Sphincter of Oddi
| sphincter of Oddi | |
|---|---|
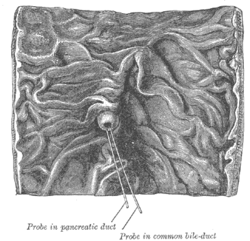 Interior of the descending portion of the duodenum, showing bile papilla. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | m. sphincter ampullae |
| MeSH | D009803 |
| TA | A05.8.02.018 |
| FMA | 15077 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The sphincter of Oddi (also hepatopancreatic sphincter or Glisson's sphincter), abbreviated as SO,[1] is a muscular valve that controls the flow of digestive juices (bile and pancreatic juice) through the ampulla of Vater into the second part of the duodenum. It is named after Ruggero Oddi.[2] The sphincter of Oddi is relaxed by the hormone cholecystokinin[3] via vasoactive intestinal peptide.[4]
Clinical significance
Opiates can cause spasms of the sphincter of Oddi, leading to increased serum amylase levels.[5]
Other animals
In many mammals (including mice, guinea pigs, dogs and opossums), the smooth muscle around the ampulla of Vater does not form a sphincter.[6]
History
The sphincter was described for the first time by Ruggero Oddi when he was a young student in 1887.[7] This followed extensive research on the physiology of dogs and had made detailed histological examinations of humans, and many other species.[1]
References
- 1 2 Yamada 2011, p. 78.
- ↑ synd/2709 at Who Named It?
- ↑ Board Review Series (5th ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins medical. March 2006. p. 220. ISBN 978-0781798761.
- ↑ Wiley, J W; O'Dorisio, T M; Owyang, C (1988). "Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide mediates cholecystokinin-induced relaxation of the sphincter of Oddi". Journal of Clinical Investigation. 81 (6): 1920–4. doi:10.1172/JCI113539. PMC 442644. PMID 3384954.
- ↑ Druart-Blazy A, Pariente A, Berthelemy P, Arotçarena R (2005). "The underestimated role of opiates in patients with suspected sphincter of Oddi dysfunction after cholecystectomy". Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 29 (12): 1220–3. doi:10.1016/s0399-8320(05)82204-3. PMID 16518275.
- ↑ Higashiyama H, Sumitomo H, Ozawa A, Igarashi H, Tsunekawa N, Kurohmaru M, Kanai Y. (2016). Anatomy of the Murine Hepatobiliary System: A Whole-Organ-Level Analysis Using a Transparency Method. The Anatomical Record. 299(2):161-172. doi:10.1002/ar.23287 PMID 26559382
- ↑ Ono K, Hada R (1988). ""Ruggero Oddi. To commemorate the centennial of his original article--"Di una speciale disposizione a sfintere allo sbocco del coledoco". Jpn J Surg. 18 (4): 373–5. doi:10.1007/bf02471459. PMID 3050213.
- Gray's Anatomy, 39th ed. p. 1228.
Sources
- Yamada, Tadataka (2011). Textbook of Gastroenterology (6 ed.). John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-1444359411.
Further reading
- Ballal, M. A.; Sanford, P. A. (2000). "Physiology of the sphincter of Oddi--the present and the future?--Part 1". Saudi Journal of Gastroenterology. 6 (3): 129–46. PMID 19864708.
- Ballal, M. A.; Sanford, P. A. (2001). "Physiology of the sphincter of Oddi: The present and the future?--Part 2". Saudi Journal of Gastroenterology. 7 (1): 6–21. PMID 19861760.