Shooting sports
|
From the final Shoot-Off at the men's skeet competition during the 2008 Summer Olympics. | |
| Highest governing body | Several organizations, see list |
|---|---|
| Nicknames | Shooting |
| First played | Switzerland in the second half of the 15th century |
| Characteristics | |
| Contact | No |
| Team members | Yes or no, depending on competition |
| Mixed gender | Yes or no, depending on discipline |
| Type | Indoor or outdoor |
| Venue | Shooting range |
| Presence | |
| Olympic | Yes |
| World Championships | Yes |
| Paralympic | Yes |
Shooting sports is a collective group of competitive and recreational sporting activities involving proficiency tests of accuracy, precision and speed in shooting, using various types of ranged weapons, mainly referring to man-portable guns (firearms and airguns, in forms such as handguns,[1] rifles[2] and shotguns[3]) and bows/crossbows.[4][5]
Different disciplines of shooting sports can be categorized by equipment, shooting distances, targets, time limits and degrees of athleticism involved. Shooting sports may involve both team and individual competition, and team performance is usually assessed by summing the scores of the individual team members. Due to the noise[6] of shooting and the high (and often lethal) impact energy of the projectiles, shooting sports are typically conducted at either designated permanent shooting ranges[7] or temporary shooting fields in the area away from settlements.
History
The National Rifle Association of the United Kingdom (NRA) was founded in 1860 to raise the funds for an annual national rifle meeting "for the encouragement of Volunteer Rifle Corps and the promotion of Rifle-shooting throughout Great Britain".[8]
For similar reasons, concerned over poor marksmanship during the American Civil War, veteran Union officers Col. William C. Church and Gen. George Wingate formed the National Rifle Association of America in 1871 for the purpose of promoting and encouraging rifle shooting on a "scientific" basis.[9] In 1872, with financial help from New York state, a site on Long Island, the Creed Farm, was purchased for the purpose of building a rifle range. Named Creedmoor, the range opened in 1872, and became the site of the first National Matches until New York politics forced the NRA to move the matches to Sea Girt, New Jersey. The popularity of the National Matches soon forced the event to be moved to its present, much larger location: Camp Perry. In 1903, the U.S. Congress created the National Board for the Promotion of Rifle Practice (NBPRP), an advisory board to the Secretary of the Army, with a nearly identical charter to the NRA. The NBPRP (now known as the Civilian Marksmanship Program) also participates in the National Matches at Camp Perry.[10]

In 1903, the NRA began to establish rifle clubs at all major colleges, universities, and military academies. By 1906, youth programs were in full swing with more than 200 boys competing in the National Matches. Today, more than one million youth participate in shooting sports events and affiliated programs through groups such as 4-H, the Boy Scouts of America, the American Legion, U.S. Jaycees, NCAA, The USA High School Clay Target League, the Scholastic Clay Target Program, National Guard Bureau, ROTC, and JROTC.
French pistol champion and founder of the modern Olympics, Pierre de Coubertin, participated in many of these early competitions. This fact certainly contributed to the inclusion of five shooting events in the 1896 Olympics. Over the years, the events have been changed a number of times in order to keep up with technology and social standards. the targets that formerly resembled humans or animals in their shape and size have are now a circular shape in order to avoid associating the sport with any form of violence. At the same time, some events have been dropped and new ones have been added. The 2004 Olympics featured three shooting disciplines (rifle, pistol, and shotgun) where athletes competed for 51 medals in 10 men's and 7 women's events—slightly fewer than the previous Olympic schedule.[9]
In the Olympic Games, the shooting sport has always enjoyed the distinction of awarding the first medals of the Games. Internationally, the International Shooting Sport Federation (ISSF) has oversight of all Olympic shooting events worldwide, while National Governing Bodies (NGBs) administer the sport within each country.
Having originally established shooting as an organized sport in the USA, the NRA was the obvious choice to administer the United States participation in the Olympic games. The NRA dutifully managed and financially supported international and conventional shooting sports (i.e., National Matches) for over 100 years until the formation of USA Shooting.
Gun shooting sports

Gun shooting sports are shot with either firearms or air guns, which can be either handguns, rifles and/or shotguns.
Handguns are handheld small arms designed to be shot off-hand without needing a shoulder stock. The two main subtypes of handguns are pistols and revolvers. They are much more convenient to carry in general, but usually have a shorter effective range and less accuracy compared to long guns such as rifles. In shooting sports, revolvers and semi-automatic pistols are the most commonly used.
A rifle is a long gun with a rifled barrel, and requires the use of both hands to hold and brace against the shoulder via a stock in order to shoot steadily. They generally have a longer range and greater accuracy than handguns, and are popular for hunting. In shooting sports, bolt action or semi-automatic rifles are the most commonly used.
A shotgun is similar to a rifle but often smoothbore and larger in caliber, and typically fires either a shell containing many smaller scattering sub-projectiles called shots, or a single large projectile called a slug. In shooting sports, shotguns are more often over/under-type break action or semi-automatic shotguns, and the majority of shotgun events are included in clay pigeon shooting.
Bullseye shooting

Bullseye shooting is a term used to describe several pistol and rifle shooting disciplines where the objective is to achieve as many points as possible by hitting a round shooting target as close to the middle as possible with slow precision fire. These disciplines place a large emphasis on precision and accuracy through sight picture, breath and trigger control. Fixed and relatively long time limits give the competitors time to concentrate for a perfect shot. An example of bullseye shooting is the ISSF pistol and rifle disciplines, but there are also many other national and international disciplines which can be classified as bullseye shooting. The shooting distances are typically given in round numbers, such as 10 15, 25, 50, 100, 200 or 300 meters depending on firearm type and discipline. Competitions are usually shot from permanent shooting ranges and with the same target arrangement and distance from match to match. Usually the competitors each have their own shooting target and shoot beside each other simultaneously. Because of the relatively simple match format, beginners are often recommended bullseye shooting in order to learn the fundamentals of marksmanship. Bullseye shooting is part of the Summer Olympic Games, and a considerable amount of training is needed to become proficient.
Bullseye shooting with handguns
- The six ISSF shooting events with pistols (four Olympic events plus two events not included in the Olympics program but are contested in World Cups and World Championships), its roots date back to the first modern Olympic Games in 1896, consist of both precision slow-fire and rapid-fire target shooting from distances of 10, 25, and 50 meters. The pistols are unique in appearance compared to normal guns and each events has its own pistols designed specifically for the job. Shooters must use one hand only to shoot at small "bullseye" target downrange. In the UK (except for Northern Ireland), it is no longer possible to practice for some of the Olympic events following the Firearms (Amendment) (No. 2) Act 1997, legislation brought in after the Dunblane Massacre.
- The CISM Rapid Fire match is similar to the ISSF 25 m Rapid Fire Pistol event.
- NRA Precision Pistol, also called conventional pistol shooting, is a bullseye shooting where up to 3 handguns of differing calibers are used. Its history is almost as old as ISSF events. Shooters must fire the pistol one-handed at 6- and 8-inch bullseye targets placed 25 and 50 yards downrange respectively.
- Precision Pistol Competition (PPC), was originally a police shooting program started in 1960 by the National Rifle Association.[11]
.jpg) The ISSF 10 meter air pistol final in the 2012 Summer Olympics.
The ISSF 10 meter air pistol final in the 2012 Summer Olympics. Boris Kokorev from Russia during the ISSF 50 meter pistol 2007 World Cup in Munich.
Boris Kokorev from Russia during the ISSF 50 meter pistol 2007 World Cup in Munich.
Bullseye shooting with rifles
- Four position small bore is a popular sport in the U.S.[10]
- The six rifle ISSF shooting events (including three Olympic events) consist of long-time target shooting from distances of 10 or 50 or 300 metres (33 or 164 or 984 ft).[10]
- Gallery rifle shooting is popular in the UK and was introduced as a substitute for many pistol shooting disciplines following the 1997 handgun ban.
- High Power Rifle (also known as "Across the Course" or 'traditional' High power) in the United States is a format that shoots 3-position (standing, kneeling, or sitting, and prone) at 200, 300, and 600 yards. The term "Across the Course" is used because the match format requires the competitors to shoot at different distances to complete the course of fire.
- Military Service Rifle shooting is a shooting discipline that involves the use of rifles that are used by military forces and law-enforcement agencies, both past and present use. Ex-military rifles, sniper rifles (both past and present) and civilian versions of current use service rifles are commonly used in the Military Service Rifle shooting competitions. It is popular in the United States and culminates each year with the National Matches being held at Camp Perry, Ohio. Some countries have outlawed civilian shooting at human-silhouette targets; silhouette targets are not used in the National Match Course of Fire. Bullseye targets are used. High Power Rifle competition often is held at the same events as Service Rifle, such as the U.S. national championships each year at Camp Perry. High Power competitors generally are civilians using whatever rifles they prefer within the rules, whereas Service Rifle entrants are limited to current or previous U.S. armed forces weapons. Although according to NRA rules only certain matches allow optical sights, normally those conducted at ranges over 600 yards.
- Project Appleseed is a rifle marksmanship program by The Revolutionary War Veterans Association that teaches both rifle marksmanship and oral history regarding the American Revolutionary War. It shoots 3-position (standing, sitting, and prone) at 25 meters at reduced scale targets, simulating shooting at 100, 200, 300, and 400 yards. The techniques taught easily apply to transitioning to High Power Rifle.
- Full bore and small bore rifle shooting in the United Kingdom.
- Three position airgun competitions, popular in the United States.
 The ISSF 10 meter air rifle discipline is part of the Olympics.
The ISSF 10 meter air rifle discipline is part of the Olympics. A junior shooter in Switzerland exercising bullseye shooting with a SIG 550. The rifle is equipped with a brass catcher to avoid disturbing other shooters with the ejection.
A junior shooter in Switzerland exercising bullseye shooting with a SIG 550. The rifle is equipped with a brass catcher to avoid disturbing other shooters with the ejection. An ISSF 50 meter rifle prone competition in Los Angeles, USA in 2012.
An ISSF 50 meter rifle prone competition in Los Angeles, USA in 2012. Two shooters during an ISSF 300 meter rifle three positions (prone, kneeling and standing).
Two shooters during an ISSF 300 meter rifle three positions (prone, kneeling and standing).
Field shooting
Field-Shooting or Terrain-Shooting [12][13] refer to a set of pistol and rifle shooting disciplines that usually are shot from temporary shooting ranges in the terrain at varying (and sometimes unknown) distances, rather than at permanent shooting ranges at fixed distances.
Field shooting with handguns
- Nordic Handgun Field-Shooting competitions are shot with pistol and revolver in different classes depending on equipment,[14] with classes up from small-bore .22 LR to large-bore .500 S&W Magnum.[15] Matches are held outdoor throughout the year with varied shooting targets and distances, and are arranged by the Norwegian Shooting Association (NSF), the Danish Gymnastics and Sports Associations (DGI Shooting) and the Swedish Pistol Shooting Association (SPSF).
Field shooting with rifles
- Nordic Rifle Field-Shooting[16] are shot with either small-bore .22 LR cartridge at 100 meters, or intermediate (such as .223 Remington or 6mm BR) or battle rifle cartridges (such as the 6.5×55mm, .308 Winchester or the .30-06 Springfield) at distances from 100 to 650 meters. With 200 and 300 meters being ordinary shooting distance in Nordic Bullseye Rifle-Shooting, those targets placed well beyond 300 meters in Rifle Field-Shooting means that the competition format also can be classified as a long range shooting discipline. Matches are usually held in the winter season with varied targets, and are arranged by the National Rifle Association of Norway (DFS), the Danish Gymnastics and Sports Associations (DGI Shooting) and the Swedish Shooting Sport Association (SvSF).
- Precision rifle competitions, like the Precision Rifle Series (PRS), is both a field and long range shooting discipline where rifles with intermediate or battle rifle cartridges are shot in the terrain at varying distances from about 10 to 1000 meters.
- Field Target is an outdoor air gun discipline originating in the United Kingdom, but gaining popularity worldwide.
 Nordic Rifle Field Shooting in Sweden during the winter in 2012.
Nordic Rifle Field Shooting in Sweden during the winter in 2012. The Norwegian Rifle Field Shooting Championship at the 2007 Landsskytterstevnet.
The Norwegian Rifle Field Shooting Championship at the 2007 Landsskytterstevnet.- Field-like shooting competition in USA using a National Match M1.
- Field target shooting in Germany
Rapid fire
Rapid fire with handguns
- The Bianchi Cup, a fusion of IPSC (without the "run and gun" element) and bullseye shooting (except shot with two hands and going prone whenever rules allow it) where accuracy under tight time limits in four simulated scenarios, known as the "Event(s)", is the basis of this competition. Shooters must start with gun in the holster on every strings of fire and distances range from 10 to 50 yards.
- Fast draw, also known as quick draw, a form of pistol action shooting from North America, based on the romanticized art of the gunslingers in the American Old West, using traditional single action revolvers. But unlike Cowboy action shooting, Fast Draw is done with special blanks or wax bullets. While some competitions are strictly against the clock, with the fastest time winning, many are set up as head to head single or double elimination matches.
.jpg) Keith Sanderson from USA during the ISSF 25 meter rapid fire pistol event at the 2016 Rio Olympic Games in Rio de Janeiro.
Keith Sanderson from USA during the ISSF 25 meter rapid fire pistol event at the 2016 Rio Olympic Games in Rio de Janeiro. John Pride at the 2008 The Bianchi Cup.
John Pride at the 2008 The Bianchi Cup.
Rapid fire with rifles
- The CISM Rapid Fire match is a sped-up version of the ISSF 300 m Standard Rifle event.
- Felthurtigskyting (literally Field Rapid Shooting) and Stangskyting are a type of variable rapid-fire rifle competitions popular in Scandinavia.
 Stang-Shooting at the 2007 Landsskytterstevnet in Norway. The nearest targets are placed at 155 meters, the farthest at 221 meters.
Stang-Shooting at the 2007 Landsskytterstevnet in Norway. The nearest targets are placed at 155 meters, the farthest at 221 meters. Field-Rapid-Shooting at the 2007 Landsskytterstevnet in Norway.
Field-Rapid-Shooting at the 2007 Landsskytterstevnet in Norway.
Clay target
Clay pigeon shooting are shotgun disciplines shot at flying clay pigeon targets.
- The three Shotgun ISSF/ Olympic shooting events are all are based on quick reaction to clay targets thrown by a machines called "Traps".
- Skeet: Targets are either thrown in singles or doubles from two throwers called "traps" placed 40 meters apart.[17]
- Trap and Double Trap: Either one (trap) or two targets (double trap) are thrown from 15 meters in front of the shooter.[17]
- The Fédération Internationale de Tir aux Armes Sportives de Chasse (FITASC) Compak Sporting is a type of shotgun sport shooting similar to sporting clays, trap and skeet.
- Other shotgun sports with (at least partial) international recognition include Sporting Clays, Down-The-Line/ATA and Five stand.
 Trap shooting in USA.
Trap shooting in USA.- Skeet shooting in USA.
 Clay targets being placed in an automatic throwing machine.
Clay targets being placed in an automatic throwing machine..jpg) Trap shooting at the 2015 World Police and Fire Games in USA.
Trap shooting at the 2015 World Police and Fire Games in USA.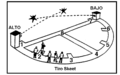 Sketch of a Skeet shooting range.
Sketch of a Skeet shooting range.
Running target
Running target shooting refers to a number of disciplines involving a shooting target—sometimes called a boar, moose, or deer—that is made to move as if it is a running animal. Events of this type include:
- ISSF 10 meter running target
- ISSF 10 meter running target mixed
- ISSF 50 meter running target
- ISSF 50 meter running target mixed
- Running moose, popular in Scandinavia both as a sport and hunting exercise. Competitions in Sweden are held at 80 meters.[18]
- Running deer, also somewhat popular in Scandinavia and Great Britain.
Practical shooting
Practical shooting, also known as action shooting or dynamic shooting, is a generic term applicable to shooting sports where speed is of equal importance as precision. Many of the disciplines involve movement, and when using handguns they are often drawn from a holster.
- The International Practical Shooting Confederation (IPSC) is the oldest and largest sanctioning body within practical shooting. IPSC is sometimes considered the "Formula One" of shooting sports, and is shot with handguns, rifles and shotguns. While the United States Practical Shooting Association (USPSA) is the U.S. regional affiliate of IPSC, many of USPSA's rules differ slightly from those used internationally. IPSC was developed by former police and civilian marksmen and later used as a basis for modern military and police exercises. It is a variation where the shooter often moves during shooting, and hits scored and shooting time are equally important. Stage procedure is generally not dictated (freestyle) and the shooter is allowed to determine the order and manner in which he or she engages the targets.
- International Defensive Pistol Association (IDPA) is an action shooting sport that uses semi-automatic handguns and revolvers with a strong emphasis on concealed shooting. Many aspects of stage engagement are dictated to competitors and penalties are given to competitors whom the safety officer determines attempted to gain a competitive advantage or engaged in a forbidden action with a "guilty mind" - that he knowingly failed to do right.
- 3-Gun (3G) or Multi-Gun (MG) are practical shooting events where each of the stages generally require the competitor to use and transition between a combination of rifles, handguns, and/ or shotguns[19] or other types of firearms. 3-Gun has a lot in common with ordinary IPSC/ USPSA matches, having courses of fire where the shooter must move through different stages and engage targets in a variety of different positions.
- Steel Challenge is a speed shooting championship solely about shooting steel targets as fast as possible, and is governed by the Steel Challenge Shooting Association (SCSA). There are eight standardized courses of fire, and a special "stop plate" must be shot last to stop the timer.
- International Confederation of Revolver Enthusiasts (ICORE) is an international community which promotes action shooting competitions with revolvers. Founded in 1991, the sport has elements from the Bianchi Cup, IPSC, and the Steel Challenge.[20]
- IPSC Action Air follows the same principle of IPSC, using airsoft instead of real firearms. The ranges, paper targets and poppers are scaled down to suit airsoft, and the sport enjoys popularity in countries such as Taiwan, Hong Kong, and Japan where civilian ownership of real firearms are either illegal or extremely difficult to obtain.
- Bowling pin shooting (primarily shot with handguns) has the competitors race against one another to knock standard bowling pins from a table in the shortest elapsed time.
- ActionAirgun is an indoor action shooting sport using semi-automatic airsoft pistols and courses of fire downloaded from a central hub. Shooters upload shooting times to a website to resolve competitions.
 An Open division practical pistol shooter during a stage.
An Open division practical pistol shooter during a stage. A Norwegian practical rifle shooter at the 2017 IPSC Rifle World Shoot in Russia.
A Norwegian practical rifle shooter at the 2017 IPSC Rifle World Shoot in Russia. Three times practical revolver world champion Ricardo López Tugendhat from Ecuador.
Three times practical revolver world champion Ricardo López Tugendhat from Ecuador.
Long range
Long range shooting is a term used to describe shooting disciplines held at such distances that sight adjustment based from judging atmospherical conditions become critical.
- Fullbore target shooting is concerned with shooting at targets at ranges of 300–1200 yards. The sport is internationally governed by ICFRA, and is popular in the UK, USA, Germany and Commonwealth countries. Similar disciplines called bullseye and field shooting are popular in Scandinavia, although fired at shorter distances.
- Palma is an ICFRA fullbore competition format that dates from 1876, featuring long-range rifle shooting, out to 1,000 yards. The first Palma match was contested by teams from the U.S., Australia, Canada, Scotland and Ireland (with muzzle loaded rifles at that time). The matches continued to the late 1920s, and the trophy was eventually lost in Washington DC around the outbreak of WW2. The match was revived in the modern era in 1966 in Canada, and continues between teams from around the world. The PALMA bolt action rifles are 7.62mm NATO caliber (Winchester .308) and fire Match Grade ammunition using a 155 grain bullet using micrometer aperature (iron) sights.[21] The last two International Long-range Target Rifle Matches were held in Australia in 2011 and the U.S. in 2015, were won by Great Britain.[22]
- F-Class is another ICFRA fullbore competition format shot with Fullbore Target Rifles at ranges up to 1000 yards, the rifles being fitted with telescopic sights and the use of fore-end and butt rests being permitted. This is a fast-growing variant of Fullbore Target Rifle. The 'F' honours George Farquharson, the Canadian inventor of F-Class.
- Precision Rifle Competitions, a relatively new long range competition format which seeks to find a balance between speed and precision, often involving movement and shooting from unusual positions with a time limit, at both known and unknown distances.
- National Rifle League (NRL) is a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization dedicated to the growth and education of precision rifle shooting in the United States. Their match format allows any caliber between .224 to .308 and not to exceed 3,200 feet per second (980 m/s), involving at least 50 shooters with each firing minimum 140 rounds in at least 12 individual stages, over the course of at least two days. Since its debut in 2017, currently 11 clubs from eight states are involved in the league.[23]
- National Rifle League 22 (NRL22) is a sub-league under the National Rifle League dedicated to .22 Long Rifle rimfire rifles. It was established to address the fact that most localities do not have access to 1000 yard ranges, but nearly all localities have 100-yard ranges and most shooters own .22 rifles. Their championship match consist of minimum 170 rounds fired in at least 15 individual stages. Currently 68 clubs from 31 states in the US participate in NRL22 matches, with addition to two overseas clubs from UK and Australia.[24]
- T-Class Shooting Sport Competitions. Practical sniping with precision rifle systems is a shooting sport, which gains tremendous popularity worldwide over a short period of time. It concentrates on shooting onto static or dynamic targets of various distances (known and unknown), from different positions, under artificially created, but realistic stressful circumstances. It proves to be extremely interesting both for implementation and observation, due to its demanding level of difficulty. The International T-Class Confederation (ITCC) is a non-profit organization, which is founded in 2014 for the purpose of promotion of the T-Class shooting sport internationally, with headquarters residing in Bulgaria. It offers a Set of Rules for designing and managing T-Class Competitions.
- Palma shooting in Canada in 2011.
 An ICFRA F-Class rifle equipped with a scope and bipod.
An ICFRA F-Class rifle equipped with a scope and bipod.
Benchrest
Benchrest shooting is concerned with shooting small groups with the rifleman sitting on a chair (bench) and the rifle supported from a table. Of all shooting disciplines, this is the most demanding equipment-wise. Depending on equipment class, international benchrest competitions are governed by either the World Benchrest Shooting Federation or World Rimfire and Air Rifle Benchrest Federation.
 An Anschütz 1903 rifle in caliber .22 LR used for benchrest shooting at 50 meters.
An Anschütz 1903 rifle in caliber .22 LR used for benchrest shooting at 50 meters. A BCM Europearms single shot benchrest rifle.
A BCM Europearms single shot benchrest rifle.
Metallic silhouette
Metallic silhouette competitors shoot at animal-shaped steel silhouettes (chickens, pigs, turkeys and rams) that must be knocked down to score. Banks of 5 targets are placed at up to 500 meters, with distance and size of target determined by firearm class. Classes include Handguns, Small Bore Rifle (Hunter, Silhouette), High Power Rifle (Hunter, Silhouette), air rifle and black powder rifle. Handguns used in the Unlimited Categories are rifle-like in appearance; Thompson Contender, Remington XP-100, and other pistols are chambered in rifle calibers with the power, aerodynamic efficiency, and external ballistics required for precise shooting at 200 meters. There are silhouette categories appropriate for virtually all types of adjustable sight pistols and rifles, only excluding high-velocity armor-piercing rounds that would damage targets. Targets for open sighted guns are placed between 25 and 200 meters, and are designed to provide a usable size of the hit zone of about 1.5 milliradians (or 5 minutes of arc).
 Cut cardboard targets of the same shape and sizes which are used for IHMSA metal targets in metallic silhouette shooting.
Cut cardboard targets of the same shape and sizes which are used for IHMSA metal targets in metallic silhouette shooting. Chicken, pig, turkey, and ram. The different targets are placed at different distances, and in this image the targets are scaled to how they would appear to the shooter in angular sizes (mil or moa).
Chicken, pig, turkey, and ram. The different targets are placed at different distances, and in this image the targets are scaled to how they would appear to the shooter in angular sizes (mil or moa).
Western
- Cowboy action shooting (CAS), almost identical to USPSA and IDPA stage design but with Western cowboy themed props, shot with long guns and revolvers of the same era. Mere act of shooting itself is not enough. Competitors must choose and go by a cowboy nickname or alias and are required to look the part by donning authentic cowboy and cowgirl garments.
- Cowboy mounted shooting, also called Western Mounted Shooting or simply Mounted Shooting, is a competitive equestrian sport involving the riding of a horse to negotiate a shooting pattern. Rule sets vary between shooting sport organizations, it can be based on the historical reenactment of historic shooting events held at Wild West Shows in the late 19th century. Modern events use blank ammunition instead of live rounds, certified to break a target balloon within twenty feet.[25]
- A Cowboy action shooter firing a lever action rifle at steel targets. The Range Officer to the left is holding a shooting timer to measure the time.
- Scenery in a Western scenario.
- The shooter uses different firearms during a stage. In this stage revolvers were used at the close range blue targets and a lever action at the red targets furthest away.
 Cowboy mounted shooting at the 2012 AQHA Mounted Shooting World Championship.
Cowboy mounted shooting at the 2012 AQHA Mounted Shooting World Championship.
Muzzleloading
Muzzleloading are concerned with shooting replica (or antique) guns.
 Competitor shooting at 1000 yards (914.4 meters) laying on back
Competitor shooting at 1000 yards (914.4 meters) laying on back Competitor from Team Norway shooting at 1000 yards (914.4 meters)
Competitor from Team Norway shooting at 1000 yards (914.4 meters) Replica Rigby rifle used at the 2015 MLAIC Muzzleloading Long Range Championship
Replica Rigby rifle used at the 2015 MLAIC Muzzleloading Long Range Championship A member of Team USA loading his blackpowder rifle
A member of Team USA loading his blackpowder rifle
Para shooting
Paralympic shooting, also known as "shooting Para sport", is an adaptation of shooting sports for competitors with disabilities. Paralympic shooting first appeared in the Summer Paralympics at the 1976 Toronto Games. Para shooting is internationally governed by the International Paralympic Committee. To help establish fair competition, a shooting classification called Para-shooting classification in place for the Paralympic Games.
 Para shooting with a rifle sitting in a wheelchair.
Para shooting with a rifle sitting in a wheelchair.


Competitions using factory and service firearms
Shooting competitions for factory and service firearms, usually called Service Rifle, Service Pistol, Production, Factory or Stock, describe a set of disciplines or equipment classes where the types of permitted firearms are subject to type approval and few aftermarket modifications are permitted. Thus the terms refer to permitted equipment and modifications rather than the type of shooting format itself. The names Service Rifle and Service Pistol stem from that the equipment permitted for these types of competitions traditionally were based on standard issue firearms used by one or several armed forces and civilian versions of these, while the terms Production, Factory and Stock often are applied to more modern disciplines with similar restrictions on equipment classes. Factory and service classes are often restrictive in nature, and the types of firearms permitted are usually rugged, versatile and affordable. In comparison, more expensive custom competition equipment are popular in more permissive equipment classes. Both types of equipment classes can be found within many disciplines, such as bullseye, field, practical and long range shooting.
 Service rifle shooting in Slovenia with the Zastava M48 rifle.
Service rifle shooting in Slovenia with the Zastava M48 rifle.
Plinking
Plinking refers to informal target shooting done for pleasure or practice typically at non-standard targets such as tin cans, logs, cartons, fruits, or any other homemade or naturally occurring objects like rocks or tree branches. The primary appeals of plinking as a sport are the broad variety of easily available locations, minimal costs, freedom in practice styles, and more relaxing and less restrictive shooting experience.
The flexibility of target choice is also why plinking is popular. A small, three-dimensional target in an outdoors setting is much more akin to a real-world hunting and varminting scenario, presenting a better simulated opportunity to practice shooting skills. A plinking target will also often react much more positively to a hit than a paper target used in formal competitions, either audibly with a sharp impact sound (hence the name "plink") or visually by bouncing, splattering or falling over. Steel targets used for formal action and long range shooting competitions are also popular for plinking due to the ease of setting up and confirming good hits.
 A woman plinking with a Hi-Point pistol in .40 S&W in Alaska.
A woman plinking with a Hi-Point pistol in .40 S&W in Alaska. Plinking with a Ruger 10/22 rifle in Burro Canyon, Arizona, USA.
Plinking with a Ruger 10/22 rifle in Burro Canyon, Arizona, USA. Plinking on a Saturday in Burro Canyon, Arizona, USA. On this range firearms must be kept unloaded in the rack, except when on the firing line.
Plinking on a Saturday in Burro Canyon, Arizona, USA. On this range firearms must be kept unloaded in the rack, except when on the firing line.
Bow shooting sports
Archery
Modern competitive archery involves shooting arrows at a target for accuracy from a set distance or distances. A person who participates in archery is typically called an archer or a bowman, and a person who is fond of or an expert at archery is sometimes called a toxophilite. The most popular competitions worldwide are called target archery. Another form, particularly popular in Europe and America, is field archery, which generally is shot at targets set at various distances in a wooded setting. There are also several other lesser-known and historical forms, as well as archery novelty games. Note that the tournament rules vary from organization to organization. World Archery Federation rules are often considered normative, but large non-WA-affiliated archery organizations do exist with different rules. Competitive archery in the United States is governed by USA Archery and National Field Archery Association (NFAA), which also certifies instructors. Run archery is a shooting discipline connecting archery with running.
.jpg) Target shooting with a recurve bow.
Target shooting with a recurve bow. Archery competition in Mönchengladbach, West Germany, June 1983.
Archery competition in Mönchengladbach, West Germany, June 1983.
Crossbow
The International Crossbow Shooting Union (Internationale Armbrustschützen Union or IAU) was founded in Landshut, Germany on June 24, 1956 as the world governing body for crossbow target shooting. The IAU supervises World, Continental and International crossbow shooting championships in 3 disciplines; 30 m Match-crossbow, 10 m Match-crossbow and Field-crossbow shooting. IAU World Championships take place every two years with Continental Championships on intervening years. Other International and IAU-Cup events take place annually.[10]
 Anna Sushko of Russia, 2006 Junior World Champion, holding an ICU 10 m Match Crossbow
Anna Sushko of Russia, 2006 Junior World Champion, holding an ICU 10 m Match Crossbow A competitor at the 30 meter event at the 2008 ICU Match-Crossbow World Championships in Sulgen, Switzerland.
A competitor at the 30 meter event at the 2008 ICU Match-Crossbow World Championships in Sulgen, Switzerland.
Athletic shooting sports
- Modern pentathlon is a Summer Olympic sport includes timed shooting with an air pistol as the first of its five parts.
- Biathlon is a Winter Olympic sport combining cross-country skiing (normally freestyle skate skiing) and shooting with .22 LR rifles.[10] In Scandinavia the discipline is simply known as "Ski Shooting" (Swedish: skidskytte, Danish: skiskydning, Norwegian: skiskyting).
- Summer biathlon, with skiing replaced by running, popular in Germany.
- Ski Field Shooting (Norwegian: DFS skifeltskyting) is a Norwegian discipline arranged by the National Rifle Association of Norway which is based on the origins of modern biathlon. It is normally held in a classic (in-track) format, but competitions can also be held in a freestyle skate skiing format. Furthermore, the shooting is done with fullbore calibers and usually in the field from temporary shooting ranges. The discipline is considered as a near precursor to modern biathlon.
- Field running (Norwegian: DFS skogsløp) is a Norwegian discipline arranged by the National Rifle Association of Norway combining running with shooting. It is considered the summer edition of Ski Field Shooting. Running distances are usually between 2 and 3 kilometers with 2 to 3 shooting series.
- Target sprint combines medium-range run (3 × 400 m) and airgun shooting.
- Military patrol was a team winter sport in which athletes competed in cross-country skiing, ski mountaineering and rifle shooting. It was usually contested between countries or military units.
- Underwater target shooting is a combined underwater and shooting sport that tests a competitors’ ability to accurately use a speargun via a set of individual and team events conducted in a swimming pool using free diving or Apnoea technique.
 Military patrol in Riesengebirge, Germany in 1932.
Military patrol in Riesengebirge, Germany in 1932.
Confrontational shooting sports
Confrontational shooting sports is a set of relatively new team sports using non-lethal ranged weapons that are safe enough to shoot at other people. Previously such games were not possible due to safety concerns since bows and guns are generally too lethal and dangerous for human targets, but the development of newer airgun and infrared technologies allowed for the development of safe confrontational disciplines. While initially only for sport and recreations, professional sport competitions are now held. These type of games are also used for tactical gunfight training by military and law enforcement agencies to some extent.
Paintball
Paintball is a competitive sport in which players from opposing teams eliminate opponents out of play by hitting them with round, breakable, dye-filled oil and gelatin pellets ("paintballs"), shot from gas-powered air weapons called paintball markers. It can be played on indoor or outdoor fields scattered with natural or artificial terrain, which players use for tactical cover. Paintball game types vary, but can include capture the flag, elimination, ammunition limits, defending or attacking a particular point or area, or capturing objects of interest hidden in the playing area. Depending on the variant played, games can last from seconds to hours, or even days in scenario play. The game is developed in the 1980s and now is regularly played at a formal sporting level with organized competition involving major tournaments, professional teams and players.
- National Xball League is the United States' professional paintball circuit. The league consists of a Professional Division, consisting of the best players the sport has to offer, that extends down to the beginner ranks of "Division 5" for those newer to the tournament atmosphere. The league hosts five national events across the country in places such as Las Vegas, Dallas, Nashville, Cleveland, Chicago, Atlantic City and Orlando throughout the year, starting in March and ending their season in early November. The league's largest event each year is the season finale known as the World Cup, with the 2016 World Cup hosted 3,554 players from 35 countries.
- National Collegiate Paintball Association is an all-volunteer, non-profit organization created by United States college players. The goal of the NCPA is to promote the positive aspects of the sport in an intercollegiate manner. The NCPA consists of two distinct classes which competes separately — Class AA is an open-class division where any college may enter and compete in regional and national tournaments. Class A is a closed-class division where only certain colleges may compete after securing a bid in the previous season, and represents the best talent of college paintball and includes universities such as Drexel University, University of Maryland, Illinois State University, Purdue University, University of Connecticut, Penn State University and 10 other teams across three conferences all fighting for a national title. The association's 2007 playoff tournament was aired on Fox Sports Net's digital cable college sports network, Fox College Sports.
 Players next to an inflatable Sup'Air bunker.
Players next to an inflatable Sup'Air bunker. View of a course during a speedball game in progress.
View of a course during a speedball game in progress.
Airsoft
Airsoft is a competitive sport similar in concept to paintball, in which participants from opposing teams eliminate opponents by hitting each other with solid round plastic pellets launched from low-powered smoothbore air guns called airsoft guns. It is different to paintball in that airsoft pellets do not visibly mark the targets like paintballs, and thus the sport relies heavily on an honor system where a hit player has the ethical duty to call himself out of play, regardless of whether anyone else sees it happen. Most airsoft guns are also magazine-fed (unlike the commonly top-mounting pellet loader of paintball markers) with mounting platforms compatible with real firearm accessories, and tend to more closely resemble real guns in appearance, making them more popular for military simulation and historical reenactments. The greater toughness of airsoft pellets also allows the use of better powerplants and apparatus such as hop-up device for improved external ballistics, making the gameplay more accurately resemble real gunfights. They are also much cheaper for casual players to participate than paintball.
Airsoft gameplay varies in style and composition just like paintball and is played in both indoor and outdoor courses. Situations on the field frequently involve the use of real-life military tactics to achieve objectives, and it is not uncommon for participants to emulate the uniforms and equipment of real military and police organizations for a sense of realism. Games are normally supervised (and sometimes umpired) by trained on-site administrators, and players' airsoft guns are usually checked through a chronograph to enforce power output restrictions.
There are currently no formal national or international governing bodies for the airsoft sport. Competitive tournaments are usually organized by private clubs or among enthusiasts and professional/semi-professional teams (often referred to as "clans"), with rules and restrictions varying from event to event.
 Three airsoft team members defending an aera during an indoor CQB game.
Three airsoft team members defending an aera during an indoor CQB game. From an outdoor airsoft game.
From an outdoor airsoft game. Three airsoft team members during a field game.
Three airsoft team members during a field game.
Laser tag
Laser tag (despite the name, laser is actually not used due to safety concerns) is a tag game played with gun-shaped infrared illuminators and sensors worn on the body of the players. Since its birth in 1979, laser tag has evolved in both indoor and outdoor games, each with gameplay styles such as annihilation, capture the flag, domination, VIP protection, (usually sci-fi) role playing, etc. When compared to paintball and airsoft, laser tag is painless and very safe because it involves no projectile impacts, and indoor games may be considered less physically demanding because most indoor venues prohibit running or roughhousing.
- Zone Laser Tag World Championships were international tournaments among professional/semi-professional teams from North American, Europe and Australia, hosted every few years since 2003.
- Bi-lateral international championships have included USA vs. Australia and Australia vs. South Africa.
- National tournaments in various countries including Australia, USA, Sweden, Finland, UK, etc.
- Private club-level events such as TagCon (annual in UK and USA), Tagfest (annual in USA), Dropzone (annual in UK), LaserStorm (annual in Australia), etc.
.jpg) An indoor laser tag competition at Long Beach, California in 2011.
An indoor laser tag competition at Long Beach, California in 2011. Soldiers equipped with professional laser tag training equipment
Soldiers equipped with professional laser tag training equipment
Archery Tag
Archery Tag is a form of combat archery sport where participants shoot one another using a bow with arrows with large foam tips. The game's rules closely resemble dodgeball. The game begins with a number of arrows in the center of the arena. At the whistle, players race to collect them, before firing them at one another across the playing field. A player is eliminated if struck by an arrow, and a player can bring an eliminated teammate back into play by catching an arrow. To avoid injury, participants wear protective facemasks and use bows with less than 30 pounds (14 kg) draw weight. It was invented in 2011 by John Jackson of Ashley, Indiana, and experienced a boost in popularity from the Hunger Games books and film series, which feature a bow-wielding protagonist Katniss Everdeen. Jackson staged Archery Tag games at local premieres of the films. By 2014, Jackson had licensed the game to 170 locations, mostly in the United States, but also in Russia, Peru and Saudi Arabia.
Battle gaming variants of Archery Tag also exist, such as Dagorhir, Amtgard, Belegarth and Darkon, where archers are pitted among melee players welding foam weapons to simulate medieval battles.
 A game of archery tag in Toronto
A game of archery tag in Toronto
See also
References
- ↑ Handgun Sports • NSSF | National Shooting Sports Foundation
- ↑ Rifle Sports • NSSF | National Shooting Sports Foundation
- ↑ Shotgun Sports • NSSF | National Shooting Sports Foundation
- ↑ Archery 101 by Archery 360
- ↑ Archery | World Archery
- ↑ Kardous, C. A.; Willson, R. D.; Hayden, C. S.; Szlapa, P.; Murphy, W. J.; Reeves, E. R. (2003). "Noise exposure assessment and abatement strategies at an indoor firing range". Applied Occupational and Environmental Hygiene. 18 (8): 629–36. doi:10.1080/10473220301409. PMID 12851012.
- ↑ Noise levels at shooting range - timesofmalta.com
- ↑ "Volunteers & The NRA", researchpress.co.uk Archived April 23, 2012, at the Wayback Machine.
- 1 2 Australia, Sporting Shooter's Association of. "Sporting Shooters' Association of Australia (SSAA)". ssaa.org.au. Retrieved 2016-08-12.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Shooting Equipment and history - Olympic Sport History". www.olympic.org. 2018-05-15. Retrieved 2016-08-12.
- ↑ "NRA Law Enforcement Division: Police Pistol Combat Competition". ppc.nra.org. National Rifle Association of America. 2015.
- ↑ Danish: Aalborg Skyttekreds af 1862 - Terrænskydning
- ↑ Norwegian: feltskyting – Store norske leksikon
- ↑ Swedish: Svenska Pistolskytteförbundet-Om pistolskytte-Fältskjutning
- ↑ Norwegian: Litt om feltskyting – Haugesund Pistolklubb (English: A little about field shooting - Haugesund Pistol Club)
- ↑ Swedish: Fältskytte gevär förklarat | Sandvikens Skyttegille
- 1 2 Topend Sports | About Shooting Sports
- ↑ "jagareforbundet.se"
- ↑ DeJesus, Ivey (January 8, 2015). "A pistol, rifle and shotgun sport part of the lineup at NRA's Great American Outdoor Show". PA Media Group.
- ↑ ICORE History and Information
- ↑ "Palma USA". Retrieved 31 March 2017.
- ↑ http://competitions.nra.org/documents/pdf/compete/nat-trophy/tro-090.pdf
- ↑ "Participating Clubs/Matches". National Rifle League.
- ↑ "Clubs". NRL 22.
- ↑ Taffin, John (28 September 2005). Single Action Sixguns. Iola, Wisconsin: Krause Publications. pp. 299–300. ISBN 978-1-4402-2694-6.
External links
- Get Inspired: How to get into Shooting - BBC Sport
- How to get into shooting - Shooting UK
- How To Get Started | NRA Explore
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Shooting sports. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Recreational shooting. |
