Timbuktu Manuscripts
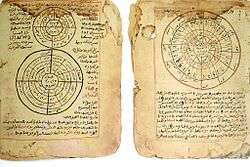

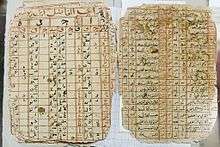
Timbuktu Manuscripts (or Tombouctou Manuscripts) is a blanket term for the large number of historically important manuscripts that have been preserved for centuries in private households in Timbuktu, Mali. The collections include manuscripts about art, medicine, philosophy, and science, as well as copies of the Quran. The number of manuscripts in the collections has been estimated as high as 700,000.[1]
The manuscripts were written in Arabic and local languages like Songhay and Tamasheq.[2] The dates of the manuscripts ranged between the late 13th and the early 20th centuries (i.e., from the Islamisation of the Mali Empire until the decline of traditional education in French Sudan).[3] Their subject matter ranged from scholarly works to short letters. The manuscripts were passed down in Timbuktu families and were mostly in poor condition.[4] Most of the manuscripts remain unstudied and uncatalogued, and their total number is unknown, affording only rough estimates. A selection of about 160 manuscripts from the Mamma Haidara Library in Timbuktu and the Ahmed Baba collection were digitized by the Tombouctou Manuscripts Project in the 2000s.
With the demise of Arabic education in Mali under French colonial rule, appreciation for the medieval manuscripts declined in Timbuktu, and many were being sold off.[5] Time magazine related the account of an imam who picked up four of them for $50 each. In October 2008 one of the households was flooded, destroying 700 manuscripts.[6]
Research

In 1970, UNESCO founded an organization which included among its tasks preservation of the manuscripts, but it went unfunded until 1977.[7] In 1998, Harvard University professor Henry Louis Gates visited Timbuktu for his PBS series Wonders of the African World. The series raised public and academic awareness of the manuscripts, which led to a pool of funding opening up.[8]
The Timbuktu Manuscripts Project was a project of the University of Oslo running from 1999 - 2007, the goal of which was to assist in physically preserving the manuscripts, digitize them and building an electronic catalogue, and making them accessible for research.[9] It was funded by the government of Luxembourg[10] along with the Norwegian Agency for Development Cooperation (NORAD), the Ford Foundation, the Norwegian Council for Higher Education's Programme for Development Research and Education (NUFU), and the United States Ambassador's Fund for Cultural Preservation. Among the results of the project are: reviving the ancient art of book binding and training a solid number of local specialists; devising and setting up an electronic database to catalogue the manuscripts held at the Institut des Hautes Études et de Recherche Islamique – Ahmad Baba (IHERI-AB); digitizing a large number of manuscripts held at the IHERIAB; facilitating scholarly and technical exchange with manuscript experts in Morocco and other countries;[11] reviving IHERI-AB's journal Sankoré; and publishing the splendidly illustrated book, The Hidden Treasures of Timbuktu: Rediscovering Africa's Literary Culture.[12]
Since the end of this project, the cooperation of Grand-Duché de Luxembourg has funded a new project called Timbuktu Manuscripts. This project aims at protecting and promoting Timbuktu Manuscripts, for economic, social and cultural development of the area. It is implemented by the Lux-Development agency and the goals are:
- a better conservation of the manuscripts (100 listed manuscripts, 10 described manuscripts, 2 digitalized manuscripts, 10 restored and protected manuscripts)
- a better scientific utilisation of the manuscripts
- use of manuscripts to promote economic, social and cultural development of the area
Since the events in the North of Mali in 2012, the project MLI/015 works with its main partners in Bamako on result 1. These key partners are the IHERI-AB (Institut des Hautes Etudes et de Recherche Islamique Ahmed Baba) and the SAVAMA DCI (Association de Sauvegarde et de Mise en Valeur des Manuscrits et de Défense de la Culture Islamique). Beginning of 2013, they had completed an important work of describing 10,000 manuscripts through standardized registration forms.
The Timbuktu Manuscripts Project is a separate project run by the University of Cape Town. In a partnership with the government of South Africa, which contributed to the Timbuktu trust fund, this project is the first official cultural project of the New Partnership for Africa's Development. It was founded in 2003 and is ongoing. They released a report on the project in 2008.[13] As well as preserving the manuscripts, the Cape Town project also aims to make access to public and private libraries around Timbuktu more widely available. The project's online database is accessible to researchers only. In 2015 it was announced that the Timbuktu trust fund would close after receiving no more funds from the South African government.[14]
A book about Timbuktu, published in 2008, contains a chapter with some discussions of a few of the texts.[15]
Digital images of thirty-two manuscripts from the private Mamma Haïdara Library are available from the United States Library of Congress;[16] a subset of these are also accessible from the United Nations' World Digital Library website.[17]
Journalistic coverage
A movie about the Timbuktu Manuscript Project, The Ancient Astronomers of Timbuktu, was released in 2009, with funding from the Ford Foundation and Oppenheimer Memorial Trust.[18]
Also in 2009, the French/German cultural TV channel ARTE produced a feature-length film about Timbuktu's manuscript heritage: Tombouctou: les manuscrits sauvés des sables | Timbuktus verschollenes Erbe: vom Sande verweht,[19] Another film on the subject was also released in 2009, entitled "Manuscripts of Timbuktu. The film was made by South African director Zola Maseko, executive produced by the South African Broadcasting Corporation and distributed by California Newsreel.[20]
In 2013, BBC Four has produced a documentary called "The Lost Libraries of Timbuktu."[21]
In 2016, a book about the manuscripts and the efforts to save them in the midst of the assault and occupation of northern Mali by Islamists jihadis, was published. The book, The Bad-Ass Librarians of Timbuktu by Joshua Hammer,[22] provides vivid details about the collection of the manuscripts into libraries, and subsequent efforts to remove them to safety during the dangerous conflict, in which the Islamist jihadis threatened to destroy them.
In 2017, Charlie English published The Storied City : The Quest for Timbuktu and the Fantastic Mission to Save Its Past which tells in alternating chapters the history of European expeditions (1795 – 1860) in search of the mystical city and the Herculean rescue efforts undertaken by Haidara and others to save the manuscripts from destruction by the jihadis (2012). [33]
Destruction and evacuation of manuscripts

Many of the manuscripts were reported destroyed in January 2013, along with many other monuments of medieval Islamic culture in Timbuktu, by the Islamist rebels of Ansar Dine in the Northern Mali conflict.[23] The Ahmed Baba Institute and a library, both containing thousands of manuscripts, were said to have been burnt as the Islamists retreated from Timbuktu.[23] Journalists, however, found that at least one of the libraries was largely undamaged, and that only a few small piles of ash were present, suggesting that at least some of the documents survived.
A former Malian presidential aide, as well as several other people involved with preserving the manuscripts, said that the documents had been evacuated into a safe location in 2012 before the fighters invaded Timbuktu.[24] U.S. based book preservation expert Stephanie Diakité and Dr. Abdel Kader Haidara,[25] curator of one of the most important libraries of Timbuktu, a position handed down in his family for generations, organized the evacuation of the manuscripts to Bamako in the south of Mali.[26] Timbuktu has a long tradition of celebrating and honoring family manuscript collections. It is traditional for a family member to “swear publicly that he will protect the library for as long as he lives.” [27] During the evacuation process, Haidara relied on local families to hide the Ahmed Baba Institute’s manuscript collection in their homes before the texts were ultimately transported to Bamako.[27] The evacuation was supported by international organizations, such as the Prince Claus Fund for Culture and Development, whose initial commitment was followed by financial support from other organisations such as the Doen Foundation and Ford Foundation.[28] Abdel Kader thanked SAVAMA-DCI and their partners in a letter for enabling the evacuation of the manuscripts to the cities in the south of the country and supporting their storage.[29]

However, once in the south the manuscripts faced a new danger from mold and humidity. Stephanie Diakité and Dr. Abdel Kader Haidara began a campaign to raise money for the preservation of the books including a crowd funding campaign called "Timbuktu Libraries in Exile,"[30] which is currently hosted by the crowdfunding site T160K.org. Whereas many institutions have provided funding, equipment and/or training, the leading role in all the proceedings is played by the local people.[31]
See also
References
- ↑ Rainier, Chris (May 27, 2003). "Reclaiming the Ancient Manuscripts of Timbuktu". National Geographic News.
- ↑ Archived January 29, 2013, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Project – Tombouctou Manuscripts Project". Tombouctoumanuscripts.org. Retrieved 2015-05-31.
- ↑ "Towards an omnilingual word retrieval system for ancient manuscripts". Pattern Recognition Volume 42, Issue 9, September 2009, Pages 2089–2105.
- ↑ "THE TIMBUKTU MANUSCRIPTS – REDISCOVERING A WRITTEN SOURCE OF AFRICAN LAW IN THE ERA OF THE AFRICAN RENAISSANCE" (PDF). Uir.unisa.ac.za. Retrieved 2015-05-31.
- ↑ Walt, Vivienne (September 28, 2009). "Lost Treasures of Timbuktu". Time. Retrieved 4 March 2015.
- ↑ Archived July 25, 2011, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Islamic Manuscripts from Mali - About the Collection - (Global Gateway from the Library of Congress)". International.loc.gov. Retrieved 2015-05-31.
- ↑ "Libraries of Timbuktu". Archived from the original on October 10, 2010. Retrieved January 5, 2011.
- ↑ "Timbuktu Manuscripts Project Continues with Preservation Study Tours". Portal.unesco.org. 2004-11-13. Archived from the original on 2012-07-15. Retrieved 2015-05-31.
- ↑ Les Chemins du Savoir / Masālik al-Maʿrifa: Manuscrits de Tombouctou: patrimoine partagé / al-turāth al-mushtarak min khilāl makhṭūṭāt Tinbuktū. Rabat: Bibliothèque Nationale du Royaume du Maroc en collaboration avec l'Institut des Hautes Etudes et de Recherches Islamiques Ahmed Baba – Tombouctou, 13–17 Juin 2005. Workshop, exhibit and catalogue. Rabat: Institut des Études Africaines, Université Mohammed V – Souissi, 2005.
- ↑ John O. Hunwick, Alida Jay Boye, Joseph Hunwick: The Hidden Treasures of Timbuktu: Rediscovering Africa's Literary Culture Archived 2012-05-15 at the Wayback Machine., London: Thames & Hudson, 2008. ISBN 9780500514214. German translation: "Timbuktu und seine verborgenen Schätze", Munich: Frederking & Thaler, 2009. ISBN 978-3894057558. See Amazon preview.
- ↑ "Towards a conceptualization of the study of Africa's indigenous manuscript heritage and tradition | Minicka | Tydskrif vir letterkunde". Ajol.info. 2008-03-05. Retrieved 2015-05-31.
- ↑ "Sands of indifference bury Mbeki's Timbuktu dream". Times Live. Retrieved 2 January 2015.
- ↑ Jeppie, Shamil; Diagne, Souleymane Bachir (2008). The Meanings of Timbukt. Cape Town: HSRC. ISBN 978-0-7969-2204-5.
- ↑ "Islamic Manuscripts from Mali Collection: Home". International.loc.gov. 2007-11-19. Retrieved 2015-05-31.
- ↑ "Letter to the warring Tribes". Wdl.org. Retrieved 2015-05-31.
- ↑ "The Ancient Astronomers of Timbuktu". Archived from the original on May 2, 2010. Retrieved January 5, 2011.
- ↑ directed by Lutz Gregor / Gruppe 5. The full film can be viewed online: Part 1 | Part 2 | Part 3.
- ↑ "California Newsreel - THE MANUSCRIPTS OF TIMBUKTU". Newsreel.org. Retrieved 2015-05-31.
- ↑ "The Lost Libraries of Timbuktu". BBC4. Retrieved 2016-05-13. Although unavailable at BBC, the movie is available at others online video platforms, as "Youtube"
- ↑ Hammer, Joshua (2016-04-19). The Bad-Ass Librarians of Timbuktu. ISBN 9781476777405.
- 1 2 Harding, Luke (January 28, 2013). "Timbuktu mayor: Mali rebels torched library of historic manuscripts". The Guardian. London. Retrieved January 28, 2013.
- ↑ Walt, Vivienne (2013-01-28). "Mali: Timbuktu's Ancient Manuscripts Are Safe, Preservationists Say | TIME.com". World.time.com. Retrieved 2015-05-31.
- ↑ Hammer, Joshua (April 15, 2016). "The Librarian who saved Timbuktu's cultural treasures from Al Qaeda". The Wall Street Journal. New York. Retrieved August 14, 2016.
- ↑ "Saved from Islamists, Timbuktu's manuscripts face new threat - CNN.com". Edition.cnn.com. 2013-05-28. Retrieved 2015-05-31.
- 1 2 Yochi Dreazen, “The Brazen Bibliophiles of Timbuktu: How a Team of Sneaky Librarians Duped Al Qaeda and Saved Some of the Ancient World’s Greatest Artifacts,” The New Republic (April 2013), 34.
- ↑ "More than 95% of the manuscripts evacuated from timbuktu in time - Prince Claus Fund". 2012-10-12. Retrieved 2016-10-02.
- ↑ Archived June 27, 2013, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ y (2013-06-20). "Timbuktu Libraries in Exile". Indiegogo. Retrieved 2015-05-31.
- ↑ Russo, Maria Luisa (January 2017). "Contemporary librarianship and special collections issues: a case study in manuscript collections of Timbuktu and other Malian cities". JLIS.it. 8 (1): 39–49. doi:10.4403/jlis.it-12136. Retrieved 2017-01-22.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Timbuktu manuscripts. |