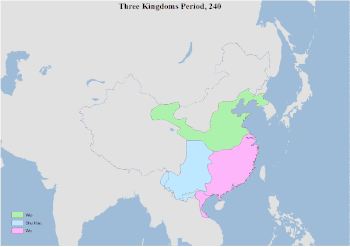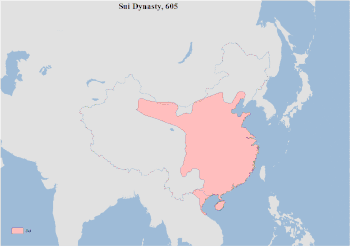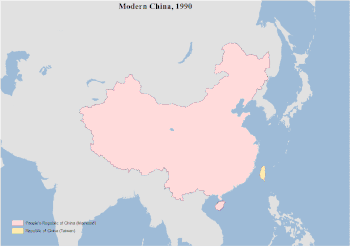
Territorial changes of China in every major dynasty
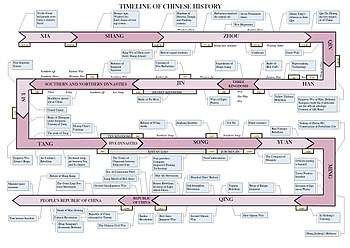
Timeline of Chinese history
This is a timeline of Chinese history, comprising important legal and territorial changes and political events in China and its predecessor states. To read about the background to these events, see History of China. See also the list of rulers of China, Chinese emperors family tree, dynasties in Chinese history and years in China.
Dates prior to 841 BC, the beginning of the Gonghe Regency, are provisional and subject to dispute.
Prehistory / Millennia: 3rd BC · 2nd BC–1st BC · 1st–2nd · 3rd · See also · Further reading · External links
Prehistoric China
≤÷←×−±| 7000 BC || || The Peiligang culture appeared.
| 20000 BC | Pottery was used in Xianren Cave.[1] | |
| 7600 BC | The Zhenpiyan culture appeared. | |
| Pigs were first domesticated in China.[2] | ||
| 7500 BC | The Pengtoushan culture appeared. | |
| Rice was first domesticated in China. | ||
| 6600 BC | The Jiahu symbols were first used at Jiahu. | |
| 6500 BC | The Cishan culture appeared. | |
| 6000 BC | Dogs were first domesticated in China.[2] | |
| 4000 BC | Symbols were carved into pottery at Banpo. | |
| 3630 BC | Silk was invented by the Yangshao culture. |
26th century BC
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 2570 BC | Silk was produced by the Liangzhu culture. |
25th century BC
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 2500 BC | Battle of Banquan: The forces of Shennong were repelled by a force of tribes allied under the Yellow Emperor. | |
| Battle of Zhuolu: A combined army of Chinese tribes under the Yellow Emperor defeated a Hmong invasion at Zhuolo. |
24th century BC
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 2366 BC | Zhi became king of China. | |
| 2361 BC | China made its first contact with Văn Lang.[3] |
22nd century BC
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 2200 BC | Great Flood: Yu the Great completed a drainage system which ended the periodic and destructive flooding of the Yellow and Yangtze Rivers. (Reliable Archaeological discoveries depict that it happened around 1920BC.
[4]) | |
| The Nine Tripod Cauldrons were forged from metal given in tribute to Yu by the Nine Provinces. | ||
| 2117 BC | Tai Kang became king of the Xia dynasty. |
21st century BC
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 2075 BC | Xiang of Xia became king of the Xia dynasty(The existence of the Xia Dynasty has not been confirmed formally). | |
| 2047 BC | Xiang was murdered and displaced as king on the orders of the warlord Han Zhou. His pregnant wife fled the capital Shangqiu. | |
| Xiang's wife gave birth to a son, Shao Kang. | ||
| 2007 BC | The people of Shangqiu welcomed an army loyal to Shao into the city. Han committed suicide. |
20th century BC
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1985 BC | Zhu of Xia became king of the Xia dynasty. | |
| 1968 BC | Zhu died. He was succeeded by his son Huai of Xia. | |
| 1924 BC | Huai died. He was succeeded by his son Mang of Xia. | |
| 1906 BC | Mang was succeeded by his son Xie of Xia. |
19th century BC
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1900 BC | The Erlitou culture appeared. | |
| 1890 BC | Xie was succeeded by his son Bu Jiang. | |
| 1831 BC | Bu abdicated in favor of his younger brother Jiong of Xia. | |
| Mount Tai earthquake: An earthquake occurred at Mount Tai. | ||
| 1810 BC | Jiong was succeeded by his son Jin of Xia. |
18th century BC
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1789 BC | Jin was succeeded by his cousin, Bu's son Kong Jia. | |
| 1758 BC | Kong was succeeded by his son Gao of Xia. | |
| 1747 BC | Gao was succeeded by his son Fa of Xia. | |
| 1728 BC | Fa was succeeded by his son Jie of Xia. |
17th century BC
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1675 BC | Jie was succeeded by Tang of Shang, marking the beginning of the Shang dynasty. |
15th century BC
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1500 BC | The Erligang culture appeared. |
13th century BC
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1290 BC | Pan Geng became king of the Shang dynasty. | |
| The capital of the Shang dynasty was moved from Yan to Yin. | ||
| 1250 BC | Wu Ding became king of the Shang dynasty. | |
| Oracle bones were first used for divination; evidence of oracle bone script first appears. |
12th century BC
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1200 BC | Wu's wife, the general and high priestess Fu Hao, died and was buried at the tomb of Fu Hao in Yinxu. | |
| 1192 BC | Wu died. He was succeeded by his son Zu Geng of Shang. | |
| 1170 BC | Geng Ding became king of the Shang dynasty. | |
| 1147 BC | Geng was succeeded by his son Wu Yi of Shang. | |
| 1112 BC | Wu was killed by lightning while out hunting. He was succeeded by his son Wen Ding. | |
| 1101 BC | Wen was succeeded by his son Di Yi. |
11th century BC
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1076 BC | Di died. | |
| 1075 BC | Di was succeeded as king of the Shang dynasty by his son King Zhou of Shang. | |
| 1050 BC | King Wen of Zhou died. | |
| 1047 BC | Zhou took Daji as his concubine. | |
| 1046 BC | Battle of Muye: The forces of the predynastic Zhou, led by King Wu of Zhou and aided by Shang dynasty defectors, dealt a bloody defeat to Shang forces at Muye, near Yinxu. | |
| Zhou committed suicide by burning himself with his jewels on the Deer Terrace Pavilion. | ||
| 1043 BC | Wu died. | |
| 1042 BC | Wu was succeeded by his son King Cheng of Zhou. | |
| 1034 BC | Chinese bronze inscriptions came into use. | |
| 1021 BC | Cheng died. | |
| 1020 BC | Cheng was succeeded by his son King Kang of Zhou. |
10th century BC
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1000 BC | The Classic of Poetry was compiled. | |
| 996 BC | Kang died. | |
| 976 BC | King Mu of Zhou became king of the Zhou dynasty. | |
| 964 BC | Mu led an unsuccessful expedition against the Quanrong. | |
| 922 BC | Mu died. He was succeeded by his son King Gong of Zhou. |
9th century BC
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 900 BC | Gong died. | |
| 899 BC | Gong's son Ji Jian, King Yi of Zhou became king of the Zhou dynasty. | |
| 892 BC | Ji Jian died. | |
| 891 BC | Ji Jian's uncle, Mu's son King Xiao of Zhou became king of the Zhou dynasty. | |
| 886 BC | Xiao died. | |
| 885 BC | Ji Jian's son Ji Xie, King Yi of Zhou became king of the Zhou dynasty. | |
| 878 BC | Ji Xie died. | |
| 877 BC | Ji Xie's son King Li of Zhou became king of the Zhou dynasty. | |
| 842 BC | A popular revolt forced Li into exile near Linfen. | |
| 841 BC | The Gonghe Regency came into power. | |
| 828 BC | Li died. | |
| 827 BC | Li's son King Xuan of Zhou became king of the Zhou dynasty. |
8th century BC
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 782 BC | Xuan died. | |
| 781 BC | Xuan's son King You of Zhou became king of the Zhou dynasty. | |
| 779 BC | You took Bao Si as his concubine. | |
| 771 BC | The Marquess of Shen, whose daughter had replaced by Bao Si as queen, led an attack on Haojing in alliance with the Quanrong. You and Bao's son Bofu were killed. | |
| 770 BC | You's son King Ping of Zhou became king of the Zhou dynasty. | |
| Ping moved the Zhou capital east to Luoyang. | ||
| 720 BC | Ping died. | |
| 719 BC | Ping's grandson King Huan of Zhou became king of the Zhou dynasty. | |
| 707 BC | Battle of Xuge: Huan, in coalition with the Zhou vassal states Chen, Cai and Wey, led a punitive expedition against Zheng. The coalition was defeated and Huan was wounded. |
7th century BC
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 697 BC | Huan died. | |
| 696 BC | Huan's son King Zhuang of Zhou became king of the Zhou dynasty. | |
| 685 BC | Duke Huan of Qi became duke of Qi. | |
| 682 BC | Zhuang died. | |
| 681 BC | Zhuang's son King Xi of Zhou became king of the Zhou dynasty. | |
| 677 BC | Xi died. | |
| 676 BC | Xi's son King Hui of Zhou became king of the Zhou dynasty. | |
| 652 BC | Hui died. | |
| 651 BC | Hui's son King Xiang of Zhou became king of the Zhou dynasty. | |
| 645 BC | The Qi chancellor Guan Zhong died. | |
| 632 BC | Battle of Chengpu: Jin and its allies decisively defeated a coalition led by Chu. | |
| 630 BC | Sunshu Ao was born. | |
| 619 BC | Xiang died. | |
| 618 BC | Xiang's son King Qing of Zhou became king of the Zhou dynasty. | |
| 613 BC | Qing died. | |
| 612 BC | Qing's son King Kuang of Zhou became king of the Zhou dynasty. | |
| 607 BC | Kuang died. | |
| 606 BC | Kuang's brother King Ding of Zhou became king of the Zhou dynasty. |
6th century BC
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 600 BC | Knife money came into use. | |
| 595 BC | Battle of Bi: Chu decisively defeated Jin at Bi, near modern Xingyang. | |
| 586 BC | Ding died. | |
| 585 BC | Ding's son King Jian of Zhou became king of the Zhou dynasty. | |
| 575 BC | Battle of Yanling: A numerically superior Chu force was defeated by Jin in modern Yanling County. King Gong of Chu was injured. | |
| 572 BC | Jian died. | |
| 571 BC | Jian's son King Ling of Zhou became king of the Zhou dynasty. | |
| 551 BC | Confucius was born. | |
| 548 BC | The earliest surviving reference to Go appeared. | |
| 545 BC | Ling died. | |
| 544 BC | Ling's son Ji Gui, King Jing of Zhou became king of the Zhou dynasty. | |
| The Chinese people were first divided into a caste system of four occupations. | ||
| 543 BC | The Zheng prime minister Zichan established the state's first written civil code. | |
| 520 BC | Ji Gui died. He was succeeded by his son King Dao of Zhou. | |
| Dao was murdered by his brother. | ||
| 519 BC | Dao's brother Ji Gai, King Jing of Zhou became king of the Zhou dynasty. | |
| 515 BC | The Wu king King Liao of Wu was killed by the assassin Zhuan Zhu. | |
| 514 BC | King Helü of Wu became king of Wu. | |
| 506 BC | Battle of Boju: Wu decisively defeated a numerically superior Chu force at Boju. |
5th century BC
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 500 BC | Cast iron was first invented in China. | |
| 486 BC | The Wu king King Fuchai of Wu ordered the building of the Han Canal. | |
| 484 BC | Wu Zixu died. | |
| 482 BC | The Yue king King Goujian of Yue captured the Wu capital in a surprise assault. | |
| 477 BC | Ji Gai died. | |
| 475 BC | Ji Gai's son King Yuan of Zhou became king of the Zhou dynasty. | |
| 473 BC | Wu was annexed by Yue. | |
| 470 BC | Mozi was born. | |
| 469 BC | Yuan died. | |
| 468 BC | Yuan's son King Zhending of Zhou became king of the Zhou dynasty. | |
| 465 BC | Goujian died. | |
| 441 BC | Zhending died. He was succeeded by his son King Ai of Zhou. | |
| Ai was murdered and succeeded as king by his younger brother King Si of Zhou. | ||
| Si was murdered by his brother King Kao of Zhou. | ||
| 440 BC | Kao became king of the Zhou dynasty. | |
| 432 BC | The tomb of Marquis Yi of Zeng was constructed. | |
| 426 BC | Kao died. | |
| 425 BC | Kao's son King Weilie of Zhou became king of the Zhou dynasty. | |
| 403 BC | Partition of Jin: Weilie recognized the Jin nobles Marquess Wen of Wei, Marquess Lie of Zhao and Marquess Jing of Han as marquesses, granting de jure independence from Jin to the states of Wei, Zhao and Han. | |
| 402 BC | Weilie died. | |
| 401 BC | Weilie's son King An of Zhou became king of the Zhou dynasty. |
4th century BC
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 400 BC | Gan De was born. | |
| Shi Shen was born. | ||
| The earliest surviving Chinese maps appeared. | ||
| The first Chinese star catalogue was compiled. | ||
| 389 BC | The Zuo Zhuan was published. | |
| 386 BC | The city of Handan was founded to serve as the Zhao capital. | |
| 381 BC | The Chu prime minister Wu Qi was murdered by nobles at the funeral of its king King Dao of Chu. | |
| 376 BC | An died. | |
| 375 BC | An's son King Lie of Zhou became king of the Zhou dynasty. | |
| Zheng was annexed by Han. | ||
| 370 BC | Zhuang Zhou was born. | |
| 369 BC | Lie died. | |
| 368 BC | Lie's brother King Xian of Zhou became king of the Zhou dynasty. | |
| 361 BC | Duke Xiao of Qin became duke of Qin. | |
| 356 BC | Xiao's adviser Shang Yang implemented a legal code in Qin based on the Canon of Laws which established punishment for complicity in a crime, established a system of military ranks, and implemented policies encouraging the cultivation of unsettled land. | |
| 354 BC | Battle of Guiling: Wei laid siege to the Zhao capital Handan. | |
| 353 BC | Battle of Guiling: The Wei army fled Handan in response to reports of a Qi attack on their capital Daliang and were defeated by Qi forces at Guiling, in modern Changyuan County. | |
| 342 BC | Battle of Maling: Qi dealt Wei a bloody defeat. | |
| The crossbow was first used in China. | ||
| 338 BC | Xiao died. He was succeeded by his son King Huiwen of Qin. | |
| Shang and his family were executed by dismemberment on charges of treason. | ||
| 321 BC | Xian died. | |
| 320 BC | Xian's son King Shenjing of Zhou became king of the Zhou dynasty. | |
| 319 BC | The Confucian Mencius became a Qi official. | |
| 316 BC | Sun Bin died. | |
| Shu was conquered and annexed by Qin. | ||
| Ba was conquered and annexed by Qin. | ||
| 315 BC | Shenjing died. | |
| 314 BC | Shenjing's son King Nan of Zhou became king of the Zhou dynasty. | |
| 311 BC | Huiwen died. | |
| 310 BC | Huiwen's son King Wu of Qin became king of Qin. | |
| Xun Kuang was born. | ||
| 307 BC | The Zhou king King Wuling of Zhao ordered his cavalry to begin wearing clothes fashioned after those of the Donghu and Xiongnu peoples. | |
| Wu died. | ||
| 306 BC | Wu's brother King Zhaoxiang of Qin became king of Qin. | |
| 305 BC | Zou Yan was born. The Tsinghua Bamboo Slips were written. |
3rd century BC
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 300 BC | Erya was published. | |
| The Guodian Chu Slips were produced. | ||
| 293 BC | Battle of Yique: Qin dealt a bloody defeat to a Wei-Han alliance. | |
| 278 BC | Qin conquered the Chu capital Ying. | |
| The Chu poet Qu Yuan wrote Lament for Ying and drowned himself in the Miluo River because he could not bear his exile any long or to his despair for the state of his fellow countrymen | ||
| 262 BC | April | Battle of Changping: Zhao intercepted a Qin invasion of the commandery of Shangdang . |
| 260 BC | July | Battle of Changping: Qin forces encircled the Zhao army, forcing its surrender. The Zhao general Zhao Kuo was killed in action. |
| July | Battle of Changping: The captured Zhao soldiers were executed. | |
| 259 BC | 18 February | Qin Shi Huang is Born. |
| 256 BC | Nan submitted to Zhaoxiang and took the title Duke of West Zhou. | |
| Nan died. His territory was annexed by Qin. | ||
| The Dujiangyan irrigation system was built. | ||
| 251 BC | Zhaoxiang died. | |
| 250 BC | The first drawings of the repeating crossbow appeared in Chu records. | |
| 13 September | Zhaoxiang's son King Xiaowen of Qin became king of Qin. | |
| 15 September | Xiaowen died. He was succeeded by his son King Zhuangxiang of Qin. | |
| 247 BC | 7 May | Zhuangxiang died. He was succeeded by his son Qin Shi Huang. |
| 246 BC | The Zhengguo Canal was completed by Zheng Guo of Qin. | |
| 230 BC | Qin's wars of unification: Qin invaded Han. | |
| 227 BC | Jing Ke failed in an assassination attempt on Qin Shi Huang. | |
| 225 BC | Qin conquered Wei. | |
| 223 BC | Qin conquered Chu. | |
| 222 BC | Qin conquered Yan. | |
| Qin conquered Zhao. | ||
| 221 BC | Qin conquered Qi. | |
| The Heirloom Seal of the Realm was carved. | ||
| 220 BC | Qin Shi Huang took the title Qin Shi Huang, first emperor of China. | |
| Construction began on the Great Wall of China. | ||
| Chancellor Li Si standardized the Chinese writing system with the creation of Small Seal Script. | ||
| 214 BC | The Lingqu Canal was built. | |
| 213 BC | Burning of books and burying of scholars: All copies of the Classic of Poetry, the Book of Documents and works of the Hundred Schools of Thought were ordered burned. | |
| 210 BC | 10 September | Qin Shi Huang died,from mercury pills made by his alchemists and court physicians ironically these pills were meant to make Qin Shi Huang immortal . |
| Qin Shi Huang was buried with the Terracotta Army in the Mausoleum of the First Qin Emperor. | ||
| October | Qin Shi Huang's son Qin Er Shi succeeded him as emperor of China. | |
| 209 BC | The Xiongnu chanyu Modu Chanyu established the Xiongnu Empire on the Eurasian Steppe. | |
| July | Dazexiang Uprising: Military officers Chen Sheng and Wu Guang began a rebellion for fear of being executed after failing to arrive at their posts. | |
| December | Dazexiang Uprising: Chen Sheng and Wu Guang were assassinated by their own men. | |
| 208 BC | Li was executed on charges of treason. Zhao Gao, who had framed him, was appointed chancellor in his stead. | |
| 207 BC | Battle of Julu: Chu forces led by the warlord Xiang Yu defeated a numerically superior Qin force, killing a large fraction of the Qin army. | |
| October | Zhao Gao had Qin Er Shi killed. Qin Er Shi's nephew Ziying succeeded him. | |
| The Chu general Emperor Gaozu of Han entered the Qin capital Xianyang. | ||
| December | Ziying killed Zhao. | |
| December | Ziying surrendered to Gaozu. | |
| 206 BC | Feast at Hong Gate: Gaozu fled a banquet after it became clear that Xiang had invited him there to be killed. | |
| Xiang led an army into Xianyang, burned the Epang Palace and killed Ziying and the royal family. | ||
| 205 BC | Battle of Jingxing: Han forces dealt a decisive defeat to a numerically superior Zhao army at Jingxing Pass. | |
| 204 BC | The Qin general Zhao Tuo established the state of Nanyue. | |
| 202 BC | Battle of Gaixia: Gaozu's Han forces destroyed the Western Chu army led by Xiang in modern Suzhou. | |
| Gaozu took the title emperor and established his capital in Luoyang. |
2nd century BC
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 200 BC | Battle of Baideng: The Xiongnu encircled and besieged a superior Han force. | |
| The multi-tube seed drill was invented. | ||
| 195 BC | 1 June | Gaozu died. He was succeeded by his son Emperor Hui of Han. |
| 193 BC | The Han chancellor Xiao He died. | |
| 190 BC | Chang'an became the eastern terminus of the Silk Road to Europe. | |
| 188 BC | Hui died. He was succeeded by his son Emperor Qianshao of Han. | |
| 186 BC | Zhang Liang died. | |
| 184 BC | Qianshao was deposed and killed on the orders of the empress dowager Empress Lü Zhi. He was succeeded by his brother Emperor Houshao of Han. | |
| 180 BC | Lü Clan Disturbance: Houshao was deposed by imperial officials led by Chen Ping and Zhou Bo. He was succeeded by his uncle, Gaozu's son Emperor Wen of Han. | |
| 168 BC | The Mawangdui Silk Texts were buried at Mawangdui. | |
| 157 BC | Summer | Wen died. He was succeeded by his son Emperor Jing of Han. |
| 141 BC | 9 March | Jing died. He was succeeded by his son Emperor Wu of Han. |
| 140 BC | Wu adopted Confucianism. | |
| 139 BC | The Eight Immortals of Huainan published the Huainanzi. | |
| 135 BC | Han campaigns against Minyue: The Han dynasty invaded Minyue after a plea for assistance from its vassal state Nanyue. | |
| Southward expansion of the Han dynasty: The Han dynasty annexed Minyue. | ||
| 133 BC | June | Battle of Mayi: A Han deception failed to lure the Xiongnu into an ambush at Mayi. |
| 125 BC | Zhang Qian returned to the Han court to report on his travels to the kingdoms of Dayuan, Kangju, the Greco-Bactrian and Indo-Greek Kingdoms, Parthia and Mesopotamia. | |
| 119 BC | January | Battle of Mobei: A Han expedition into the Orkhon Valley began which would deal a decisive and bloody defeat to the Xiongnu. |
| 111 BC | Han campaigns against Minyue: The Minyue rump state of Dongyue was invaded and annexed by the Han dynasty. | |
| Han–Nanyue War: The Han dynasty conquered and annexed Nanyue. | ||
| 109 BC | Han campaigns against Dian: The Han dynasty invaded and annexed the Dian Kingdom. | |
| 108 BC | December | Battle of Loulan: Han forces attacked the Loulan Kingdom at Lop Nur. |
| 102 BC | Han forces laid siege to Kokand. |
1st century BC
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 100 BC | Steel was first used in China. | |
| 91 BC | Sima Qian completed the Records of the Grand Historian. | |
| 87 BC | 29 March | Wu died. He was succeeded by his young son Emperor Zhao of Han, with Huo Guang, Jin Midi and Shangguang Jie acting as regents. |
| 86 BC | Jin died. | |
| 74 BC | Zhao died. | |
| 18 July | The Prince of Changyi was appointed emperor of Han by Huo Guang. | |
| 14 August | The Prince of Changyi was deposed. | |
| Huo appointed Wu's great grandson, then a commoner, Emperor Xuan of Han. | ||
| 67 BC | December | Battle of Jushi: Han forces defeated the people of the Gushi culture, at that time subject to the Xiongnu, at Jiaohe in modern Turpan. |
| 60 BC | The Protectorate of the Western Regions was established. | |
| 49 BC | Xuan died. | |
| 48 BC | Xuan's son Emperor Yuan of Han became emperor of the Han dynasty. | |
| Consort Ban was born. | ||
| 40 BC | The earliest surviving Chinese record of the treadle-operated tilt hammer appeared. | |
| 37 BC | Jing Fang died. | |
| 36 BC | December | Battle of Zhizhi: A Han force breached and destroyed a fortress occupied by the Xiongnu chanyu Zhizhi Chanyu at Taraz, killing him. |
| 33 BC | Yuan died. He was succeeded by his son Emperor Cheng of Han. | |
| 30 BC | The earliest surviving mention of the wheelbarrow appeared. | |
| 18 BC | Liu Xiang compiled the Biographies of Exemplary Women. | |
| 7 BC | Cheng died. He was succeeded by his nephew Emperor Ai of Han. | |
| 1 BC | Ai died. | |
| Ai's young cousin Emperor Ping of Han was appointed emperor of the Han dynasty, with Wang Mang acting as regent. |
1st century
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | The first model of a stern-mounted rudder was produced. | |
| 2 | A census counted fifty-nine million people in the Han empire. | |
| 3 | Ping established a national school system. Ban Biao, first author of the Book of Han, is born. | |
| 6 | 3 February | Ping died after being poisoned by Wang, who became acting emperor. |
| 8 | Liu Xin completed a star catalogue and calculated the length of the year. | |
| 9 | Wang declared himself emperor of the Xin dynasty. | |
| Wang introduced the well-field system of land distribution and agricultural production. | ||
| 10 | Wang introduced an income tax of ten percent for professionals and skilled laborers. | |
| Wang outlawed the private use of crossbows. | ||
| 12 | Wang abandoned the well-field system under pressure from the aristocracy. | |
| 17 | Wang imposed government monopolies on liquor, salt, iron, coinage, forestry, and fishing. | |
| Mother Lü initiated a rebellion against a county magistrate in Haiqu County, near modern Rizhao. | ||
| 18 | Yang Xiong died. | |
| 23 | Battle of Kunyang: Lülin forces broke the siege of Kunyang, in modern Ye County, by a vastly superior Xin army. | |
| 6 October | Lülin rebels stormed the Weiyang Palace and killed Wang. The Gengshi Emperor ascended the throne, restoring the Han dynasty. | |
| 25 | Red Eyebrows Rebellions: The Gengshi Emperor was executed. | |
| Red Eyebrows Rebellions: The Red Eyebrows appointed Liu Penzi their emperor. | ||
| 5 August | The Han warlord Emperor Guangwu of Han took the title emperor. | |
| 27 | Red Eyebrows Rebellions: The Red Eyebrows surrendered to the Han dynasty. | |
| 31 | Du Shi invented waterwheel-powered bellows for smelting cast iron. | |
| 32 | Ban Gu, co-author of the Book of Han, is born. | |
| 33 | A blockade of the Yangtze River by the rebel Gongsun Shu was broken by Han castle ships. | |
| 43 | Second Chinese domination of Vietnam: Vietnam fell into Han control. | |
| 45 | Ban Zhao, China's first female historian, is born. | |
| 52 | The Yuejue Shu was written. | |
| 57 | 29 March | Guangwu died. He was succeeded by his son Emperor Ming of Han. |
| 58 | The Han chancellor Deng Yu died. | |
| 65 | Ming's half brother Liu Ying converted to Buddhism. | |
| 68 | The Buddhist White Horse Temple was established in Luoyang. | |
| 73 | February | Battle of Yiwulu: A punitive Han expedition against the Xiongnu captured territory in the area of modern Hami City. |
| 75 | Ming died. He was succeeded by his son Emperor Zhang of Han. | |
| 83 | Wang Chong correctly theorized the nature of the water cycle. | |
| 87 | Yuan An was appointed situ. | |
| 88 | Zhang died. He was succeeded by his son Emperor He of Han. | |
| 89 | June | Battle of the Altai Mountains: Han and allied forces defeated the army of the Northern Chanyu and accepted the surrender of two hundred thousand Xiongnu soldiers in the Altai Mountains. |
| 97 | The Han general Ban Chao sent the envoy Gan Ying to the outskirts of the Roman Empire. | |
| 100 | Xu Shen completed the Shuowen Jiezi. |
2nd century
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 105 | Cai Lun invented papermaking. | |
| 13 February | He died. | |
| He's infant son Emperor Shang of Han was made emperor of Han with empress dowager Deng Sui acting as regent. | ||
| 106 | Shang died. | |
| Shang's young cousin Emperor An of Han became emperor, with Deng Sui continuing to act as regent. | ||
| 111 | Ban Zhao completed the Book of Han. | |
| 120 | Zhang Heng completed a star catalogue which also argued for a spherical moon that reflects light. | |
| 125 | Zhang invented the first hydraulic-powered armillary sphere. | |
| The earliest known Chinese depiction of a mechanical distance-marking odometer was drawn. | ||
| 30 April | An died. | |
| The Marquess of Beixiang became emperor of the Han dynasty. | ||
| The Marquess of Beixiang died. | ||
| An's son Emperor Shun of Han became emperor of the Han dynasty. | ||
| 132 | Zhang invented a seismometer capable of indicating the direction of earthquakes. | |
| Cai Yong was born. | ||
| 142 | The Cantong qi was published. | |
| 144 | Shun died. He was succeeded by his infant son Emperor Chong of Han, with empress dowager Liang Na and her brother Liang Ji acting as regents. | |
| 145 | Chong died. | |
| Chong's young third cousin Emperor Zhi of Han became emperor of the Han dynasty, with Liang Na acting as regent. | ||
| 146 | Liang Ji poisoned Zhi, killing him. | |
| 1 August | Emperor Huan of Han became emperor of the Han dynasty. | |
| 147 | Lokaksema was born. | |
| 148 | The Buddhist missionary An Shigao arrived in China. | |
| 166 | Sino-Roman relations: A Roman envoy arrived at the Han capital Luoyang. | |
| Disasters of the Partisan Prohibitions: Several ministers and some two hundred university students, who had opposed the influence of corrupt eunuchs at the royal court, were arrested. | ||
| 168 | Huan died. | |
| Emperor Ling of Han became emperor of the Han dynasty. | ||
| 177 | Cai Wenji was born. | |
| 179 | The earliest known reference to The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art appeared. | |
| 180 | Ding Huan invented the rotary fan. | |
| 184 | Yellow Turban Rebellion: The Taoist sect leader Zhang Jue called on his followers in the Han provinces to rebel against the government. | |
| Winter | Liang Province Rebellion: The Qiang people launched a rebellion against Han authority in the area of modern Wuwei. | |
| 185 | Zhi Yao first translated Buddhist texts into Chinese. | |
| 189 | 13 May | Ling died. |
| Ling's son Liu Bian became emperor of the Han dynasty. | ||
| Forces loyal to the warlords Yuan Shao and Yuan Shu massacred some two thousand eunuchs in the Han capital Luoyang. | ||
| 28 September | The Han general Dong Zhuo deposed Liu Bian as emperor and appointed his brother Emperor Xian of Han in his stead. | |
| 190 | February | Campaign against Dong Zhuo: A coalition led by Yuan Shao gathered at Hangu Pass in anticipation of an expedition against Dong. |
| 192 | 22 May | Dong was assassinated by his foster son Lü Bu. |
| 194 | Sun Ce's conquests in Jiangdong: The warlord Sun Ce attacked and conquered territory administered by Lu Kang. | |
| 198 | Winter | Battle of Xiapi: The allied forces of the warlords Cao Cao and Liu Bei defeated an army loyal to Lü Bu in Xuzhou. |
| 200 | November | Battle of Guandu: Forces loyal to Cao Cao dealt a bloody defeat to Yuan Shao near the confluence of the Bian and Yellow Rivers. |
3rd century
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 204 | The warlord Gongsun Kang established the Daifang Commandery on the Korean Peninsula. | |
| 208 | Winter | Battle of Red Cliffs: Forces loyal to the warlords Liu Bei and Sun Quan decisively repelled Cao Cao in an attempted invasion across the Yangtze River. |
| 211 | September | Battle of Tong Pass: Cao Cao defeated an alliance of anti-Han rebels in modern Tongguan County, securing his control over Guanzhong. |
| 215 | Liu Bei's takeover of Yi Province: Liu Zhang, the governor of Yi Province in modern Sichuan and Chongqing, surrendered Chengdu to Liu Bei. | |
| Battle of Xiaoyao Ford: A plague outbreak forced Sun Quan to abandon the attempted conquest from Cao Cao of a fortress at Hefei. | ||
| 219 | Battle of Han River: Liu Bei ambushed and dealt a bloody defeat to Cao Cao's army in Hanzhong. | |
| September | Battle of Fancheng: Cao Cao repelled an attack by Liu Bei's general Guan Yu in modern Fancheng District, at great cost to both sides. | |
| December | Lü Meng's invasion of Jing Province: Liu Bei's generals Shi Ren and Mi Fang defected to Sun Quan, surrendering to his general Lü Meng the main defense posts of Jingzhou. | |
| 220 | 10 December | End of the Han dynasty: Cao Cao's son Cao Pi forced Xian to abdicate the throne and declared himself emperor of Cao Wei. |
| 221 | Liu Bei declared himself emperor of Shu Han. | |
| Battle of Xiaoting: The Shu Han generals Wu Ban and Feng Xi attacked and destroyed an Eastern Wu army at Wu Gorge. | ||
| 222 | Sun Quan declared himself king of Eastern Wu. | |
| Battle of Xiaoting: Eastern Wu forces attacked and burned the Shu Han camps and dealt serious casualties during their retreat. | ||
| 223 | 10 June | Liu Bei died. He was succeeded by his son Liu Shan, with Li Yan and chancellor Zhuge Liang acting as regents. |
| 225 | Autumn | Zhuge Liang's Southern Campaign: The rebel leader Meng Huo surrendered Nanzhong to Zhuge Liang. |
| 226 | 29 June | Cao Pi died. He was succeeded by Cao Rui, who may have been his son or his wife Lady Zhen's by a previous marriage to Yuan Xi. |
| 228 | Battle of Jieting: Cao Wei forces encircled and destroyed a Shu Han army guarding the supply line for an invasion in modern Qin'an County. | |
| Battle of Shiting: A Cao Wei army was lured into an ambush by Eastern Wu in modern Qianshan County and dealt heavy casualties on its retreat. | ||
| 232 | Cao Zhi died. | |
| 234 | Autumn | Battle of Wuzhang Plains: Shu Han forces made an orderly retreat from Cao Wei forces on the Wuzhang Plains after Zhuge Liang fell ill and died. |
| 239 | 22 January | Cao Rui died. He was succeeded by his young adopted son Cao Fang, with Cao Shuang and Sima Yi acting as regents. |
| 244 | April | Battle of Xingshi: Shu Han forces stalled a Cao Wei invasion at Mount Xingshi in the modern Changqing National Nature Reserve. |
| 247 | Jiang Wei's Northern Expeditions: Cao Wei pushed back an invasion by the Shu Han general Jiang Wei across the Tao River. | |
| 248 | Eastern Wu forces killed the Vietnamese rebel Lady Triệu. | |
| 249 | Incident at Gaoping Tombs: Sima Yi took control of the Cao Wei capital Luoyang during Cao Fang and Cao Shuang's absence. | |
| 252 | Sun Quan died. He was succeeded by his young son Sun Liang, with the general Zhuge Ke acting as regent. | |
| 254 | Sima Yi's son, the regent Sima Shi, deposed Cao Fang, who was succeeded by Cao Pi's grandson Cao Mao. | |
| 255 | Ma Jun invented the south-pointing chariot. | |
| 258 | Sun Liang was deposed by the regent Sun Chen. | |
| Sun Liang's brother Sun Xiu was made emperor of Eastern Wu. | ||
| 260 | Coup of Cao Mao: Cao Mao was murdered in a failed attempt to kill the regent Sima Zhao at his residence. | |
| Cao Cao's grandson Cao Huan was made emperor of Cao Wei. | ||
| 263 | November | Conquest of Shu by Wei: The Cao Wei general Deng Ai accepted the surrender of the Shu Han emperor Liu Shan outside the capital Chengdu. |
| Liu Hui published a revised version of The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art. | ||
| 264 | 3 September | Sun Xiu died. |
| Sun Quan's grandson Sun Hao was made emperor of Eastern Wu. | ||
| 265 | Cao Wei instituted the nine-rank system of civil servants. | |
| 6 September | Sima Zhao died. His eldest son and heir, Sima Yan, inherited his position as regent of Cao Wei and noble title of King of Jin. | |
| Pei Xiu introduced the grid reference and the concept of scale to Chinese mapmaking. | ||
| 266 | 4 February | Cao Huan, last emperor of Cao Wei, abdicated in favour of Sima Yan. |
| 8 February | Sima Yan formally enthroned himself as Emperor of Jin, establishing the Jin dynasty. Sima Yan is posthumously known as Emperor Wu of Jin. | |
| 20 March | Emperor Wu of Jin established his wife Yang Yan as Empress. | |
| 267 | 4 February | Emperor Wu of Jin established his oldest living son, the developmentally disabled Sima Zhong, as Heir. |
| 280 | 15 March | Conquest of Wu by Jin: Sun Hao presented himself as a prisoner to the Jin general Wang Jun. |
| Chen Shou compiled the Records of the Three Kingdoms. | ||
| 290 | 17 May | Emperor Wu died. He was succeeded by his developmentally disabled son Emperor Hui of Jin, with Yang Jun acting as regent. |
| 291 | War of the Eight Princes: Hui's wife Jia Nanfeng invited troops loyal to his brother Sima Wei into the Jin capital Luoyang to imprison the empress dowager Empress Yang Zhi and her relatives. |
4th century
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 304 | The Xiongnu noble Liu Yuan declared himself prince of Former Zhao. | |
| The Di warlord Li Xiong declared himself prince of Cheng Han. | ||
| 307 | 8 January | Hui was poisoned, probably by the regent Sima Yue. |
| Hui's brother Emperor Huai of Jin became emperor of the Jin dynasty. | ||
| 311 | Huai was kidnapped from the capital Luoyang by Former Zhao forces. | |
| 313 | Goguryeo conquered and annexed the Lelang Commandery. | |
| 14 March | Huai was executed. | |
| Huai's nephew Emperor Min of Jin became emperor of the Jin dynasty. | ||
| 316 | Min surrendered to the Former Zhao general Liu Yao during a siege of the Jin capital Chang'an. | |
| 317 | Emperor Yuan of Jin declared himself prince of Jin, with his capital at Jiankang. | |
| 318 | Min was executed. | |
| 319 | The Jie warlord Shi Le declared himself prince of Later Zhao. | |
| 320 | Zhang Mao issued a general pardon to the people of Former Liang. | |
| 322 | The first accurate tomb depiction of stirrups appeared. | |
| 323 | 3 January | Yuan died. He was succeeded by his son Emperor Ming of Jin. |
| 324 | The rebel Wang Dun died. | |
| 325 | 18 October | Ming died. He was succeeded by his young son Emperor Cheng of Jin. |
| 328 | The rebel Su Jun was defeated by the Jin generals Tao Kan and Wen Jiao. | |
| 329 | The Later Zhao general Shi Hu captured Shanggui in modern Tianshui and killed the Former Zhao emperor Liu Xi and his nobility. | |
| 337 | 23 November | The Xianbei Murong Huang declared himself prince of Former Yan. |
| 342 | 26 June | Cheng died. He was succeeded by his brother Emperor Kang of Jin. |
| 344 | 17 November | Kang died. He was succeeded by his infant son Emperor Mu of Jin. |
| 347 | The Jin general Huan Wen captured the Cheng Han capital Chengdu. | |
| 351 | The Jin general and Di chief Fu Jian declared himself Tian Wang of Former Qin. | |
| The Later Zhao emperor Shi Zhi and his court were killed by one of his generals on the orders of the warlord Ran Min. | ||
| 353 | Wang Xizhi wrote the Lantingji Xu. | |
| 361 | 10 July | Mu died. |
| Mu's cousin Emperor Ai of Jin became emperor of the Jin dynasty. | ||
| 365 | 30 March | Ai died. He was succeeded by his brother Emperor Fei of Jin. |
| 366 | Gu Kaizhi became a Jin officer. | |
| 369 | A Jin army led by Huan was annihilated as it retreated from the Former Yan capital Ye by the general Murong Chui. | |
| 370 | The Former Yan emperor Murong Wei was captured by the Former Qin prime minister Wang Meng. | |
| 372 | 6 January | Huan deposed Fei in favor of his granduncle Emperor Jianwen of Jin. |
| 12 September | Jianwen died. He was succeeded by his young son Emperor Xiaowu of Jin. | |
| 376 | 26 September | Duke Zhang Tianxi of Former Liang surrendered to Former Qin. |
| 383 | November | Battle of Fei River: A Jin army defeated a massively larger Former Qin force, inflicting some seven hundred thousand casualties and expanding Jin territory north to the Yellow River. |
| 384 | The Xianbei Former Qin general Murong Chui declared himself prince of Later Yan. | |
| The Former Qin general Yao Chang declared himself prince of Later Qin. | ||
| 385 | The Xianbei chief and Former Qin vassal Qifu Guoren joined an active rebellion and declared the independence of Western Qin. | |
| 386 | 20 February | Emperor Daowu of Northern Wei declared himself prince of Northern Wei. |
| The Former Qin general Lü Guang declared himself Tian Wang of the majority-Di Later Liang. | ||
| 394 | The Former Qin emperor Fu Chong was killed and his territory annexed by Western Qin forces. | |
| 396 | Xiaowu was suffocated by one of his concubines. He was succeeded by his young and severely disabled son Emperor An of Jin. | |
| 397 | Xiongnu rebels established the Northern Liang, with the Han Duan Ye as king. | |
| The Xianbei chief Tufa Wugu declared the independence of Southern Liang from Later Liang. | ||
| 398 | Murong Chui's brother Murong De declared himself prince of Southern Yan. | |
| 399 | Faxian left for India to acquire Buddhist texts. | |
| 400 | Six commanderies of Northern Liang seceded as Western Liang, under the kingship of the Han Li Gao. |
5th century
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 403 | Under military pressure from Southern Liang and Northern Liang, the Later Liang emperor Lü Long surrendered his capital Guzang, in modern Wuwei, to the Later Qin emperor Yao Xing. | |
| 404 | Huiyuan wrote On Why Monks Do Not Bow Down Before Kings, arguing for the independence of Buddhist clergy from the monarchy. | |
| 405 | Tao Yuanming retired. | |
| 407 | The Later Yan emperor Murong Xi was beheaded by his adoptive nephew, the Korean people Gao Yun, who became emperor of the successor state of Northern Yan. | |
| The Later Qin general Helian Bobo declared himself Tian Wang of the majority-Xiongnu Xia. | ||
| 410 | 25 March | The Southern Yan emperor Murong Chao was executed by Jin along with his court and nobility. |
| 414 | Western Qin conquered the Southern Liang capital Ledu, in modern Haidong. | |
| 417 | The Later Qin emperor Yao Hong surrendered to the Jin general Emperor Wu of Liu Song. | |
| 419 | 28 January | An was strangled on Wu's orders and succeeded by his brother Emperor Gong of Jin. |
| 420 | Wu deposed Gong, marking the beginning of the Liu Song dynasty. | |
| 421 | The Western Liang prince Li Xun committed suicide during the siege of his capital Dunhuang by Northern Liang. | |
| 431 | Summer | The Western Qin prince Qifu Mumo was executed along with his nobility by the Xia emperor Helian Ding. |
| Helian Ding was captured by the khan of Tuyuhun. | ||
| 436 | 4 June | The Northern Yan emperor Feng Hong fled the capital Helong in the face of an attack by Northern Wei. |
| 460 | Juqu Anzhou, the prince of Northern Liang in exile in Gaochang, was killed with his family by the Rouran Khaganate. | |
| 475 | Bodhidharma arrived in China. | |
| 477 | The oldest known painted depiction of a horse collar was made in the Mogao Caves. | |
| 479 | The Liu Song emperor Emperor Shun of Liu Song was deposed by his general Emperor Gao of Southern Qi. | |
| 485 | The Northern Wei emperor Emperor Xiaowen of Northern Wei introduced the equal-field system. | |
| 496 | Change of Xianbei names to Han names: Xianbei names were converted to Han names in Northern Wei. |
6th century
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 501 | Compilation began of the Spring and Autumn Annals of the Sixteen Kingdoms. | |
| 502 | The young Southern Qi emperor Emperor He of Southern Qi was deposed by his general Emperor Wu of Liang. | |
| 523 | The Songyue Pagoda was built. | |
| 534 | The Northern Wei emperor Emperor Xiaowu of Northern Wei fled the capital Luoyang to Chang'an at the advance of his general Gao Huan. | |
| Gao Huan appointed Emperor Xiaojing of Eastern Wei emperor of Eastern Wei with his capital at Ye. | ||
| 543 | The Yupian was completed. | |
| 550 | 5 June | The Eastern Wei general Emperor Wenxuan of Northern Qi deposed Xiaojing and established the state of Northern Qi. |
| 557 | The Liang general Emperor Wu of Chen deposed the emperor Emperor Jing of Liang, establishing the Chen dynasty. | |
| 15 February | The Western Wei general Yuwen Hu deposed the emperor Emperor Gong of Western Wei in favor of his own cousin Emperor Xiaomin of Northern Zhou, establishing the successor state of Northern Zhou. | |
| 577 | 4 February | The Northern Qi emperor Gao Heng and his father, the Taishang Huang Gao Wei, were executed with their family by Northern Zhou. |
| 581 | The Northern Zhou emperor Emperor Jing of Northern Zhou was forced to abdicate in favor of his regent Emperor Wen of Sui, initiating the Sui dynasty. | |
| 582 | Compilation began of the Jingdian Shiwen. | |
| 589 | Yan Zhitui first referred to toilet paper. | |
| 10 February | Sui forces captured the Chen capital Jiankang and its emperor Chen Shubao. | |
| 598 | Goguryeo–Sui War: A Sui army of some three hundred thousand, led by the general Yang Liang, invaded Goguryeo. |
7th century
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 601 | The Qieyun was published. | |
| 602 | Sui–Former Lý War: Sui conquered and annexed the Early Lý dynasty. | |
| 604 | 13 August | Wen died. He was succeeded by his son Emperor Yang of Sui. |
| 605 | The imperial examination was first used as the sole criterion for appointing local officials in Sui. | |
| The Zhaozhou Bridge was completed. | ||
| 607 | Japanese missions to Sui China: The Wa emissary Ono no Imoko arrived in Sui. | |
| 609 | The Grand Canal was completed. | |
| 610 | Engineers Geng Xun and Yuwen Kai invented an improved water clock. | |
| Yang ordered his commanderies to submit maps and gazetteers to the central government. | ||
| 611 | The Four Gates Pagoda was completed. | |
| 612 | Battle of Salsu: Goguryeo routed a Sui invasion force at the Chongchon River, inflicting some three hundred thousand casualties. | |
| 616 | Sa'd ibn Abi Waqqas first visited China. | |
| 617 | 18 December | The rebel Emperor Gaozu of Tang, in control of the Sui capital Chang'an, declared Yang Taishang Huang and his grandson Yang You emperor. |
| 618 | 12 June | Transition from Sui to Tang: Gaozu deposed Yang You. |
| 621 | 28 May | Battle of Hulao: Tang forces defeated and captured the warlord Dou Jiande at Hulao Pass. |
| 624 | Ouyang Xun completed the Yiwen Leiju. | |
| 626 | 2 July | Xuanwu Gate Incident: Gaozu's son Emperor Taizong of Tang assassinated his brothers Li Yuanji and the crown prince Li Jiancheng. |
| 4 September | Gaozu retired. Taizong succeeded him. | |
| 630 | Tang campaign against the Eastern Turks: Tang forces captured the khan of the Eastern Turkic Khaganate in the Yin Mountains. | |
| 635 | The first Christian missionaries arrived in China. | |
| Nestorian monks from Anatolia and the Sasanian Empire built the Daqin Pagoda. | ||
| Alopen wrote the Jesus Sutras. | ||
| Emperor Taizong's campaign against Tuyuhun: The Tuyuhun khan Murong Fuyun, in flight from Tang forces and with much of his army destroyed, was killed by his officers. | ||
| The Book of Liang was published. | ||
| 636 | The Xumi Pagoda was completed. | |
| The Book of Chen, Book of Northern Qi, Book of Zhou, and Book of Sui were compiled. | ||
| 638 | Tibetan attack on Songzhou: Tibetan forces raided the city of Songzhou, in modern Songpan County. | |
| 640 | The Protectorate General to Pacify the West was established. | |
| Tang campaign against Karakhoja: Tang defeated and annexed Gaochang. | ||
| 641 | Emperor Taizong's campaign against Xueyantuo: Taizong sent his general Li Shiji to support the restoration of the Eastern Turkic Khaganate under Qilibi Khan against Xueyantuo. | |
| 643 | Taizong commissioned Yan Liben to paint portraits of his officials at Lingyan Pavilion. | |
| 644 | Tang campaigns against Karasahr: A Tang army captured Karasahr and installed a friendly king. | |
| 645 | 20 July | First campaign in the Goguryeo–Tang War: Tang forces dispersed a Goguryeo army which had arrived in defense of Ansi City. |
| 646 | Bianji compiled the Great Tang Records on the Western Regions. | |
| 647 | The Protectorate General to Pacify the North was established. | |
| 648 | The Book of Jin was compiled. | |
| Tang campaigns against Karasahr: Tang forces captured the king of Karasahr. | ||
| 649 | The four arts were first written of as skills required of a Chinese scholar-official. | |
| 19 January | Tang campaign against Kucha: Kucha surrendered to Tang forces. | |
| 10 July | Taizong died. | |
| 15 July | Taizong's son Emperor Gaozong of Tang became emperor of the Tang dynasty. | |
| 657 | Gaozong commissioned the compilation of a materia medica. | |
| Battle of Irtysh River: Tang forces ambushed and largely destroyed the army of the Western Turkic Khaganate at the Irtysh River. | ||
| 659 | The History of the Southern Dynasties and the History of the Northern Dynasties were completed. | |
| 663 | Battle of Baekgang: The allied navies of Silla and the Tang dynasty defeated a combined Baekje restorationist and Japanese force in the lower reaches of the Geum River. | |
| 666 | The Chinese Buddhist monks Zhiyu and Zhiyou crafted a mechanical south-pointing chariot for the Japanese emperor Emperor Tenji. | |
| 668 | The Protectorate General to Pacify the East was established. | |
| 683 | 27 December | Gaozong died. |
| 684 | The Qianling Mausoleum was completed. | |
| Luo Binwang died. | ||
| 690 | 16 October | Gaozong's wife Wu Zetian became emperor of the Tang dynasty. |
| 692 | Tang forces reconquered the Four Garrisons of Anxi from Tibet. | |
| 700 | The Dunhuang map was created. |
8th century
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 704 | The Giant Wild Goose Pagoda was rebuilt. | |
| 705 | 22 February | Wu Zetian was forced to abdicate the throne in favor of her son Emperor Zhongzong of Tang. |
| 23 February | Zhongzong became emperor of Tang. | |
| 709 | The Small Wild Goose Pagoda was completed. | |
| 710 | Liu Zhiji compiled the Shitong. | |
| Shangguan Wan'er died. | ||
| 3 July | Zhongzong died after being poisoned, probably by his wife Empress Wei. | |
| 8 July | Zhongzong's son Emperor Shang of Tang became emperor of Tang, with Wei acting as regent. | |
| 25 July | A coup led by Gaozong's daughter Princess Taiping and grandson Emperor Xuanzong of Tang killed Wei and deposed Shang in favor of his uncle, Gaozong's son Emperor Ruizong of Tang. | |
| 712 | 8 September | Ruizong abdicated the throne to Xuanzong. |
| The Pear Garden was established. | ||
| 713 | The Kaiyuan Za Bao was first published. | |
| 725 | Yi Xing invented a water-powered armillary sphere. | |
| 729 | Gautama Siddha completed the compilation of the Treatise on Astrology of the Kaiyuan Era. | |
| 740 | Wu Daozi died. | |
| Meng Haoran died. | ||
| 744 | Du Fu and Li Bai first met. | |
| 751 | July | Battle of Talas: After the defection of their Karluk mercenaries, a Tang force was defeated by a vastly superior Abbasid-Tibetan allied army on the Talas River, probably near modern Talas. |
| 755 | 16 December | An Lushan Rebellion: The Tang jiedushi An Lushan declared himself emperor of Yan. |
| Zhang Xuan died. | ||
| 756 | Spring | Battle of Yongqiu: Yan forces retreated from their siege of a Tang fortress in Yongqiu, in modern Kaifeng. |
| 12 August | The Tang army declared Xuanzong's son Emperor Suzong of Tang emperor at Lingwu. | |
| 10 September | Xuanzong recognized Suzong as emperor. | |
| 757 | Battle of Suiyang: Yan forces finally conquered Suiyang, in modern Suiyang District, after a siege that cost the lives of some sixty thousand Yan soldiers and thirty thousand Tang civilians were lost to starvation and cannibalism. | |
| 758 | Arab and Persian pirates looted and burned the Tang seaport of Guangzhou. | |
| 759 | Wang Wei died. | |
| 760 | Lu Yu composed The Classic of Tea. | |
| Yangzhou massacre (760): Arab and Persian merchants are killed by Chinese rebels. | ||
| 762 | 16 May | Suzong died of a heart attack. |
| 18 May | Suzong's son Emperor Daizong of Tang became emperor of the Tang dynasty. | |
| Du Huan wrote the Jingxingji. | ||
| 763 | An Lushan Rebellion: The Yan emperor Shi Chaoyi committed suicide in flight from Tang forces. | |
| 779 | 23 May | Daizong died. |
| 12 June | Daizong's son Emperor Dezong of Tang became emperor of the Tang dynasty. | |
| 781 | The Nestorian Stele was composed. | |
| 783 | Han Gan died. | |
| 785 | The Tang official Jia Dan began work on a map of Tang and its former colonies. | |
| 794 | Prince Li Gao ordered the construction of the first Chinese paddle-wheel ships. |
9th century
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 801 | Du You completed the Tongdian. | |
| 805 | 25 February | Dezong died. |
| 28 February | Dezong's son Emperor Shunzong of Tang became emperor of the Tang dynasty. | |
| 31 August | Shunzong abdicated in favor of his son Emperor Xianzong of Tang. | |
| 806 | Xianzong launched the first of a series of military campaigns against the provinces. | |
| 820 | 14 February | Xianzong died, possibly after being poisoned by one of his eunuch officers. |
| 20 February | Xianzong's son Emperor Muzong of Tang became emperor of the Tang dynasty. | |
| 824 | 25 February | Muzong died. |
| 29 February | Muzong's young son Emperor Jingzong of Tang became emperor of the Tang dynasty. | |
| Han Yu died. | ||
| 827 | 9 January | Jingzong was assassinated. |
| 13 January | Jingzong's brother Emperor Wenzong of Tang became emperor of the Tang dynasty. | |
| 831 | An Uyghur sued the son of a Tang general for failure to repay a debt. | |
| 840 | 10 February | Wenzong died. |
| 20 February | Wenzong's brother Emperor Wuzong of Tang became emperor of the Tang dynasty. | |
| 843 | A large fire consumed four thousand buildings in an eastern neighborhood of the Tang capital Chang'an. | |
| 845 | Great Anti-Buddhist Persecution: Wuzong abolished Buddhist monasteries as well as establishments of Zoroastrianism and Christianity, which were thought to be Buddhist heresies. | |
| 846 | 22 April | Wuzong died. |
| 25 April | Wuzong's uncle, Xianzong's son Emperor Xuānzong of Tang became emperor of the Tang dynasty. | |
| Bai Juyi died. | ||
| 851 | The Arab merchant Sulaiman al-Tajir visited Guangzhou. | |
| 852 | Du Mu died. | |
| 853 | Duan Chengshi published the Miscellaneous Morsels from Youyang. | |
| 858 | A flood along the Grand Canal and on the North China Plain killed tens of thousands. | |
| 859 | 7 September | Xuānzong died. |
| 13 September | Xuānzong's son Emperor Yizong of Tang became emperor of the Tang dynasty. | |
| 863 | Duan Chengshi published a work describing the slave trade, ivory trade and ambergris trade in Bobali, probably modern Berbera. | |
| 868 | 11 May | The Diamond Sutra was printed. |
| 873 | 15 August | Yizong died. |
| 16 August | Yizong's son Emperor Xizong of Tang became emperor of the Tang dynasty. | |
| 874 | Wang Xianzhi launched a rebellion against the Tang government. | |
| 879 | Guangzhou massacre: The rebel Huang Chao burned and looted Guangzhou and killed as many as two hundred thousand foreigners, mainly Arabs and Persians. | |
| 884 | 13 July | Huang was murdered with his immediate family while in flight from Tang forces. |
| 888 | 20 April | Xizong died. He was succeeded by his brother Emperor Zhaozong of Tang. |
10th century
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 904 | 22 September | Zhaozong was killed on the orders of the warlord Zhu Wen, then in control of the Tang capital Chang'an. |
| 26 September | Zhu Wen appointed Zhaozong's young son Emperor Ai of Tang emperor of the Tang dynasty. | |
| 907 | 27 February | The Khitan chieftain Abaoji became emperor of the Liao dynasty. |
| 12 May | Zhu Wen deposed Ai and declared himself emperor of Later Liang. The princes Yang Wo and Wang Jian, who did not recognize Zhu Wen, became de facto independent, as did their states Wu and Former Shu, respectively. | |
| Zhu Wen created Qian Liu the prince of Wuyue. | ||
| Zhu Wen created Ma Yin, the jiedushi of the Wu'an Circuit, prince of Chu. | ||
| 909 | 27 April | Zhu Wen created Wang Shenzhi prince of Min. |
| 917 | The earliest Chinese reference to Greek fire appeared. | |
| 5 September | Liu Yan declared himself emperor of Southern Han. | |
| 919 | The flamethrower was first described in China. | |
| 923 | 13 May | Prince Li Cunxu of Jin declared himself emperor of Later Tang. |
| 18 November | The Later Liang emperor Zhu Youzhen was killed by one of his generals at the approach of Li Cunxu to his capital Daliang. | |
| 924 | 14 April | Gao Jixing declared himself king of Jingnan. |
| 925 | 15 December | The Former Shu emperor Wang Zongyan surrendered to the Later Tang army at his capital Chengdu. |
| 926 | 6 September | Abaoji died. |
| 927 | 11 December | Abaoji's son Emperor Taizong of Liao became emperor of the Liao dynasty. |
| 934 | 16 March | Meng Zhixiang, the Later Tang jiedushi of the territory of the defunct Former Shu, declared himself emperor of Later Shu. |
| 936 | 28 November | Taizong recognized the Shatuo Later Tang general Shi Jingtang emperor of Later Jin in exchange for the promised cession of the Sixteen Prefectures that formed a natural border around the North China Plain. |
| 937 | 11 January | The Later Tang emperor Li Congke burned himself to death with his family and servants as the joint armies of Liao and Later Jin approached his capital Luoyang. |
| 10 November | The Wu emperor Yang Pu was deposed by his general Li Bian, who declared himself emperor of the Wu successor state of Southern Tang. | |
| 945 | 2 October | Min was conquered and annexed by Southern Tang. |
| 947 | 11 January | The Later Jin emperor Shi Chonggui was deposed and his territory annexed by the Liao dynasty. |
| 10 March | The Shatuo Liu Zhiyuan, a jiedushi of the defunct Later Jin, declared himself emperor of Later Han. | |
| 15 May | Taizong died. | |
| 16 May | Taizong's nephew Emperor Shizong of Liao, whom he had raised, became emperor of the Liao dynasty. | |
| 950 | The earliest known depiction of a fire lance and lobbed grenade appeared. | |
| 951 | 2 January | The Later Han emperor Liu Chengyou was killed by one of his officers while attempting to escape the siege of the capital Ye by his general Guo Wei. |
| 13 February | Guo Wei declared himself emperor of Later Zhou. | |
| 7 October | Shizong was murdered by one of his officers. | |
| 11 October | Shizong's cousin, Taizong's son Emperor Muzong of Liao became emperor of the Liao dynasty. | |
| Southern Tang conquered and annexed Chu. | ||
| Liu Zhiyuan's brother Liu Chong declared himself declared himself emperor of Northern Han. | ||
| 960 | Gu Hongzhong painted the Night Revels of Han Xizai. | |
| 3 February | Emperor Guo Zongxun of Later Zhou was overthrown by his general Emperor Taizu of Song. | |
| 4 February | Taizu became emperor of the Song dynasty. | |
| Taizu was presented with gunpowder-impregnated fire arrows. | ||
| The Hundred Family Surnames was composed. | ||
| 961 | The Huqiu Tower was built. | |
| 963 | The Song dynasty conquered and annexed Jingnan. | |
| 965 | 23 February | The Later Shu emperor Meng Chang surrendered to the Song army at his capital Chengdu. |
| 969 | 12 March | Muzong was murdered by his servants on a hunting trip. |
| 13 March | Shizong's son Emperor Jingzong of Liao became emperor of the Liao dynasty. | |
| 971 | Southern Han was conquered and annexed by the Song dynasty. | |
| 974 | Song troops constructed a floating pontoon bridge across the Yangtze River in order to secure supply lines while fighting against the Southern Tang. | |
| 976 | 1 January | Song forces conquered and annexed Southern Tang. |
| 14 November | Taizu died. | |
| 15 November | Taizu's brother Emperor Taizong of Song became emperor of the Song dynasty. | |
| The Yuelu Academy was founded. | ||
| 977 | The pagoda of the Longhua Temple was built. | |
| 978 | The Taiping Guangji was completed. | |
| The Wuyue king Qian Chu surrendered his territory to Taizong. | ||
| 979 | The Northern Han emperor Liu Jiyuan surrendered to Song. | |
| 981 | Battle of Bạch Đằng: A Song naval invasion of the Early Lê dynasty via the Bạch Đằng River was aborted after the land invasion was stalled. | |
| 982 | 13 October | Jingzong died. |
| 14 October | Jingzong's young son Emperor Shengzong of Liao became emperor, with his widow Empress Xiao Yanyan acting as regent. | |
| 983 | The Taiping Yulan was completed. | |
| 984 | Qiao Weiyo invented the canal pound lock. | |
| 986 | The Wenyuan Yinghua was completed. | |
| 990 | Fan Kuan was born. | |
| 993 | November | First conflict in the Goryeo–Khitan War: Liao forces invaded Goryeo. |
| 997 | The Longkan Shoujian was completed. | |
| 8 May | Taizong died. He was succeeded by his son Emperor Zhenzong. | |
| 1000 | The Chinese first used coke in place of charcoal for blast furnaces. |
11th century
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1005 | Song signed the Chanyuan Treaty, under which it agreed to pay Liao an annual tribute in silk and silver. | |
| 1008 | The Guangyun was completed. | |
| 1010 | Second conflict in the Goryeo–Khitan War: Liao captured the Goryeo general Gang Jo and burned the capital Kaesong. | |
| An atlas of China was completed. | ||
| 1013 | Cefu Yuangui was completed. | |
| 1018 | Third conflict in the Goryeo–Khitan War: Liao invaded Goryeo. | |
| 1019 | 10 March | Battle of Kuju: Goryeo forces decisively defeated a retreating Liao army at Kuju, near modern Kusong. |
| 1022 | 23 March | Zhenzong died. |
| 24 March | Zhenzong's son Emperor Renzong of Song became emperor of the Song dynasty. | |
| 1031 | 25 June | Shengzong died. He was succeeded by his son Emperor Xingzong of Liao. |
| 1037 | The Jiyun was published. | |
| 1038 | 10 November | The Tangut chieftain Emperor Jingzong of Western Xia declared himself emperor of Western Xia. |
| 1041 | Bi Sheng invented movable type. | |
| 1043 | Ouyang Xiu and the vice chancellor Fan Zhongyan drafted the Qingli Reforms in Song. | |
| 1044 | The Wujing Zongyao was completed. | |
| 1045 | The Lingxiao Pagoda was completed. | |
| 1048 | 19 January | Jingzong died. He was succeeded by his infant son Emperor Yizong of Western Xia. |
| 1049 | The Iron Pagoda was completed. | |
| 1055 | The Liaodi Pagoda was completed. | |
| 28 August | Xingzong died. He was succeeded by his son Emperor Daozong of Liao. | |
| 1056 | The Pagoda of Fogong Temple was completed. | |
| 1060 | Ouyang Xiu completed the New Book of Tang. | |
| 1063 | 30 April | Renzong died. |
| 1 May | Emperor Yingzong of Song became emperor of the Song dynasty. | |
| The Pizhi Pagoda was completed. | ||
| 1067 | Yizong died. He was succeeded by his young son Emperor Huizong of Western Xia. | |
| 25 January | Yingzong died. He was succeeded by his son Emperor Shenzong of Song. | |
| 1068 | The dry dock was first used in China. | |
| 1069 | The Song chancellor Wang Anshi ordered an extensive government reform including the introduction of the baojia system of community-based law enforcement. | |
| 1070 | The Song ambassador Su Song published the Bencao Tujing. | |
| 1072 | Guo Xi painted Early Spring. | |
| 1075 | The Song diplomat Shen Kuo used court archives to reject Daozong's territorial claims. | |
| A proto-Bessemer process was first observed in Cizhou. | ||
| 1076 | Wang resigned. | |
| 1077 | Su was sent on a mission to Liao. | |
| 1080 | Shen was appointed to defend Yan'an. | |
| 1081 | A Song army was dealt some sixty thousand casualties defending Yan'an against an attempted invasion of Song by Western Xia forces. | |
| Su published a 200-volume work on Song-Liao relations. | ||
| 1084 | Sima Guang completed the Zizhi Tongjian. | |
| Li Qingzhao was born. | ||
| 1085 | 1 April | Shenzong died. He was succeeded by his young son Emperor Zhezong, with his widow Empress Xiang acting as regent. |
| Xiang ousted the court faction affiliated with Wang's reforms at Sima's urging. | ||
| 1086 | Huizong died. | |
| Huizong's son Emperor Chongzong of Western Xia became emperor of Western Xia. | ||
| 1088 | Shen published the Dream Pool Essays. | |
| 1090 | The earliest known description of the mechanical belt appeared. | |
| 1094 | Su completed a clock tower in Kaifeng. | |
| The Dongpo Academy was established on Hainan. | ||
| 1100 | 23 February | Zhezong died. He was succeeded by his younger brother Emperor Huizong of Song. |
12th century
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1101 | 12 February | Daozong was murdered. He was succeeded by his grandson Emperor Tianzuo of Liao. |
| 1103 | The Yingzao Fashi was published. | |
| 1107 | Mi Fu died. | |
| 1111 | The Donglin Academy was founded. | |
| 1115 | 28 January | The Wanyan chieftain Emperor Taizu of Jin declared himself emperor of the Jin dynasty. |
| August | Taizu conquered the Liao city of Huanglongfu. | |
| 1119 | Zhu Yu published the Pingzhou Table Talks. | |
| 1120 | The pagoda of Tianning Temple was completed. | |
| 1123 | 19 September | Taizu died. |
| 27 September | Taizu's brother Emperor Taizong of Jin became emperor of the Jin dynasty. | |
| 1124 | The Liao general Yelü Dashi established the Khitan Qara Khitai in the Liao northwest. | |
| 1125 | 26 March | Jin dynasty forces captured Tianzuo. |
| November | Jin–Song Wars: The Jin army invaded Song. | |
| 1126 | 18 January | Huizong abdicated in favor of his son Emperor Qinzong. |
| 19 January | Emperor Qinzong became emperor of the Song dynasty. | |
| 1127 | 9 January | Jingkang Incident: The Song capital Kaifeng fell to a Jin siege. Huizong and Qinzong were captured with much of their court. |
| 12 June | Huizong's son Emperor Gaozong of Song became emperor of the Song dynasty at Lin'an City. | |
| 1132 | Song established a standing navy headquartered at Dinghai in modern Dinghai District. | |
| A fire destroyed some thirteen thousand homes in the Song capital Lin'an City. | ||
| 1135 | The Song general Yue Fei defeated the bandit Yang Yao at Dongting Lake. | |
| 9 February | Taizong died. | |
| 10 February | Emperor Xizong of Jin became emperor of the Jin dynasty. | |
| 1139 | Chongzong died. | |
| Chongzong's son Emperor Renzong of Western Xia became emperor of Western Xia. | ||
| 1141 | Song signed the Treaty of Shaoxing, under which it relinquished all claims to its former territories north of the Huai River and agreed to pay Jin an annual tribute in silk and silver. | |
| 1142 | 27 January | Yue was executed on false charges of treason spurred by the Song chancellor Qin Hui. |
| 1150 | 9 January | Xizong was murdered in a coup by Wanyan Liang, who succeeded him as emperor of Jin. |
| 1153 | The Jin capital was moved from Huining Prefecture to Zhongdu. | |
| 1157 | The Jin capital was moved to Kaifeng. | |
| 1161 | 27 October | Wanyan Liang's cousin Emperor Shizong of Jin was declared emperor of Jin in the capital Kaifeng. |
| 16 November | Battle of Tangdao: The Jin navy suffered heavy losses in an attempted invasion of Song near the Shandong Peninsula. | |
| 27 November | Battle of Caishi: Jin forces suffered as many as four thousand casualties at the hands of the Song dynasty in a naval battle which stalled their invasion across the Yangtze. | |
| 15 December | Wanyan Liang was assassinated by one of his officers near the Yangtze battlefront. | |
| The Yunjing was compiled. | ||
| 1162 | 24 July | Gaozong abdicated in favor of Emperor Xiaozong of Song. |
| The Beisi Pagoda was completed. | ||
| 1164 | Song and Jin concluded the Treaty of Longxing. | |
| 1165 | The Liuhe Pagoda was completed. | |
| 1179 | Zhu Xi rebuilt the White Deer Grotto Academy. | |
| 1189 | 20 January | Shizong died. He was succeeded by his grandson Emperor Zhangzong of Jin. |
| 18 February | Xiaozong abdicated in favor of his son Emperor Guangzong of Song. | |
| The Chengling Pagoda was built. | ||
| 1193 | Renzong died. | |
| Renzong's son Emperor Huanzong of Western Xia became emperor of Western Xia. | ||
| 1194 | 24 July | Guangzong was forced to abdicate in favor of his son Emperor Ningzong. |
13th century
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1206 | Huanzong was overthrown in a coup. | |
| Emperor Xiangzong of Western Xia became emperor of Western Xia. | ||
| 1208 | 29 December | Zhangzong died. He was succeeded by his brother Wanyan Yongji. |
| 1211 | Emperor Shenzong of Western Xia deposed and replaced Xiangzong as emperor of Western Xia. | |
| August | Battle of Yehuling: The army of the Mongol Empire captured or killed over four hundred thousand Jin soldiers defending an important mountain pass at Zhangjiakou. | |
| 1213 | 11 September | Wanyan Yongji was assassinated. |
| 22 September | Emperor Xuanzong of Jin became emperor of the Jin dynasty. | |
| 1214 | The Jin dynasty signed a treaty under which it became a vassal state paying tribute to the Mongol Empire. | |
| 1215 | 1 June | Battle of Zhongdu: Mongol forces breached the walls of Zhongdu and massacred its inhabitants. |
| 1217 | Jin–Song Wars: A Song army captured the Jin city of Xihezhou in modern Xihe County. | |
| 1223 | Shenzong abdicated in favor of his son Emperor Xianzong of Western Xia. | |
| 1224 | 14 January | Xuanzong died. |
| 15 January | Xuanzong's son Emperor Aizong of Jin became emperor of the Jin dynasty. | |
| 17 September | Ningzong died. He was succeeded by Emperor Lizong. | |
| 1226 | Xianzong died. | |
| Emperor Mozhu of Western Xia became emperor of Western Xia. | ||
| 1227 | 18 August | The Mongol khagan Genghis Khan died. |
| Mozhu surrendered to the Mongol Empire during the siege of the Western Xia capital Zhongxing. | ||
| 1233 | 26 February | Mongol siege of Kaifeng: The Jin general in charge of the defense of the capital Kaifeng surrendered to the besieging Mongol army. Aizong had fled during the siege; his family members still in the city were executed. |
| 1234 | 9 February | Siege of Caizhou: Aizong passed the throne to his general Emperor Mo of Jin and hanged himself in the face of a Mongol siege of Caizhou. The Mongols breached the city. |
| 10 February | Siege of Caizhou: Mo died fighting the Mongols at Caizhou. | |
| 1247 | Qin Jiushao wrote the Mathematical Treatise in Nine Sections. | |
| 1259 | 11 August | The Mongol khagan Möngke Khan died during a siege of Diaoyu Fortress. |
| 1260 | Toluid Civil War: Möngke's brother Ariq Böke declared himself khagan of the Mongol Empire. | |
| 5 May | Toluid Civil War: Kublai Khan, brother to Möngke and to Ariq Böke, was crowned khagan of the Mongol Empire. | |
| Kublai appointed the Sakya lama Drogön Chögyal Phagpa Imperial Preceptor. | ||
| 1261 | Yang Hui first drew Pascal's triangle. | |
| 1264 | 16 November | Lizong died. He was succeeded by his nephew Emperor Duzong. |
| 1265 | Mongol conquest of the Song dynasty: The Mongol Empire invaded Song. | |
| 1267 | Battle of Xiangyang: Kublai ordered his general Aju to take Xiangyang. | |
| 1270 | Sambyeolcho Rebellion: The Sambyeolcho rebelled against Wonjong of Goryeo, the Mongol-allied king of Goryeo. | |
| 1271 | Marco Polo left Venice. | |
| Kublai declared himself emperor of the Yuan dynasty. | ||
| 1273 | 14 March | Battle of Xiangyang: The Yuan army breached and captured Xiangyang. |
| 1274 | 12 August | Duzong died. He was succeeded by his young son Emperor Gong of Song. |
| 5 October | Mongol invasions of Japan: A Yuan fleet landed at Tsushima Island. | |
| 1275 | The Yuan general Bayan of the Baarin defeated a Song army led by the chancellor Jia Sidao. | |
| 1276 | 4 February | Gong and his great aunt the grand empress dowager Xie Daoqing surrendered themselves to the Yuan army besieging the Song capital Lin'an City. |
| 14 June | Gong's older brother, the young Emperor Duanzong, was crowned emperor of the Song dynasty at Fuzhou. | |
| Qian Xuan retired. | ||
| The Gaocheng Astronomical Observatory was built. | ||
| 1278 | The Song general Wen Tianxiang was captured by Yuan forces. | |
| 8 May | Duanzong died. | |
| 10 May | Duanzong's younger brother Emperor Bing of Song became emperor of the Song dynasty. | |
| 1279 | 19 March | Battle of Yamen: A Yuan fleet destroyed a vastly superior Song force near Yamen. The Song chancellor Lu Xiufu drowned himself with Bing. |
| 1287 | The Zhongdu-born Rabban Bar Sauma left for Europe as an ambassador of Arghun, the khan of the Ilkhanate. | |
| December | Battle of Pagan: Yuan forces captured the Pagan capital Bagan. | |
| 1288 | Battle of Bạch Đằng: Đại Việt decisively defeated a numerically superior Yuan invasion fleet on the Bạch Đằng River. | |
| 1289 | Europeans in Medieval China: Franciscan friars first conducted missionary work in China. | |
| 1294 | 18 February | Kublai died. |
| 10 May | Kublai's grandson Temür Khan became emperor of the Yuan dynasty. | |
| 1293 | John of Montecorvino arrives in China and is appointed Archbishop of Khanbaliq (Beijing). | |
| 1298 | Wang Zhen invented movable wooden type. |
14th century
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1307 | 10 February | Temür died. |
| 21 June | Temür's nephew Külüg Khan became emperor of the Yuan dynasty. | |
| 1311 | 27 January | Külüg died. |
| 7 April | Külüg's younger brother Ayurbarwada Buyantu Khan became emperor of the Yuan dynasty. | |
| 1316 | Guo Shoujing died. | |
| 1320 | 1 March | Ayurbarwada died. |
| 19 April | Ayurbarwada's son Gegeen Khan became emperor of the Yuan dynasty. | |
| 1323 | 4 September | Gegeen was assassinated by the Asud in a coup led by the Khongirad grand censor Tegshi. |
| 4 October | Yesün Temür became emperor of the Yuan dynasty. | |
| 1324 | Zhongyuan Yinyun was published. | |
| 1328 | 15 August | Yesün Temür died. |
| October | Yesün Temür's son Ragibagh Khan was appointed emperor of the Yuan dynasty in Shangdu. | |
| 16 October | The Yuan general El Temür crowned Jayaatu Khan Tugh Temür emperor in Khanbaliq. | |
| 14 November | Forces loyal to El Temür captured Shangdu and may have executed Ragibagh. | |
| 1329 | 27 February | Tugh Temür's brother Khutughtu Khan Kusala crowned himself emperor of the Yuan dynasty in Karakorum with the support of the Chagatai Khanate. |
| 3 April | Tugh Temür abdicated in Khutughtu's favor. | |
| 30 August | Khutughtu died, probably after being poisoned by Tugh Temür. | |
| 8 September | Tugh Temür was crowned emperor of the Yuan dynasty. | |
| 1330 | The Pagoda of Bailin Temple was completed. | |
| 1332 | 2 September | Tugh Temür died. |
| 23 October | El Temür crowned Khutughtu's young son Rinchinbal Khan emperor of the Yuan dynasty. | |
| 14 December | Rinchinbal died. | |
| 1333 | 19 July | Rinchinbal's older brother Toghon Temür became emperor of the Yuan dynasty. |
| 1334 | Wang Dayuan travelled to North Africa. | |
| 1342 | Papal missionary Giovanni de Marignolli leaves Europe for Khanbaliq (Beijing). | |
| 1351 | Red Turban Rebellion: The millenarian White Lotus sect first plotted armed rebellion against the Yuan dynasty. | |
| 1352 | Red Turban Rebellion: The Hongwu Emperor joined the rebellion. | |
| 1356 | Red Turban Rebellion: The rebel army captured Nanjing. | |
| 1363 | 30 August | Battle of Lake Poyang: A Red Turban fleet commanded by the Hongwu Emperor met a fleet led by Chen Youliang, the self-proclaimed king of the rebel state of Han, on Poyang Lake. |
| 4 October | Battle of Lake Poyang: The Han navy was destroyed. Chen Youliang was killed. | |
| 1368 | 20 January | Red Turban Rebellion: The Hongwu Emperor declared himself emperor of the Ming dynasty. |
| September | Toghon Temür fled Khanbaliq for Shangdu in the face of a Ming advance. | |
| 1371 | Ming implemented the haijin, a ban on all private maritime commerce. | |
| 1373 | The Hongwu Emperor abolished the imperial examination in favor of a recommendation system for appointing local Ming officials. | |
| The Temple of the Six Banyan Trees was rebuilt. | ||
| 1375 | 16 May | Liu Bowen died. |
| 1380 | The Hongwu Emperor abolished the office of chancellor and took over direct control of the Three Departments and Six Ministries. | |
| 1382 | 6 January | Ming conquest of Yunnan: Basalawarmi, the prince of Liang and a Yuan loyalist, committed suicide during a massive Ming invasion of Yunnan. |
| The Jinyiwei was established and given supreme judicial authority and complete autonomy in making arrests and issuing punishments. | ||
| 1384 | The Hongwu Emperor reinstituted the imperial examination. | |
| 1397 | A legal code based on the Tang Code was implemented in Ming. | |
| 1398 | 24 June | The Hongwu Emperor died. |
| 30 June | The Hongwu Emperor's young grandson the Jianwen Emperor became emperor of the Ming dynasty. |
15th century
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1402 | 13 July | Jingnan Campaign: Forces loyal to the Jianwen Emperor's uncle the Yongle Emperor entered the capital Nanjing and burned the imperial palace with the Jianwen Emperor inside. |
| 17 July | The Yongle Emperor became emperor of the Ming dynasty. | |
| 1405 | 11 July | Treasure voyages: The Yongle Emperor ordered a fleet of Chinese treasure ships under the command of the admiral Zheng He to reestablish tributary relationships with states in the South China Sea and Indian Ocean. |
| The Ming Xiaoling Mausoleum was completed. | ||
| 1406 | Construction began on the Forbidden City and Beijing city fortifications. | |
| 1407 | 10 April | The Kagyu karmapa Deshin Shekpa, 5th Karmapa Lama arrived at the Ming capital Nanjing. |
| 16 June | Ming–Hồ War: Ming forces captured the Hồ king Hồ Hán Thương. | |
| 1408 | The Yongle Encyclopedia was completed. | |
| 1415 | Restoration work on the Grand Canal was completed. | |
| 1420 | Construction of the Forbidden City and Beijing city fortifications was completed. The Yongle Emperor moved the Ming capital from Nanjing to Beijing. | |
| The Ming tombs were built. | ||
| 1424 | 12 August | The Yongle Emperor died. |
| 7 September | The Yongle Emperor's son the Hongxi Emperor became emperor of the Ming dynasty. | |
| 1425 | 29 May | The Hongxi Emperor died, probably from a heart attack. |
| 27 June | The Hongxi Emperor's son the Xuande Emperor became emperor of the Ming dynasty. | |
| 1427 | Shen Zhou was born. | |
| 1431 | Ming recognized the Lê dynasty as a tributary state. | |
| 1435 | 31 January | The Xuande Emperor died. |
| 7 February | The Xuande Emperor's son the Zhengtong Emperor became emperor of the Ming dynasty. | |
| 1443 | The Zhihua Temple was built. | |
| 1446 | The Precious Belt Bridge was rebuilt. | |
| 1449 | 1 September | Tumu Crisis: A Four Oirat force defeated a vastly superior Ming army at Tumu in modern Huailai County and captured the Zhengtong Emperor. |
| 22 September | The Zhengtong Emperor's brother the Jingtai Emperor became emperor of the Ming dynasty. | |
| 1457 | 11 February | The Zhengtong Emperor overthrew the Jingtai Emperor in a coup and took power as the Tianshun Emperor. |
| 1461 | 7 August | Rebellion of Cao Qin: An uprising of Mongol soldiers in the Ming capital Beijing, led by the general Cao Qin, was crushed. |
| 1464 | 23 February | The Zhengtong Emperor died. |
| 28 February | The Zhengtong Emperor's son the Chenghua Emperor became emperor of the Ming dynasty. | |
| The Miao and Yao peoples rebelled against Ming authority in Guangxi. | ||
| 1473 | The Zhenjue Temple was completed. | |
| 1487 | 9 September | The Chenghua Emperor died. |
| 22 September | The Chenghua Emperor's son the Hongzhi Emperor became emperor of the Ming dynasty. | |
| 1488 | The Joseon official Choe Bu suffered a shipwreck in Zhejiang. |
16th century
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1505 | 8 June | The Hongzhi Emperor died. |
| 19 June | The Hongzhi Emperor's son the Zhengde Emperor became emperor of the Ming dynasty. | |
| 1510 | 12 May | Prince of Anhua rebellion: Ming tax collectors were murdered on the orders of Zhu Zhifan, the prince of Anhua in modern Shaanxi. |
| 1511 | 15 August | Capture of Malacca: A Portuguese invasion force conquered the Malacca Sultanate. |
| 1513 | The Portuguese explorer Jorge Álvares arrived on Lintin Island in the Pearl River Delta. | |
| 1516 | The Portuguese explorer Rafael Perestrello arrived in Guangzhou. | |
| 1517 | The Portuguese ambassadors Fernão Pires de Andrade and Tomé Pires arrived in Guangzhou. | |
| 1519 | 10 July | Prince of Ning rebellion: The prince of Ning Zhu Chenhao declared that the Zhengde Emperor was an usurper and led an expedition toward Nanjing. |
| 1521 | 20 April | The Zhengde Emperor died. |
| 27 May | The Zhengde Emperor's cousin, the Chenghua Emperor's grandson the Jiajing Emperor, became emperor of the Ming dynasty. | |
| The Jiajing Emperor expelled the Portuguese embassy. | ||
| 1529 | Wang Yangming died. | |
| 1530 | An improved sand-driven mechanical clock was invented. | |
| 1549 | Portuguese trade ships first stopped at Shangchuan Island. | |
| 1550 | The Mongol chieftain Altan Khan burned and looted the Ming capital Beijing and its suburbs. | |
| 1553 | The Ming capital Beijing was expanded to the south, increasing its size from four to four and a half square miles. | |
| 1554 | The Luso-Chinese agreement (1554) for Macau is made between the Kingdom of Portugal and the Ming dynasty. | |
| 1556 | 23 January | 1556 Shaanxi earthquake: An earthquake in and around modern Shaanxi killed some eight hundred thousand people. |
| 1557 | The Kingdom of Portugal established a permanent settlement in Macau. | |
| 1558 | Ming forces led by Qi Jiguang dealt the wokou a defeat at Cengang. | |
| 1567 | 23 January | The Jiajing Emperor died. |
| 4 February | The Jiajing Emperor's son the Longqing Emperor became emperor of the Ming dynasty. | |
| The Ming haijin (ban on private maritime commerce) was repealed. | ||
| 1572 | 5 July | The Longqing Emperor died. |
| 19 July | The Longqing Emperor's son the Wanli Emperor became emperor of the Ming dynasty. | |
| 1573 | Spain established a permanent base at Manila. | |
| 1574 | Qin Liangyu was born. | |
| 1576 | The Pagoda of Cishou Temple was built. | |
| 1577 | The Wanshou Temple was built. | |
| 1580 | The grand secretary Zhang Juzheng instituted the single whip law, under which all monetary and labor obligations to the central government were consolidated into a single silver payment. | |
| 1582 | Jesuit China missions: The Jesuit missionary Matteo Ricci arrived in Macau. | |
| Private newspapers were first published in Beijing. | ||
| 1584 | The earliest known depiction of the sailing carriage appeared. | |
| 1587 | Li Shizhen published the Compendium of Materia Medica. | |
| 1590 | Wu Cheng'en wrote Journey to the West. | |
| 1592 | Japanese invasions of Korea: Some two hundred thousand Japanese troops invaded Joseon. | |
| 1593 | 8 January | Siege of Pyongyang: A combined Ming-Joseon force drove the Japanese army from Pyongyang. |
| 1597 | 23 December | Siege of Ulsan: A combined Ming-Joseon force arrived at the Japanese-controlled Ulsan Japanese Castle. |
| 1598 | 29 September | Battle of Sacheon: A Japanese army under siege at Sacheon drove off a numerically superior Ming-Joseon force after the accidental explosion of the Ming powder cache. |
| 16 December | Battle of Noryang: The allied navies of Ming and Joseon dealt heavy damage to a Japanese fleet attempting to break their blockade of Suncheon Japanese Castle. | |
| The Peony Pavilion was first performed at the Pavilion of Prince Teng. |
17th century
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1602 | The Dutch East India Company (VOC) began shipping Chinese ceramics to Europe. | |
| 1604 | The grand secretary Gu Xiancheng reopened the Donglin Academy in Wuxi, establishing the Donglin movement. | |
| 1607 | Euclid's Elements was first translated into Chinese. | |
| 1609 | Sancai Tuhui was published. | |
| 1610 | Jin Ping Mei was published. | |
| 1615 | The Zihui was compiled. | |
| 1616 | 17 February | Nurhaci declared himself khan of the later Jin dynasty. |
| All foreign Jesuits were expelled from the Ming imperial court and astronomy bureau. | ||
| 1619 | 18 April | Battle of Sarhu: The last of four Ming armies was destroyed during a retreat from a punitive expedition against Nurhaci and the later Jin. Its commander Li Rubai committed suicide |
| Wang Fuzhi was born. | ||
| 1620 | 18 August | The Wanli Emperor died. |
| 28 August | The Wanli Emperor's son the Taichang Emperor became emperor of the Ming dynasty. | |
| 26 September | The Taichang Emperor died. | |
| 1 October | The Taichang Emperor's young son the Tianqi Emperor became emperor of the Ming dynasty. | |
| 1624 | The VOC established the state of Dutch Formosa. | |
| 1626 | Johann Adam Schall von Bell wrote the first Chinese language treatise on the telescope. | |
| The Jesuit Nicolas Trigault invented the first system for the romanization of Chinese. | ||
| Battle of Ningyuan: A Ming force defended Xingcheng against a numerically superior later Jin army. Nurhaci suffered fatal wounds. | ||
| 1627 | January | First Manchu invasion of Korea: Nurhaci's son Hong Taiji, the khan of the later Jin dynasty, invaded Joseon. |
| 30 September | The Tianqi Emperor died. | |
| 2 October | The Tianqi Emperor's younger brother the Chongzhen Emperor became emperor of the Ming dynasty. | |
| 13 December | The eunuch Wei Zhongxian committed suicide on hearing that the Jinyiwei had issued a warrant for his arrest. | |
| The Zhengzitong was published. | ||
| The Polish Jesuit Michał Boym first introduced the heliocentric model of the solar system into Chinese astronomy. | ||
| 1632 | The later Jin dynasty conquered Inner Mongolia. | |
| 1634 | The Chongzhen Emperor acquired the telescope of the late Johann Schreck. | |
| 1635 | Liu Tong wrote a preface to the Dijing Jingwulue. | |
| 1637 | 30 January | Second Manchu invasion of Korea: The Joseon king Injo of Joseon recognized Hong Taiji's Qing dynasty as the legitimate rulers of China. |
| Song Yingxing published the Tiangong Kaiwu. | ||
| 1638 | The Peking Gazette first used moveable type. | |
| 1639 | Xu Guangqi published a treatise on agriculture. | |
| Chen Hongshou arrived in Beijing. | ||
| 1641 | 8 March | Xu Xiake died. |
| 1642 | 1642 Yellow River flood: The Ming governor of Kaifeng destroyed the levees holding back the Yellow River in order to break the siege of the peasant army of Li Zicheng. The resulting flood destroyed Kaifeng and killed some three hundred thousand people. | |
| A Han army was made the last of the Qing Eight Banners. | ||
| 1643 | 21 September | Hong Taiji died. |
| 8 October | Hong Taiji's young son the Shunzhi Emperor became emperor of the Qing dynasty. | |
| 1644 | 25 April | The Chongzhen Emperor hanged himself from the Zuihuai as the army of Li Zicheng's Shun dynasty breached the walls of the Ming capital Beijing. |
| 27 May | Battle of Shanhai Pass: A Shun army was dealt a heavy defeat by the Qing and the former Ming general Wu Sangui at Shanhai Pass. | |
| 4 June | Li Zicheng fled Beijing. | |
| 1645 | 20 May | Yangzhou massacre: Qing forces conquered Yangzhou from the Southern Ming. A ten-day massacre began in which some eight hundred thousand people would be killed. |
| 1653 | January | The 5th Dalai Lama, the Dalai Lama of Tibet, visited the Qing capital Beijing. |
| 1659 | Jesuits Martino Martini and Ferdinand Verbiest arrived in China. | |
| 1661 | 5 February | The Shunzhi Emperor died. He was succeeded by his young son the Kangxi Emperor, with the Four Regents of the Kangxi Emperor acting as regents. |
| 14 June | The Southern Ming admiral Koxinga declared the establishment of the Kingdom of Tungning on Taiwan. | |
| 1662 | 1 February | Siege of Fort Zeelandia: The VOC surrendered Fort Zeelandia on Taiwan to Koxinga. |
| 1664 | Schall von Bell was imprisoned. | |
| 1673 | Revolt of the Three Feudatories: Wu rebelled against the Qing dynasty on the pretext of seeking to restore the Ming. | |
| 1682 | The Belgian Jesuit Antoine Thomas arrived in China. | |
| 1683 | Battle of Penghu: A Qing fleet destroyed the Tungning navy at Penghu. The king of Tungning Zheng Keshuang surrendered to the Qing. | |
| 1684 | The first of the Qing Thirteen Factories, neighborhoods where foreigners were allowed to live and trade, were established outside Guangzhou. | |
| 1689 | 27 August | The Qing dynasty signed the Treaty of Nerchinsk with Russia, under which the two countries mutually agreed to a border at the Stanovoy Range. |
| 1690 | Yun Shouping died. | |
| 1698 | The Lugou Bridge was reconstructed. |
18th century
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1705 | 4 December | The papal legate Charles-Thomas Maillard De Tournon arrived in the Qing capital Beijing. |
| 1711 | The East India Company (EIC) established a trading post in Guangzhou. | |
| The Peiwen Yunfu was completed. | ||
| 1715 | 19 March | Chinese Rites controversy: The pope Pope Clement XI issued a papal bull forbidding veneration of the dead and worship of Confucius among Chinese converts to Catholicism. |
| 1716 | The Kangxi Dictionary was published. | |
| 1720 | Chinese expedition to Tibet: A Qing expedition expelled the invading forces of the Dzungar Khanate from Tibet. | |
| 1721 | Chinese Rites controversy: The Kangxi Emperor banned Christian missions in China. | |
| 1722 | 20 December | The Kangxi Emperor died. |
| 27 December | The Kangxi Emperor's son the Yongzheng Emperor became emperor of the Qing dynasty. | |
| 1725 | The Gujin Tushu Jicheng was completed. | |
| 1732 | Jiang Tingxi died. | |
| 1735 | 8 October | The Yongzheng Emperor died. He was succeeded by his son the Qianlong emperor. |
| 1750 | The French Jesuit Jean Joseph Marie Amiot was sent to China. | |
| 1755 | Ten Great Campaigns: The khan of the Dzungar Khanate surrendered to invading Qing forces. | |
| The Puning Temple was built to commemorate the defeat of the Dzungar Khanate. | ||
| 1760 | The Canton System was established, under which the Chinese merchants operating in the Thirteen Factories were organized into a guild, the Cohong, and given an official monopoly. | |
| 1771 | The Putuo Zongcheng Temple was completed. | |
| 1774 | The Wenjin Chamber was built. | |
| 1780 | A pagoda was built at Fragrant Hills. | |
| 1782 | The Siku Quanshu was completed. | |
| 1791 | Dream of the Red Chamber was published. | |
| 1793 | 14 September | Macartney Embassy The British ambassador George Macartney, 1st Earl Macartney was introduced to the Qianlong Emperor. |
| 1796 | 9 February | The Qianlong Emperor abdicated in favor of his son the Jiaqing Emperor. |
| White Lotus Rebellion: White Lotus began an armed rebellion against the Qing dynasty. |
19th century
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1807 | Protestant missions in China 1807–1953: The Protestant missionary Robert Morrison arrived in China. | |
| 1820 | 2 September | The Jiaqing Emperor died. |
| 3 October | The Jiaqing Emperor's son the Daoguang Emperor became emperor of the Qing dynasty. | |
| 1823 | The Bible was first published in Chinese. | |
| 1839 | 3 June | Destruction of opium at Humen: The Qing Imperial Commissioner Lin Zexu ordered the destruction of roughly a thousand tons of opium seized from EIC merchants in Humen. |
| 1842 | 29 August | First Opium War: The Qing dynasty and the United Kingdom signed the Treaty of Nanking, under which the former agreed to end the monopoly of the Cohong, pay reparations for the war and the destruction of opium, and cede Hong Kong Island in perpetuity. |
| 1844 | Wei Yuan published the Illustrated Treatise on the Maritime Kingdoms. | |
| 3 July | The Qing dynasty and the United States signed the Treaty of Wanghia, according to which the United States was granted most favoured nation (MFN) status and extraterritoriality was granted to its citizens resident in China. | |
| 1850 | 25 February | The Daoguang Emperor died. |
| 9 March | The Daoguang Emperor's son the Xianfeng Emperor became emperor of the Qing dynasty. | |
| 1851 | 11 January | Jintian Uprising: The followers of Hong Xiuquan, who believed him to be the younger brother of Jesus, announced their rebellion against the Qing dynasty and the establishment of the Taiping Heavenly Kingdom in modern Guiping. |
| 1855 | Third plague pandemic: A plague pandemic began in Yunnan which would kill hundreds of thousands in China and millions worldwide. | |
| Punti-Hakka Clan Wars: An ethnic conflict began in Guangdong between the Punti and Hakka peoples which would claim roughly a million lives. | ||
| 1856 | 23 October | Second Opium War: The British navy began a bombardment of Guangzhou. |
| 1858 | 28 May | The Qing dynasty signed the Treaty of Aigun, ceding to Russia the land north of the Amur River. |
| June | Second Opium War: The Qing dynasty signed the Treaty of Tientsin, under which foreigners were granted greater freedom of movement within China and France and the United Kingdom were promised war reparations. | |
| 18 November | Battle of Sanhe: A Taiping army encircled and destroyed a much smaller Qing force in Anhui. | |
| 1860 | 18 October | Second Opium War: British and French forces looted and burned down the Old Summer Palace in the Qing capital Beijing. |
| 24 October | The Qing prince Prince Gong signed the Convention of Peking, ratifying the Treaty of Tientsin and ceding the Kowloon Peninsula in perpetuity to the United Kingdom. | |
| 1861 | Gong established the Zongli Yamen to temporarily supervise the conduct of foreign affairs throughout the Qing government. | |
| 22 August | The Xianfeng Emperor died. | |
| 11 November | The Xianfeng Emperor's young son the Tongzhi Emperor became emperor of the Qing dynasty. | |
| 1862 | Dungan Revolt: A disordered uprising began among the Hui people living on the west bank of the Yellow River. | |
| The Tongwen Guan school of European languages was established. | ||
| 1864 | May | The Ever Victorious Army of the Qing dynasty was disbanded. |
| 1868 | 22 August | Yangzhou riot: Scholar-officials resident in Yangzhou instigated a riot in which the headquarters of the British missionary society OMF International were attacked and burned. |
| Nian Rebellion: The last of the rebel armies was destroyed. | ||
| 1870 | June | Tianjin massacre: A riot took place in Tianjin in which some sixty people, including foreigners and Chinese Christians, were killed. |
| 1871 | Li Hongzhang was appointed Viceroy of Zhili. | |
| 1873 | Panthay Rebellion: The last surviving Panthay rebels were defeated by the Qing dynasty in Tengchong. | |
| 1875 | 12 January | The Tongzhi Emperor died. |
| 21 February | Margary Affair: The British diplomat Augustus Raymond Margary was murdered with his retinue in Tengchong. | |
| 25 February | The young Guangxu Emperor became emperor of the Qing dynasty, with the empress dowagers Empress Dowager Ci'an and Empress Dowager Cixi acting as regents. | |
| 1876 | 21 August | The Qing dynasty and the United Kingdom signed the Chefoo Convention, under which Qing promised to punish those responsible for Margary's murder and repeal the likin. |
| 1884 | 23 August | Battle of Fuzhou: A French fleet destroyed the Qing Fujian Fleet at the mouth of the Min River. |
| 1891 | Foreign businessmen established the Shanghai Sharebrokers' Association in Shanghai. | |
| 1894 | 1 August | First Sino-Japanese War: War was officially declared between Japan and the Qing dynasty. |
| 1895 | 17 April | First Sino-Japanese War: The Qing dynasty signed the Treaty of Shimonoseki, under which it recognized the independence of Joseon, granted Japan MFN status and ceded to it Penghu, Taiwan and the Liaodong Peninsula. |
| 1898 | 11 June | Hundred Days' Reform: The Guangxu Emperor instituted reforms including radical changes in the imperial examination and the elimination of sinecures. |
| 21 September | The Guangxu Emperor was removed from the imperial palace in a coup organized by Cixi and Ronglu, the Viceroy of Zhili. | |
| 1900 | 21 June | Boxer Rebellion: Cixi responded to anti-foreign unrest by issuing the Imperial Decree of declaration of war against foreign powers in the Guangxu Emperor's name. |
20th century
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1901 | 7 September | Boxer Rebellion: The Qing dynasty and Eight-Nation Alliance signed the Boxer Protocol, under which the Alliance was granted war reparations and the right to station troops in the capital Beijing. |
| 1908 | 14 November | The Guangxu Emperor died of arsenic poisoning. |
| 2 December | The Guangxu Emperor's young nephew Puyi became emperor of the Qing dynasty. | |
| 1911 | 27 April | Second Guangzhou uprising |
| 10 October | Wuchang uprising: New Army soldiers staged a mutiny in Wuchang District and occupied the residence of the Viceroy of Huguang. | |
| 29 December | Republic of China provisional presidential election, 1911: Sun Yat-sen was elected president of the Provisional Government of the Republic of China, with a majority of sixteen of the seventeen provincial representatives of the Tongmenghui in Nanjing. | |
| 1912 | 1 January | Xinhai Revolution: Sun Yat-sen was inaugurated president of the Provisional Government of the Republic of China. |
| 12 February | Xinhai Revolution: Puyi's regent, the empress dowager Empress Dowager Longyu, signed an edict under which Puyi would retain his imperial title but all power would pass to the Provisional Government of the Republic of China. | |
| 10 March | Sun Yat-sen resigned in favor of Yuan Shikai. | |
| 25 August | The Tongmenghui and several smaller revolutionary parties merged to form the Kuomintang (KMT). | |
| Republic of China National Assembly election, 1912: An election to the National Assembly under the Provisional Constitution of the Republic of China began which would produce pluralities for the KMT in the House and Senate. | ||
| 1915 | 8 January | Japan issued the Twenty-One Demands to the Republic of China, including demands for territory in Shandong, Manchuria and Inner Mongolia, rights of extraterritoriality for its citizens in China, and influence in China's internal affairs. |
| 15 September | Chen Duxiu founded the magazine New Youth. | |
| 12 December | Yuan declared himself the Hongxian Emperor of the Empire of China. | |
| The progressive, anti-Confucian New Culture Movement was founded. | ||
| 25 December | National Protection War: The republican generals Cai E and Tang Jiyao declared the independence of Yunnan from the Empire of China. | |
| 1916 | 16 June | Yuan died. |
| 1919 | 4 May | May Fourth Movement: A student protest against the Treaty of Versailles took place at Tiananmen. |
| 28 June | The Treaty of Versailles, among whose provisions was the transfer of German territories in Shandong to Japan, was signed. | |
| 1921 | 1 June | The Communist Party of China (CPC) was founded. |
| 4 December | The first installment of Lu Xun's novel The True Story of Ah Q, the first work written in written vernacular Chinese, was published. | |
| 1923 | January | The Radio Corporation of China was founded. |
| The KMT and CPC agreed to the First United Front, under which Communists would join the KMT as individuals to help combat warlordism. | ||
| 1926 | 9 July | Northern Expedition: The KMT general Chiang Kai-shek launched an expedition of some hundred thousand National Revolutionary Army (NRA) soldiers from Guangdong against the warlords Zhang Zuolin, Wu Peifu and Sun Chuanfang. |
| 1927 | 12 April | Shanghai massacre of 1927: KMT forces led by Chiang attack Communist allies in Shanghai, initiating a full-scale purge of Communists in regions under KMT control. |
| 1 August | Nanchang uprising: Communist forces launched an uprising against the KMT in Nanchang. | |
| 1928 | 7 May | Jinan Incident: The Japanese general Hikosuke Fukuda tortured and killed seventeen of Chiang's representatives in Jinan. |
| 4 June | Huanggutun incident: Zhang Zuolin's train was blown up by the Japanese Kwantung Army, killing him. | |
| 10 October | Chiang became chairman of the Nationalist government of the Republic of China. | |
| 1931 | July | Encirclement Campaign against Northeastern Jiangxi Soviet: The NRA encircled and invested the Northeastern Jiangxi Soviet. |
| July | 1931 China floods: Flooding began in the valleys of the Yellow, Yangtze and Huai Rivers which would claim as many as four million lives. | |
| 18 September | Mukden Incident: In a false flag operation against the Republic of China, Japanese agents set off a dynamite explosion near a South Manchuria Railway line. | |
| Japanese invasion of Manchuria: The Kwantung Army invested all Manchurian territory along the South Manchuria Railway. | ||
| 7 November | The Chinese Soviet Republic was established in Ruijin. | |
| 15 December | Chiang resigned under pressure from the KMT. Lin Sen became acting chairman of the Nationalist government. | |
| 1932 | 1 January | Lin Sen became chairman of the Nationalist government. |
| 28 January | January 28 Incident: Japanese aircraft carriers began bombing Shanghai in a series of raids which would kill some four thousand soldiers of the 19th Route Army and as many as twenty thousand Chinese civilians. | |
| 4 February | Defense of Harbin: Japanese bombs and artillery forced the Jilin Self-Defence Army to retreat from Harbin. | |
| 18 February | The independent state of Manchukuo was established on the territory of Japanese-occupied Manchuria. | |
| 9 March | Pacification of Manchukuo: The Big Swords Society rebelled en masse against the government of Manchukuo. | |
| 1934 | February | Chiang and his wife Soong Mei-ling established the quasi-fascist New Life Movement. |
| 16 October | Long March: The Chinese Workers' and Peasants' Red Army broke through the KMT lines attempting to encircle them at Ganzhou. | |
| 1935 | 5 February | First Encirclement Campaign against Hubei–Henan–Shaanxi Soviet: Red Army forces forced the retreat of a KMT army attempting to encircle the soviet of Hubei, Henan and Shaanxi. |
| 9 December | December 9th Movement: A student protest took place in Beijing demanding internal liberalization and stronger anti-Japanese resistance. | |
| 1936 | 12 December | Xi'an Incident: Zhang Xueliang arrested Chiang in Xi'an due to concerns he was insufficiently committed to anti-Japanese resistance. |
| 1937 | 7 March | Marco Polo Bridge Incident: Roughly one hundred Chinese soldiers were killed defending the Marco Polo Bridge in Beijing from a Japanese attack. |
| 22 September | The KMT and CPC joined to establish the Second United Front. The Red Army was reorganized into the Eighth Route and New Fourth Armies, which were nominally part of the NRA chain of command. | |
| 25 September | Battle of Pingxingguan: The Eighth Route Army wiped out a Japanese force of a few hundred attempting to bring supplies through Pingxing Pass. | |
| 26 October | Battle of Shanghai: The NRA began withdrawing from downtown Shanghai in the face of a Japanese onslaught. | |
| 10 December | Battle of Nanking: The Japanese Central China Area Army launched a full-scale assault on Nanjing. | |
| 13 December | Nanking massacre: Nanjing fell to the Japanese Central China Area Army. A six-week massacre began in which tens of thousands of women were raped and as many as three hundred thousand civilians were killed. | |
| 1938 | 18 February | Bombing of Chongqing: The Japanese army and naval air services began a bombing campaign against civilian targets in Chongqing which would kill some ten thousand people. |
| 7 April | Battle of Taierzhuang: The Japanese army was forced to withdraw after suffering heavy losses in an attempted conquest of Tai'erzhuang District. | |
| 1939 | 1 September | The nominally independent Mengjiang was established on the Mongol territories of the Japanese-occupied Chahar and Suiyuan provinces. |
| 17 September | Battle of Changsha: The Japanese army attacked Changsha. | |
| 1940 | 20 August | Hundred Regiments Offensive: Communist NRA soldiers under Peng Dehuai began a campaign of terrorism and sabotage against Japanese targets in North China. |
| 1941 | 1 February | The Communist official Mao Zedong gave a speech in Yan'an entitled "Reform in Learning, the Party and Literature," establishing the Yan'an Rectification Movement and beginning an ideological purge which would claim some ten thousand lives. |
| 30 September | Battle of Changsha: A Japanese army began a general retreat after failing to take Changsha. | |
| 1942 | 15 January | Battle of Changsha: A Japanese army crossed the Xinqiang River after suffering heavy losses in a failed attempt to conquer Changsha. |
| 1943 | 1 August | Lin Sen died. Chiang became acting chairman of the Nationalist government. |
| 27 November | Cairo Conference: Chiang, United States president Franklin D. Roosevelt, and British prime minister Winston Churchill issued the Cairo Declaration, under which the three powers expressed their desire for the independence of Korea and the return of Chinese territories. | |
| 1944 | 27 May | Battle of Changsha: The Japanese army launched a general offensive against Changsha. |
| 1945 | 26 June | The United Nations Charter establishing the United Nations (UN) was signed at the San Francisco War Memorial and Performing Arts Center by fifty nations including China. |
| 6 August | Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki: As many as eighty thousand Japanese, largely civilians, were killed in the atomic bombing of Hiroshima by a United States aircraft. | |
| 9 September | Surrender of Japan: Japanese forces in China formally surrendered to Chiang Kai-shek. | |
| 25 October | Surrender of Japan: China regains control of Taiwan from Japan and was proclaimed as Retrocession Day. Chen Yi of the Kuomintang was appointed Chief Executive. | |
| November | Campaign to Suppress Bandits in Northeast China: The Communist People's Liberation Army (PLA) launched a campaign against bandits and KMT guerillas in northeast China. | |
| 1946 | 20 July | Chinese Civil War: The NRA invaded PLA-held territory en masse. |
| 1947 | 28 February | February 28 Incident: Nationalist forces violently suppressed an anti-government protest in Taiwan Province. |
| 25 December | The Constitution of the Republic of China came into force, dissolving the Nationalist government and renaming the NRA the Republic of China (ROC) Armed Forces. | |
| 1948 | 2 November | Liaoshen Campaign: The last ROC garrison in Manchuria, in Yingkou, retreated in the face of a PLA advance. |
| 15 December | Huaihai Campaign: The PLA encircled an ROC army in Xuzhou. | |
| 1949 | 21 January | Chiang resigned the presidency of the Republic of China due to military failures and under pressure from his vice president Li Zongren, who succeeded him as acting president. |
| 31 January | Pingjin Campaign: The PLA took Beijing. | |
| 23 April | Chinese Civil War: The PLA conquered the ROC capital Nanjing. The ROC moved its capital to Guangzhou. | |
| 1 October | Mao declared the establishment of the People's Republic of China (PRC). | |
| 10 December | The ROC moved its capital from Chengdu to Taipei. |
| After 10 December 1949, the history of the Republic of China continues at Timeline of Taiwanese history. |
| 1950 | 5 March | Landing Operation on Hainan Island: Chinese forces landed on ROC-controlled Hainan. |
| 25 June | Korean War: The North Korean army launched a 135,000-man surprise assault across the 38th parallel into South Korea. | |
| 25 November | Battle of the Ch'ongch'on River: The Chinese 38th Group Army broke the UN line between the 7th Infantry Division and 8th Infantry Division in the valley of the Chongchon River. | |
| Mass executions of political prisoners took place in the Canidrome. | ||
| 1951 | 23 May | Representatives of the Dalai Lama of Tibet the 14th Dalai Lama and of the Central People's Government of the People's Republic of China signed the Seventeen Point Agreement for the Peaceful Liberation of Tibet, which guaranteed Tibetan autonomy within China and called for the integration of the Tibetan Army into the PLA. |
| 1952 | January | The five-anti campaign, which encouraged accusations against the bourgeoisie of crimes such as bribery and tax evasion, was founded. see Three-anti and Five-anti Campaigns |
| 1953 | The first of the five-year plans of China, which called for construction of heavy industry, began to be carried out. | |
| 1956 | An outbreak of the Influenza A virus subtype H2N2 occurred in China. | |
| 1957 | 27 February | Mao published a speech entitled "On the Correct Handling of the Contradictions Among the People," marking the founding of the Hundred Flowers Campaign which encouraged criticism of the government and the Communist Party. |
| July | Mao instigated the Anti-Rightist Movement during which hundreds of thousands of alleged rightists, including many who had criticized the government during the Hundred Flowers Campaign, were purged from the CPC or sentenced to labor or death. | |
| 1958 | Great Leap Forward: The CPC led campaigns to massively overhaul the Chinese economy and society with such innovations as collective farming and the use of backyard furnaces. | |
| Mao launched the Four Pests Campaign, which encouraged the eradication of rats, flies, mosquitos and sparrows. | ||
| Great Chinese Famine: A famine began which would claim as many as forty million lives over three years. | ||
| 1959 | 10 March | 1959 Tibetan uprising: A rebellion broke out in the Tibetan regional capital Lhasa after rumors the government was planning to arrest the 14th Dalai Lama at the local PLA headquarters. |
| 1960 | 16 April | Sino-Soviet split: A CPC newspaper accused the Soviet leadership of "revisionism." |
| 1962 | 20 October | Sino-Indian War: The PLA attacked Indian forces across the Line of Actual Control. |
| 1964 | 5 January | Quotations from Chairman Mao Tse-tung was first published. |
| 16 October | 596: The Chinese government detonated its first nuclear weapon at Lop Nur. | |
| The second of two volumes of Simplified Chinese characters ordered by the State Council of the People's Republic of China was published. | ||
| 1966 | 19 August | Cultural Revolution: The CPC launched a campaign to destroy the Four Olds. |
| The Three-Self Patriotic Movement, the sole government-sanctioned Protestant church, was abolished. | ||
| 1968 | Deng Pufang was thrown from a third-story window at Peking University by Red Guards, crippling him. | |
| 22 December | The People's Daily published an editorial entitled "We too have two hands, let us not laze about in the city," invigorating the Down to the Countryside Movement under which the sent-down youth, many former Red Guards, were relocated from the cities to the country. | |
| 1969 | 2 March | Sino-Soviet border conflict: PLA forces attacked the Soviet Border Troops of the Soviet Union on Zhenbao Island, killing 59. |
| 1 October | The Beijing Subway opened in Beijing. | |
| 1970 | 24 April | China launched Dong Fang Hong I, its first satellite. |
| 1971 | July | United States secretary of state Henry Kissinger visited Beijing. |
| 13 September | Cultural Revolution: Lin Biao dies in mysterious air crash after failed coup. | |
| 25 October | China and the United Nations: The People's Republic of China is admitted to the United Nations, replacing the Republic of China. | |
| 1972 | 28 February | 1972 Nixon visit to China: The United States and China issued the Shanghai Communiqué pledging to normalize relations during the visit of the former's president Richard Nixon. |
| 1974 | 19 January | Battle of the Paracel Islands: Some fifty South Vietnamese soldiers were killed in a Chinese conquest of the Paracel Islands. |
| 1976 | 8 January | The premier Zhou Enlai died. |
| 5 April | Tiananmen Incident: Some four thousand people were arrested during a protest against the removal of wreaths, flowers and poems laid at the Monument to the People's Heroes in Zhou's memory. | |
| 27 July | 1976 Tangshan earthquake: An earthquake with its epicenter near Tangshan killed roughly a quarter of a million people. | |
| 9 September | Mao died. | |
| 6 October | The Gang of Four, a political faction including Mao's wife Jiang Qing, was arrested on the orders of the premier Hua Guofeng. | |
| 7 October | Hua became Chairman of the Communist Party of China. | |
| 1977 | Beijing Spring: A brief period of political liberalization began. | |
| 1978 | 11 October | The poet Huang Xiang pasted pro-democracy, anti-Mao poems on the Democracy Wall in Beijing. |
| December | The Communist official Deng Xiaoping became paramount leader of China. | |
| December | Chinese economic reform: Economic liberalization measures including the replacement of collective farming with the household-responsibility system began to be instituted. | |
| December | Deng Xiaoping first advocated for the Four Modernizations, of agriculture, industry, national defense and science and technology. | |
| 1979 | 1 January | China and the United States issued the Joint Communiqué on the Establishment of Diplomatic Relations, under which the latter recognized the PRC as the legitimate government of China and terminated its participation in the Sino-American Mutual Defense Treaty with Taiwan. |
| 6 March | Sino-Vietnamese War: China declared that the punitive objective of its invasion of Vietnam had been achieved and began to retreat. | |
| 30 March | Deng Xiaoping declared in a speech the Four Cardinal Principles not subject to debate within China. | |
| 1980 | The first of the Special Economic Zones of China, characterized by low regulation and the encouragement of foreign investment, were established. | |
| 28 June | Sino-Vietnamese conflicts 1979–90: Chinese forces began shelling the Vietnamese Cao Bằng Province. | |
| 18 September | The one-child policy, under which Chinese couples are heavily fined for additional children after their first, with some exceptions, came into force, and then phased out in 2015. | |
| 1984 | 19 December | The Sino-British Joint Declaration, under which China and the United Kingdom agreed to the transfer of Hong Kong to China and the preservation there of democracy and capitalism under the one country, two systems model, was signed during the visit of the British prime minister Margaret Thatcher. |
| 1988 | 14 March | Johnson South Reef Skirmish: The PLA took control of the Johnson South Reef after a short naval battle in which some seventy Vietnamese soldiers were killed. |
| 1989 | 15 April | Tiananmen Square protests of 1989: A crowd gathered at the Monument to the People's Heroes. |
| 4 June | Tiananmen Square protests of 1989: Anywhere from 1 to 5 thousand people brutally murdered in the Tiananmen Square Massacre. | |
| 24 June | Jiang Zemin became General Secretary of the Communist Party of China. | |
| 1990 | Shanghai Stock Exchange re-opened on November 26 and began operation on December 19. | |
| 1991 | The first McDonald's restaurant in mainland China opened in Beijing. | |
| 1992 | Deng Xiaoping traveled south to reassert the economy policy. | |
| 1993 | 27 April | Wang–Koo summit took place in Singapore: the first public meeting between figures of non-governmental organization (NGO) since 1949. |
| 1994 | 8 December | 1994 Karamay fire: A fire at a theater in Karamay killed some three hundred people. |
| 1997 | 19 February | Deng Xiaoping died. |
| 1 July | Hong Kong handover ceremony: A ceremony marked the transfer of sovereignty over Hong Kong to China from the United Kingdom under the terms of the Sino-British Joint Declaration. | |
| The term Great Firewall was coined to describe the tools of Internet censorship in China. | ||
| 1998 | June | 1998 China floods: China experienced massive flooding including floods of the Yangtze River, the Nen River, the Songhua River and the Pearl River. Chinese People's Liberation Army earned people's respects because of their heroic behaving against the floods. |
| 1999 | 7 May | United States bombing of the Chinese embassy in Belgrade: United States bombers under the command of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization accidentally bombed the Chinese embassy in Belgrade. |
| 22 July | The Chinese government declared the religious organization Falun Gong illegal. | |
| 20 December | Transfer of sovereignty over Macau: Sovereignty over Macau was transferred from Portugal to China. | |
| 2000 | China passed Japan as the country with which the United States has the largest trade deficit. |
21st century
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 2001 | 23 January | Tiananmen Square self-immolation incident: Five declared by Chinese government members of Falun Gong may have burned themselves to death in Tiananmen Square. |
| 1 April | Hainan Island incident: A United States intelligence aircraft was intercepted and forced to make an emergency landing on Hainan. | |
| 10 November | World Trade Organization Ministerial Conference of 2001: China joined the World Trade Organization, subjecting it to that body's free trade and dispute resolution agreements. | |
| 2002 | 16 November | An outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome began in Guangdong. |
| 2003 | 15 March | Hu Jintao succeeded Jiang Zemin as president. |
| 15 October | China launched its first manned space mission Shenzhou 5. | |
| 2004 | 19 September | Jiang Zemin resigned his position as chairman of the Central Military Commission of the CPC. |
| 2005 | 14 March | The Anti-Secession Law was passed, reasserting China's desire for peaceful reunification with Taiwan and its right to resolve the issue by force. |
| 15 April | 2005 anti-Japanese demonstrations: Mass demonstrations against Japan took place. | |
| 13 November | 2005 Jilin chemical plant explosions: A series of explosions at a chemical plant in Jilin City killed six and forced the evacuation of tens of thousands. | |
| 2007 | 7 May | 2007 Chinese slave scandal: A local television station first reported on missing children kidnapped to work as slaves at brickyards in Shanxi. |
| 10 July | Zheng Xiaoyu, the former head of the State Food and Drug Administration, was executed for corruption. | |
| 3 August | The State Administration for Religious Affairs issued State Religious Affairs Bureau Order No. 5, which required tulkus who planned to be reincarnated to submit an application to the government. | |
| 24 October | The lunar orbiter Chang'e 1 was launched. | |
| 2008 | 25 January | 2008 Chinese winter storms: A series of severe winter storms began which would claim over a hundred lives. |
| 1 May | The Hangzhou Bay Bridge opened to the public. | |
| 12 May | 2008 Sichuan earthquake: An earthquake with its epicenter in Wenchuan County killed nearly seventy thousand people. | |
| 16 July | 2008 Chinese milk scandal: Sixteen infants were diagnosed with kidney stones in Gansu after drinking formula contaminated with melamine. | |
| 8 August | 2008 Summer Olympics opening ceremony: A ceremony marked the beginning of the Olympic Games in Beijing. | |
| 6 September | 2008 Summer Paralympics: The thirteenth Paralympic Games began in Beijing. | |
| 27 September | The astronaut Zhai Zhigang completed China's first spacewalk on Shenzhou 7. | |
| 2009 | 5 July | July 2009 Ürümqi riots: A riot of some thousand Uyghurs began which involved ethnic violence against the Han in Ürümqi. |
| 1 October | 60th anniversary of the People's Republic of China: A military parade on Chang'an Avenue in Beijing commemorated the establishment of the PRC. | |
| 2010 | 14 April | 2010 Yushu earthquake: An earthquake with its epicenter in Yushu killed as many as three thousand people. |
| 1 May | Expo 2010: A world's fair began in Shanghai. | |
| 2011 | 21 September | Wukan protests: Farmers in Wukan attacked a government building due to the government's seizure without compensation of their farmland. |
| 29 September | Tiangong-1 was launched as China's first prototype space station. | |
| 2012 | 6 February | Wang Lijun incident: Wang Lijun, a deputy of Bo Xilai, the Party Committee Secretary of Chongqing, sought refuge at a United States consulate. |
| 4 July | The Three Gorges Dam went into operation. | |
| 19 August | 2012 China anti-Japanese demonstrations: Anti-Japanese protests took place in China due to a dispute over ownership of the Diaoyu Islands. | |
| 15 November | 18th National Congress of the Communist Party of China: Xi Jinping succeeded Hu Jintao as General Secretary of the Communist Party of China. | |
| 2013 | One Belt, One Road was proposed to connect and cooperate among countries primarily between China and rest of Eurasia. | |
| 29 September | The Shanghai Free-Trade Zone was established. | |
| 28 October | 2013 Tiananmen Square attack: A car was driven into a crowd in Tianamen Square, killing the driver and two passengers, Uyghurs associated with the East Turkestan Islamic Movement, and two pedestrians. | |
| 14 December | The lunar lander Chang'e 3 landed on the moon. | |
| 2014 | China became the world's second largest economy. | |
| 1 March | 2014 Kunming attack is a terrorist attack, killing 31 civilians and injuring more than 140 others. No group or individual stepped forward to claim responsibility for the attack. | |
| 2015 | 17 June | 2015–16 Chinese stock market turbulence started. |
| 3 September | 2015 China Victory Day Parade was held on the Tiananmen Square. | |
| 2016 | 15 September | Tiangong-2 was launched with mission of more than ten scientific experiments. |
| 4 September | 2016 G20 Hangzhou summit was held in the city of Hangzhou. | |
See also
- Cities in China
References
- ↑ Xiaohong, et al. (2002).
- 1 2 Huang et al. (2002).
- ↑
- ↑ Wu, Qinglong; Zhao, Zhijun; Liu, Li; Granger, Darryl E.; Wang, Hui; Cohen, David J.; Wu, Xiaohong; Ye, Maolin; Bar-Yosef, Ofer (2016-08-05). "Outburst flood at 1920 BCE supports historicity of China's Great Flood and the Xia dynasty". Science. 353 (6299): 579–582. doi:10.1126/science.aaf0842. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 27493183.
Further reading
- Published in the 19th century
- George Henry Townsend (1867), "China", A Manual of Dates (2nd ed.), London: Frederick Warne & Co.
- William Henry Overall, ed. (1870). "China". Dictionary of Chronology. London: William Tegg.
- Published in the 20th century
- Charles E. Little (1900), "China", Cyclopedia of Classified Dates, New York: Funk & Wagnalls – via Internet Archive
- Benjamin Vincent (1910), "China", Haydn's Dictionary of Dates (25th ed.), London: Ward, Lock & Co. – via Hathi Trust
- Published in the 21st century
- Ian Preston, ed. (2001). "People's Republic of China". Political Chronology of Central, South and East Asia. Political Chronologies of the World. Europa Publications. pp. 32–64. ISBN 978-1-135-35680-4.
- David B.H. Denoon, ed. (2007). "Chronology of Recent Events (1993– )". China: Contemporary Political, Economic, and International Affairs. New York University Press. ISBN 978-0-8147-2140-7.
- Lawrence R. Sullivan (2007). "Chronology". Historical Dictionary of the People's Republic of China. Scarecrow Press. ISBN 978-0-8108-6443-6.
- "China and the world comparative timeline" (PDF). China: Journey to the East. British Museum. 2009.
- James Z. Gao (2009). "Chronology". Historical Dictionary of Modern China (1800–1949). Scarecrow Press. ISBN 978-0-8108-6308-8.
- Xinzhong Yao; Yanxia Zhao (2010). "Timeline for Chinese Religion". Chinese Religion: a Contextual Approach. London: Continuum. ISBN 978-1-84706-476-9.
- Rongxing Guo (2011). "Historical Chronology (1949– )". Introduction to the Chinese Economy. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-0-470-82675-1.
- Lawrence R. Sullivan; Nancy Y. Liu (2015). "Chronology". Historical Dictionary of Science and Technology in Modern China. Rowman & Littlefield. ISBN 978-0-8108-7855-6.
External links
- BBC News. "China Profile: Timeline".
- Chinese History and Dynasties
- "Timeline of Chinese History and Dynasties". Asia for Educators. USA: Columbia University.
- "China". Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History. New York: Metropolitan Museum of Art.
- Freer Gallery of Art. "China History Timeline". Washington DC: Smithsonian Institution. Archived from the original on 2015-07-14.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.