Bedaquiline
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Sirturo |
| Synonyms | Bedaquiline fumarate,[1] TMC207,[2] R207910, AIDS222089 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | by mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | >99.9% [3] |
| Metabolism | Liver, by CYP3A4[4] |
| Elimination half-life | 5.5 months [4] |
| Excretion | fecal[4] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
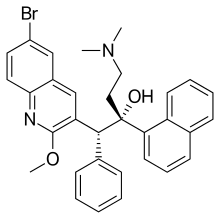
| Formula | C32H31BrN2O2 |
| Molar mass | 555.5 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Bedaquiline, sold under the brand name Sirturo, is a medication used to treat active tuberculosis.[1] It is specifically used to treat multi-drug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) when other treatment cannot be used.[1][5] It should be used along with at least three other medications for tuberculosis.[1][5] It is used by mouth.[5]
Common side effects include nausea, joint pains, headaches, and chest pain.[1] Serious side effects include QT prolongation, liver dysfunction, and an increased risk of death.[1] While harm during pregnancy has not been found, it has not been well studied in this population.[6] It is in the diarylquinoline antimycobacterial class of medications.[1] It works by blocking the ability of M. tuberculosis to make adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP).[1]
Bedaquiline was approved for medical use in the United States in 2012.[1] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system.[7] The cost for six months is approximately $900 USD in low income countries, $3,000 USD in middle income countries, and $30,000 USD in high income countries.[5]
Medical uses
Its use was formally approved (Dec 2012) by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in tuberculosis (TB) treatment, as part of a Fast-Track accelerated approval, for use only in cases of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis, and the more resistant extensively drug resistant tuberculosis.[8]
As of 2013 Both the World Health Organization (WHO) and US Centers for Disease Control (CDC) have recommended (provisionally) that bedaquiline be reserved for patients with multidrug-resistant tuberculosis when an otherwise recommended regimen cannot be designed.[9][10]
Clinical trials
Bedaquiline has been studied in phase IIb studies for the treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis while phase III studies are currently underway.[11] It has been shown to improve cure rates of smear-positive multidrug-resistant tuberculosis, though with some concern for increased rates of death (further detailed in the Adverse effects section).[12]
Small studies have also examined its use as salvage therapy for non-tuberculous mycobacterial infections.[11]
It is a component of the experimental BPaMZ combination treatment (bedaquiline + pretomanid + moxifloxacin + pyrazinamide).[13][14]
Side effects
The most common side effects of bedaquiline in studies were nausea, joint and chest pain, and headache. The drug also has a black-box warning for increased risk of death and arrhythmias, as it may prolong the QT interval by blocking the hERG channel.[15] All patients on bedaquiline should have monitoring with a baseline and repeated ECGs.[16] If a patient has a QTcF of > 500ms or a significant ventricular arrythmia, bedaquiline and other QT prolonging drugs should be stopped.
There is considerable controversy over the approval for the drug, as one of the largest studies to date had more deaths in the group receiving bedaquiline that those receiving placebo.[17] 10 deaths occurred in the bedaquiline group out of 79, while 2 occurred in the placebo group, out of 81.[12] Of the 10 deaths on bedaquiline, 1 was due to a motor vehicle accident, 5 were judged as due to progression of the underlying tuberculosis and 3 were well after the patient had stopped receiving bedaquiline.[17] However, there is still significant concern for the higher mortality in patients treated with bedaquiline, leading to the recommendation to limit its use to situations where a 4 drug regimen cannot otherwise be constructed, limit use with other medications that prolong the QT interval and the placement of a prominent black box warning.[17][11]
Drug interactions
Bedaquiline should not be co-administered with other drugs that are strong inducers or inhibitors of CYP3A4, the hepatic enzyme responsible for oxidative metabolism of the drug.[16] Co-administration with rifampin, a strong CYP3A4 inducer, results in a 52% decrease in the AUC of the drug. This reduces the exposure of the body to the drug and decreases the antibacterial effect. Co-administration with ketoconazole, a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, results in a 22% increase in the AUC, and potentially an increase in the rate of adverse effects experienced[16]
Since bedaquiline can also prolong the QT interval, use of other QT prolonging drugs should be avoided.[9] Other medications for tuberculosis that can prolong the QT interval include fluoroquinolones and clofazimine.
Mode of action
Bedaquiline blocks the proton pump for ATP synthase of mycobacteria. ATP production is required for cellular energy production and its loss leads to cell death, even in dormant or nonreplicating mycobacteria.[18] It is the first member of a new class of drugs called the diarylquinolines.[18] Bedaquiline is bactericidal.[18]
Resistance
The specific part of ATP synthase affected by bedaquiline is subunit c which is encoded by the gene atpE. Mutations in atpE can lead to resistance. Mutations in drug efflux pumps have also been linked to resistance.[19]
History
Bedaquiline was described for the first time in 2004 at the Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy (ICAAC) meeting, after the drug had been in development for over seven years.[20] It was discovered by a team led by Koen Andries at Janssen Pharmaceutica.[21]
Bedaquiline was approved for medical use in the United States in 2012.[1]
It is manufactured by Johnson & Johnson (J&J), who sought accelerated approval of the drug, a type of temporary approval for diseases lacking other viable treatment options.[22] By gaining approval for a drug that treats a neglected disease, J&J is now able to request expedited FDA review of a future drug.[23]
When it was approved by the FDA on the 28th December 2012, it was the first new medicine for TB in more than forty years.[24][25]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 "Bedaquiline Fumarate". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
- ↑ Diacon AH, Pym A, Grobusch M, et al. (2009). "The diarylquinoline TMC207 for multidrug-resistant tuberculosis". N Engl J Med. 360 (23): 2397&ndash, 405. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0808427. PMID 19494215.
- ↑ "Sirturo: Clinical Pharmacology". Archived from the original on 28 February 2015. Retrieved 28 April 2014.
- 1 2 3 "Bedaquiline". Archived from the original on 20 May 2013. Retrieved 28 April 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 The selection and use of essential medicines: Twentieth report of the WHO Expert Committee 2015 (including 19th WHO Model List of Essential Medicines and 5th WHO Model List of Essential Medicines for Children) (PDF). World Health Organization. 2015. p. vii, 29. ISBN 9789241209946. Archived (PDF) from the original on 20 December 2016. Retrieved 10 December 2016.
- ↑ "Bedaquiline (Sirturo) Use During Pregnancy". www.drugs.com. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016. Retrieved 10 December 2016.
- ↑ "WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (19th List)" (PDF). World Health Organization. April 2015. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 December 2016. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
- ↑ "Press Announcements - FDA approves first drug to treat multi-drug resistant tuberculosis". www.fda.gov. Dec 2012. Archived from the original on 2016-12-19.
- 1 2 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2013-10-25). "Provisional CDC guidelines for the use and safety monitoring of bedaquiline fumarate (Sirturo) for the treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis". MMWR. 62 (RR-09): 1–12. ISSN 1545-8601. PMID 24157696.
- ↑ WHO (2013). The use of bedaquiline in the treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis : interim policy guidance. Archived from the original on 2017-09-10.
- 1 2 3 Field, Stephen K. (2015-07-01). "Bedaquiline for the treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: great promise or disappointment?". Therapeutic Advances in Chronic Disease. 6 (4): 170–184. doi:10.1177/2040622315582325. ISSN 2040-6223. PMC 4480545. PMID 26137207. Archived from the original on 2015-10-28.
- 1 2 Diacon, Andreas H.; Pym, Alexander; Grobusch, Martin P.; de los Rios, Jorge M.; Gotuzzo, Eduardo; Vasilyeva, Irina; Leimane, Vaira; Andries, Koen; Bakare, Nyasha (2014-08-21). "Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis and Culture Conversion with Bedaquiline". New England Journal of Medicine. 371 (8): 723–732. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1313865. ISSN 0028-4793. PMID 25140958.
- ↑ BPaMZ @ TB Alliance Archived 2017-02-19 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Two new drug therapies might cure every form of tuberculosis. Feb 2017 Archived 2017-02-20 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Drugs.com: Sirturo Side Effects Archived 2013-09-23 at the Wayback Machine.
- 1 2 3 "Prescribing Information for Bedaquiline" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 24 August 2013. Retrieved 28 April 2014.
- 1 2 3 Cox, Edward; Laessig, Katherine (2014-08-21). "FDA Approval of Bedaquiline — The Benefit–Risk Balance for Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis". New England Journal of Medicine. 371 (8): 689–691. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1314385. ISSN 0028-4793. PMID 25140952.
- 1 2 3 Worley, Marylee V.; Estrada, Sandy J. (2014-11-01). "Bedaquiline: A Novel Antitubercular Agent for the Treatment of Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis". Pharmacotherapy. 34 (11): 1187–1197. doi:10.1002/phar.1482. ISSN 1875-9114. PMID 25203970.
- ↑ Andries, Koen; Villellas, Cristina; Coeck, Nele; Thys, Kim; Gevers, Tom; Vranckx, Luc; Lounis, Nacer; Jong, Bouke C. de; Koul, Anil (2014-07-10). "Acquired Resistance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis to Bedaquiline". PLOS ONE. 9 (7): e102135. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0102135. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 4092087. PMID 25010492.
- ↑ Protopopova M, Bogatcheva E, Nikonenko B, Hundert S, Einck L, Nacy CA (May 2007). "In search of new cures for tuberculosis" (PDF). Medicinal Chemistry. 3 (3): 301–16. doi:10.2174/157340607780620626. PMID 17504204.
- ↑ de Jonge MR, Koymans LH, Guillemont JE, Koul A, Andries K (June 2007). "A computational model of the inhibition of Mycobacterium tuberculosis ATPase by a new drug candidate R207910". Proteins. 67 (4): 971–80. doi:10.1002/prot.21376. PMID 17387738.
- ↑ Walker, Joseph; Tadena, Nathalie (December 31, 2012). "J&J Tuberculosis Drug Gets Fast-Track Clearance". Wall Street Journal. Archived from the original on September 23, 2015. Retrieved 2013-01-01.
- ↑ Edney, Anna (December 31, 2012). "J&J&J Sirturo Wins FDA Approval to Treat Drug-Resistant TB". Bloomberg. Archived from the original on January 4, 2013. Retrieved 2013-01-01.
- ↑ "FDA Approves 1st New Tuberculosis Drug in 40 Years". ABC News. Archived from the original on 4 January 2013. Retrieved 31 December 2012.
- ↑ Thomas, Katie (2012-12-31). "F.D.A. Approves New Tuberculosis Drug". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 8 January 2013. Retrieved 31 December 2012.