Thorin (chemistry)
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
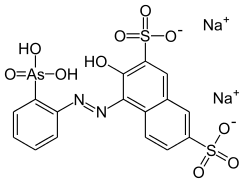
| Preferred IUPAC name
Disodium 3-hydroxy-4-[(2-arsonophenyl)diazenyl]naphthalene-2,7-disulfonate | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Disodium 4-[2-(2-arsonophenyl)hydrazin-1-ylidene]-3-oxo-3,4-dihydronaphthalene-2,7-disulfonate | |
| Other names
Disodium 4-[2-(2-arsonophenyl)hydrazin-1-ylidene]-3-oxonaphthalene-2,7-disulfonate 2-(3,6-Disulfo-2-hydroxy-1-naphthylazo)benzenearsonic acid disodium salt | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 2957648 | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.020.903 |
| EC Number | 222-993-1 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UN number | 1557 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H11AsN2O10S2 | |
| Molar mass | 530.31 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Orange-yellow crystals |
| Melting point | 300 °C (572 °F; 573 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Toxic (T), Dangerous for the environment (N) |
| R-phrases (outdated) | R23/25, R50/53 |
| S-phrases (outdated) | S20/21, S28, S45, S60, S61 |
| NFPA 704 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Thorin (also called Thoron or Thoronol) is an indicator used in the determination of barium, beryllium, lithium, uranium and thorium compounds. Being a compound of arsenic, it is highly toxic.
References
Analytical Chemistry, 51, 2293 (1979).
External links
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.
